The n-puzzle is a sliding puzzle with n×n - 1 numbered tiles in an n×n frame, leaving one empty spot. Tiles can slide horizontally or vertically into the open space. The goal is to arrange the tiles in spiral order.
- Basics of graph theory
- Dijkstra’s algorithm
- BFS and DFS
- A* algorithm
- Heuristic functions
- Admissible Heuristic
- Consistent Heuristic
- Priority Queue
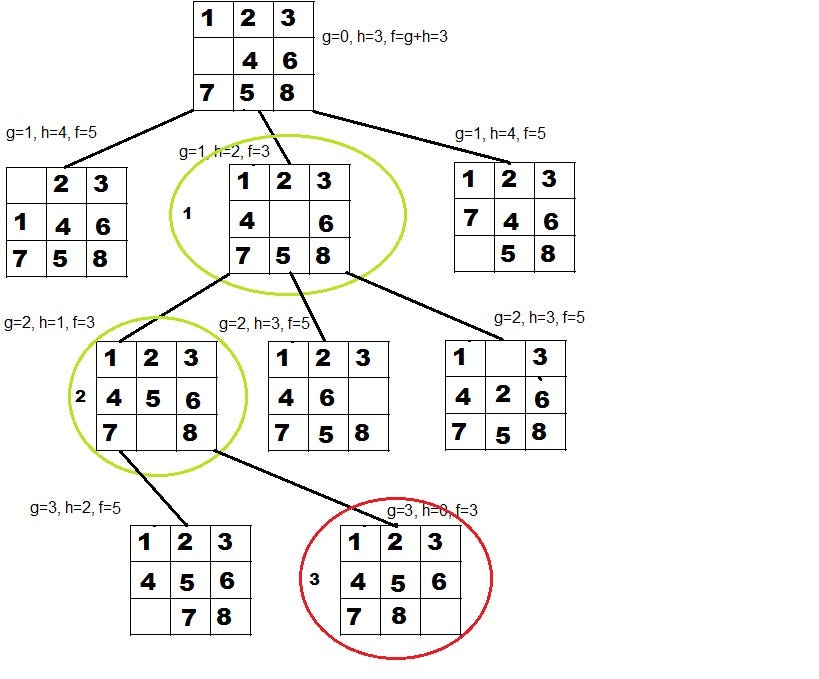
A* is a best-first search algorithm that finds the shortest path from a start node to a goal node. It uses a combination of the actual cost from the start node and a heuristic estimate to guide its search.
A function that prioritizes options in search algorithms at each branching step based on available information to guide the search direction.
 Admissible Heuristic: A heuristic is admissible if it never overestimates the true cost to reach the goal.
Admissible Heuristic: A heuristic is admissible if it never overestimates the true cost to reach the goal.
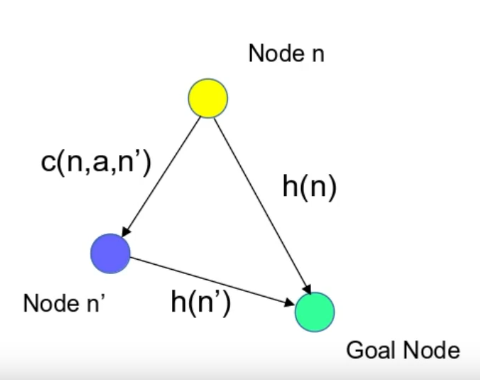
Consistent heuristic: heuristic h is consistent if for any node n and its successor n′
- basically it ensures that the estimated cost to reach the goal from a node does not decrease when transitioning from one node to another.
- Manhattan distance
- linear conflicts
- If two tiles are in the same row/column, and their goal positions are in the same row/colum, a linear conflict happens.
Linear Conflict=Manhattan Distance+ 2 ×(number of linear conflicts)
- Euclidean distance
- Hamming distance
- Out of place tiles
- Uninformed Search
- Does not use any heuristic information. like (Breath first search and depth first search)
- Informed Search
- Uses a heuristic to guide the search. like A*
- Uniform-Cost Search
- Finds the optimal path,
complete(guaranteed to find a solution if one exists), does not require a heuristic. - Slower and more memory-intensive due to exhaustive exploration.
- Finds the optimal path,
- Greedy Search
- Faster and efficient with a good heuristic, less memory-intensive.
- Not guaranteed to find the optimal path, performance dependent on the quality of the heuristic.
# Generate the puzzle
python3 ./src/npuzzle-gen.py 3 -s > puzzle.txt # generate a solvable puzzle of size 3
# Or
make generator && ./npuzzle-gen.out 3 -s > puzzle.txt
make && ./n-puzzle.out -f puzzle.txt --manhattan
Usage: n-puzzle [-f {file_input}] ... [Heuristics] ... [SearchType]
Heuristics:
--manhattan: uses manhattan distance
--conflicts: linear conflicts
--euclidean: euclidean distance
--hamming: hamming distance aka "tiles out of place"
Search Type:
-g: greedy search: ignores the g(n) in A* formula f(n) = g(n) + h(n), quickly finds solution.
-u: uniform cost search: discards the h(n) in A* formula.