Single Image Super-Resolution-GAN
This is implementation of the paper Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. I have implementated the above paper in keras
Although we have breakthroughs in accuracy and speed of single image super-resolution using faster and deeper convolutional neural networks, we still have one largely unsolved problem of recovering the fibner texture details when we super-resolve at large upscaling factors. Most of the methods of super-resolution tries to minimize the mean square error. But the resulted images are perceptually unsatisfying in the sense that they fail to match the fidelity expected at the higher resolution. The paper uses Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in order to solve the problem of producing photo realistic super resolution images.
Implementation Details
I have used coco dataset. A total of 800 high resolution images are used for training purpose. In orginal paper they have 350 thousand images from ImageNet daataset. I have also reduced the flatten layer sizes from 1024 to 100 due to low ram. I have further converted the images of different dimensions into a comman dimension of (384,384,3) using Bicubic kernel. As it was suggested in paper low resolution images are obtaibed by downsampling to a factor of 4 using bicubic kernel. The model was trained for around 31 epochs only because of the non availabilty of high performing hardwares and time constraints although in original paper they have trained the model for around 100k epochs.
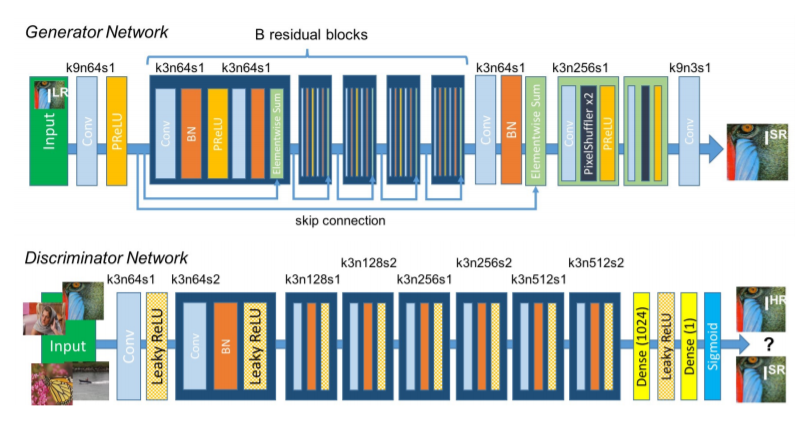
Model Architecture
##the image is taken from the original paper
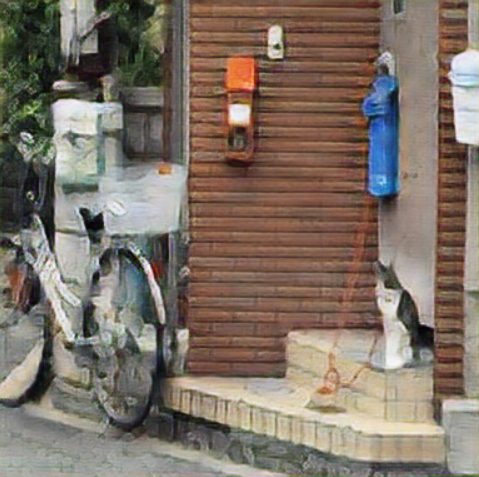
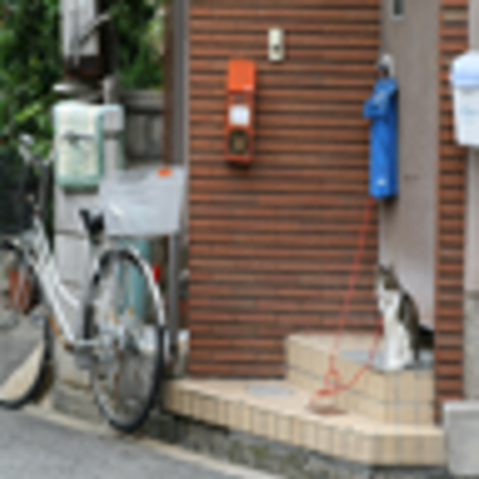
Results
On Training images
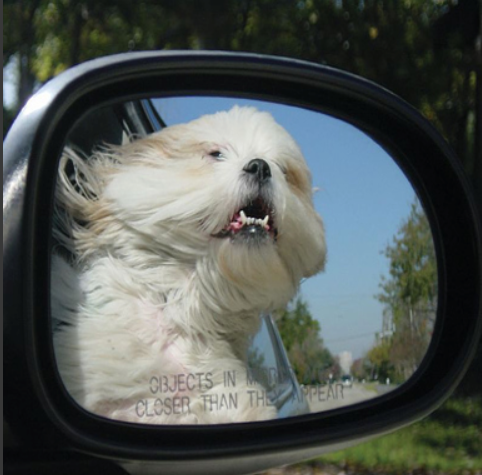
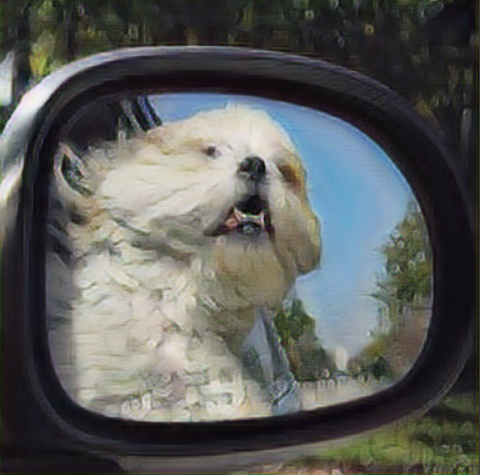
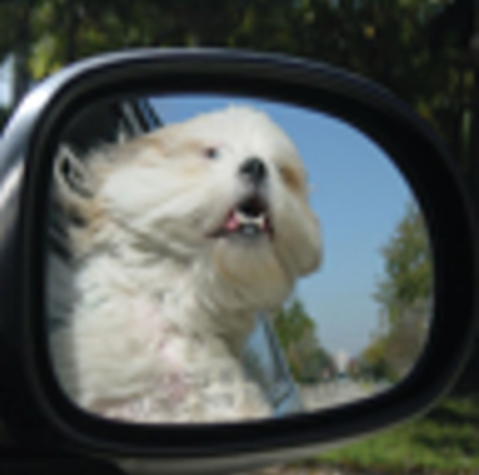
Low resolution image
high resolution
High redolution using gan
High resolution using Bicubic
On Test images
Low resolution image
high resolution
High redolution using gan
High resolution using Bicubic
Acknowledgment
I would like to thanks Deepak Birla for his blog Blog link. It was a great help and the coded was inspired from that.