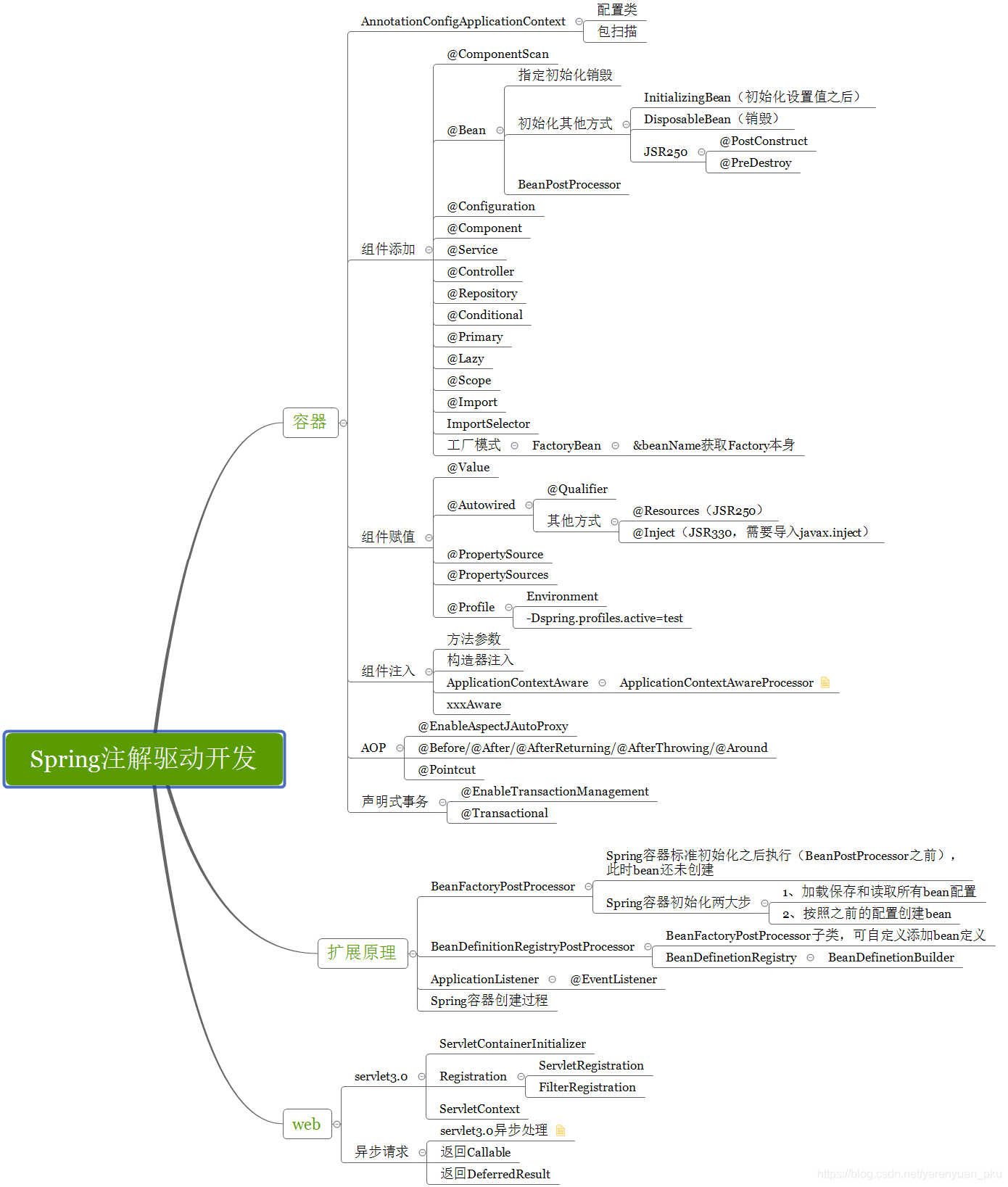
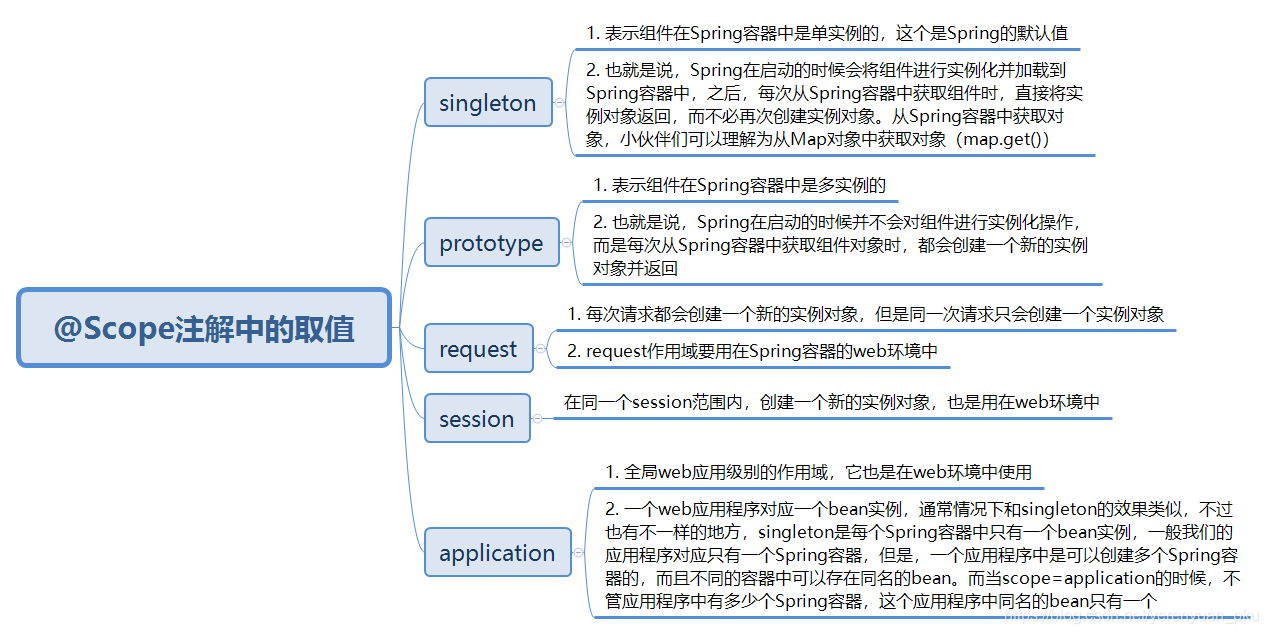
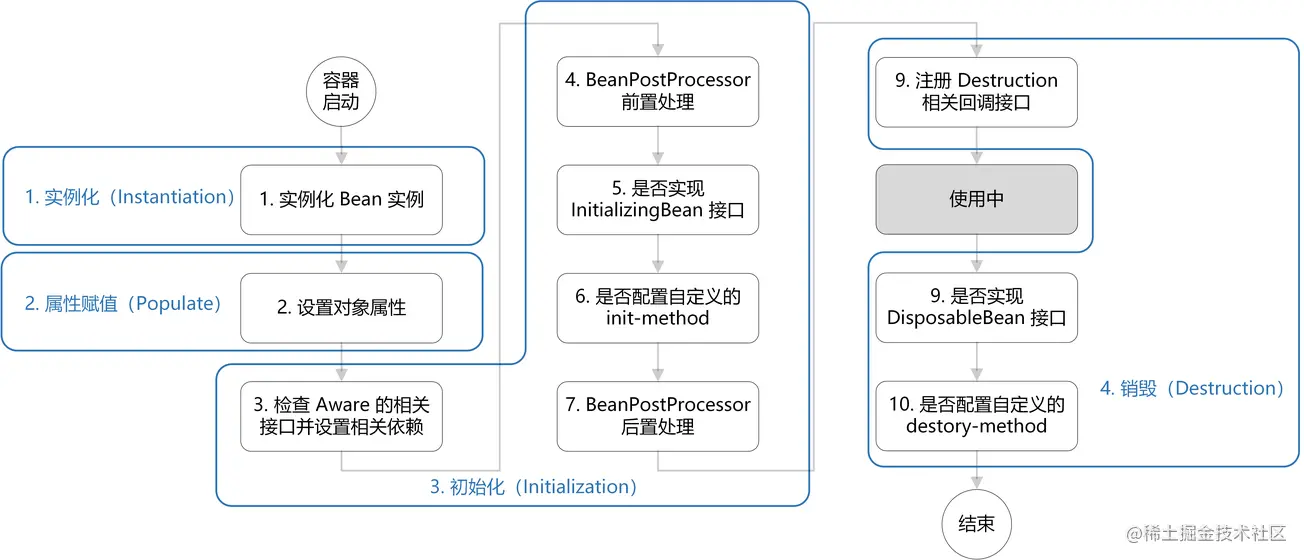
根据 link 的学习记录
- 基于 spring 5.3.15
- 真正创建 bena 的地方: org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean
// https://juejin.cn/post/6844904065457979405
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// 1. 实例化
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 2. 属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 3. 初始化
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
// 4. 销毁-注册回调接口
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
return exposedObject;
}// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 3. 检查 Aware 相关接口并设置相关依赖
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
// 4. BeanPostProcessor 前置处理
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
// 5. 若实现 InitializingBean 接口,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法
// 6. 若配置自定义的 init-method方法,则执行
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
// 7. BeanPostProceesor 后置处理
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}// DisposableBeanAdapter.java
public void destroy() {
// 9. 若实现 DisposableBean 接口,则执行 destory()方法
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
return null;
}, this.acc);
}
else {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
}
}
}
// 10. 若配置自定义的 detory-method 方法,则执行
if (this.destroyMethod != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);
}
else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {
Method methodToInvoke = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName);
if (methodToInvoke != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(methodToInvoke));
}
}
}bean 的生命周期 来自
aware 接口有两个执行时机
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 第一次
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
// 第二次
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
// ...
return wrappedBean;
}- 第一次执行
- BeanNameAware:注入当前 bean 对应 beanName;
- BeanClassLoaderAware:注入加载当前 bean 的 ClassLoader;
- BeanFactoryAware:注入 当前BeanFactory容器 的引用。
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}- 第二次注入
- EnvironmentAware:注入 Enviroment,一般用于获取配置属性;
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware:注入 EmbeddedValueResolver(Spring EL解析器),一般用于参数解析;
- ApplicationContextAware(ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisherAware、MessageSourceAware):注入 ApplicationContext 容器本身。
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware) {
((ApplicationStartupAware) bean).setApplicationStartup(this.applicationContext.getApplicationStartup());
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}| Aware interface | Method to override | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
ApplicationContextAware |
void setApplicationContext (ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException; |
Interface to be implemented by any object that wishes to be notified of the ApplicationContext that it runs in. 可以向组件中注入IOC容器, 用于获取 ApplicationContext |
ApplicationEventPublisherAware |
void setApplicationEventPublisher (ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher); |
Set the ApplicationEventPublisher that this object runs in. |
BeanClassLoaderAware |
void setBeanClassLoader (ClassLoader classLoader); |
Callback that supplies the bean class loader to a bean instance. 注入加载当前 bean 的 ClassLoader |
BeanFactoryAware |
void setBeanFactory (BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; |
Callback that supplies the owning factory to a bean instance. 注入 当前 BeanFactory 容器 的引用 |
BeanNameAware |
void setBeanName(String name); |
Set the name of the bean in the bean factory that created this bean. 注入当前 bean 对应 beanName |
BootstrapContextAware |
void setBootstrapContext (BootstrapContext bootstrapContext); |
Set the BootstrapContext that this object runs in. |
LoadTimeWeaverAware |
void setLoadTimeWeaver (LoadTimeWeaver loadTimeWeaver); |
Set the LoadTimeWeaver of this object’s containing ApplicationContext. |
MessageSourceAware |
void setMessageSource (MessageSource messageSource); |
Set the MessageSource that this object runs in. |
NotificationPublisherAware |
void setNotificationPublisher (NotificationPublisher notificationPublisher); |
Set the NotificationPublisher instance for the current managed resource instance. |
PortletConfigAware |
void setPortletConfig (PortletConfig portletConfig); |
Set the PortletConfig this object runs in. |
PortletContextAware |
void setPortletContext (PortletContext portletContext); |
Set the PortletContext that this object runs in. |
ResourceLoaderAware |
void setResourceLoader (ResourceLoader resourceLoader); |
Set the ResourceLoader that this object runs in. |
ServletConfigAware |
void setServletConfig (ServletConfig servletConfig); |
Set the ServletConfig that this object runs in. |
ServletContextAware |
void setServletContext (ServletContext servletContext); |
Set the ServletContext that this object runs in. |
// 1.容器启动
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfLifeCycle.class);
// 2.
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh
// 3.
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization
// 4.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons
// 5.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(java.lang.String)
// 6.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean
// 7.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(java.lang.String, org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory<?>)
// 8.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(java.lang.String, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition, java.lang.Object[])
// 9.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean
// 10.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition)
// 11.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
// 12. 执行初始化方法 initMethod
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.invokeInitMethods
// 13.
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
// 之后循环依赖检查 afterPropertiesSet