Elk Stack Project for CSBC.
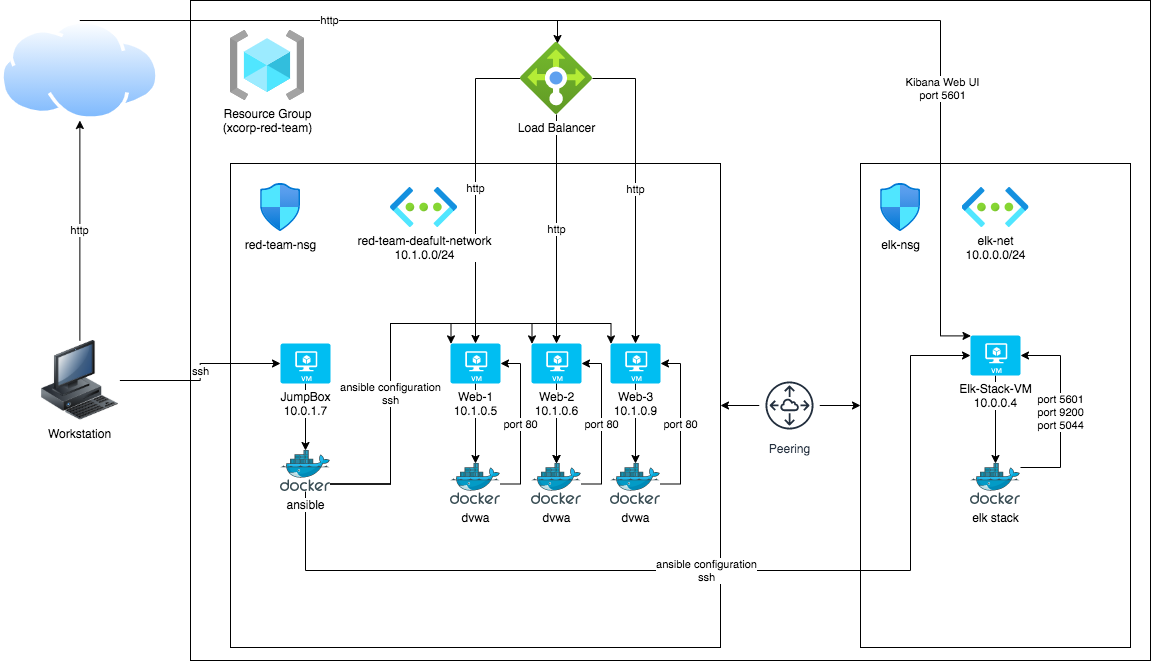
The files in this repository were used to configure the network depicted in the diagram below.
These files have been tested and used to generate a live ELK deployment on Azure. They can be used to recreate the entire deployment pictured above. Alternatively, select portions of the following Ansible playbook files can be used to install only certain portions of it, such as Filebeat.
- Elk Installation Playbook to install and configure the ELK server.
- Filebeat Playbook to install and configure Filebeat on the target machines.
- Metricbeat Playbook to install and configure Metricbeat on the target machines.
This document contains the following details of the deployment:
- Description of Network Topology
- Access Policies
- ELK Configuration
- Beats in Use
- Machines being Monitored
- Usage Instructions for Ansible Build
The main purpose of this network is to expose a load-balanced and monitored instance of DVWA, the Damn Vulnerable Web Application.
Load balancing ensures that the application will be highly available, in addition to restricting access to the network. The use of a load-balancer ensures the machines running DVWA are not directly accessible from the internet, and protected from unauthorized SSH access from outside the network. The use of the jump box ensures we can only access the other machines from the docker container running within.
Integrating an ELK server allows users to easily monitor the vulnerable VMs for changes to the VM metrics and system logs. The Metricbeat and Filebeat modules were installed on the DVWA VMs, and monitor the following:
- Filebeat: Monitors system logs on the machines.
- Metricbeat: Monitors VM metrics, including network I/O, CPU usage, CPU load, and memory pressure.
The configuration details of each machine may be found in the table below:
| Name | Function | IP Address | Operating System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jump-Box-Provisioner | Gateway | 10.1.0.4 | Linux (Ubunutu) |
| Web-1 | DVWA Server | 10.1.0.5 | Linux (Ubunutu) |
| Web-2 | DVWA Server | 10.1.0.6 | Linux (Ubunutu) |
| Web-3 | DVWA Server | 10.1.0.9 | Linux (Ubunutu) |
| Elk-Stack-VM | ELK Stack | 10.0.0.4 | Linux (Ubuntu) |
Machines on the internal network are not exposed to the public internet.
Only the Jump-Box-Provisioner machine can accept connections from the internet. Access to this machine is only allowed from the following IP addresses:
- 184.96.25.XXX (Redacted for security purposes)
Machines within the network can only be accessed by the Jump Box, which has the
IP address 10.1.0.4.
A summary of access policies in place can be found in the table below:
| Name | Publicly Accessible | Allowed IP Addresses |
|---|---|---|
| Jump-Box-Provisioner | Yes | 184.96.25.XXX |
| Web-1 | No | 10.1.0.4 |
| Web-2 | No | 10.1.0.4 |
| Web-3 | No | 10.1.0.4 |
| Elk-Stack-VM | No | 10.1.0.4 |
Ansible was used to automate configuration of the ELK machine. No configuration was performed manually, which is advantageous because it reduces the chance of typos and human error when configuring the machine.
Three playbooks in total were used, each implementing the following tasks:
-
- Install docker.io package using
apt - Install python3-pip package manager using
apt - Install the docker module using
pip - Configure the VM to use more memory using the
sysctlmodule - Download and launch the docker container for the ELK stack
- Install docker.io package using
-
- Download and install Filebeat
- Copy Filebeat configuration
- Enable Filebeat system module
- Setup Filebeat
- Start and enable Filebeat service
-
- Download and install Metricbeat
- Copy Metricbeat configuration
- Enable Metricbeat docker module
- Setup Metricbeat
- Start and enable Metricbeat service
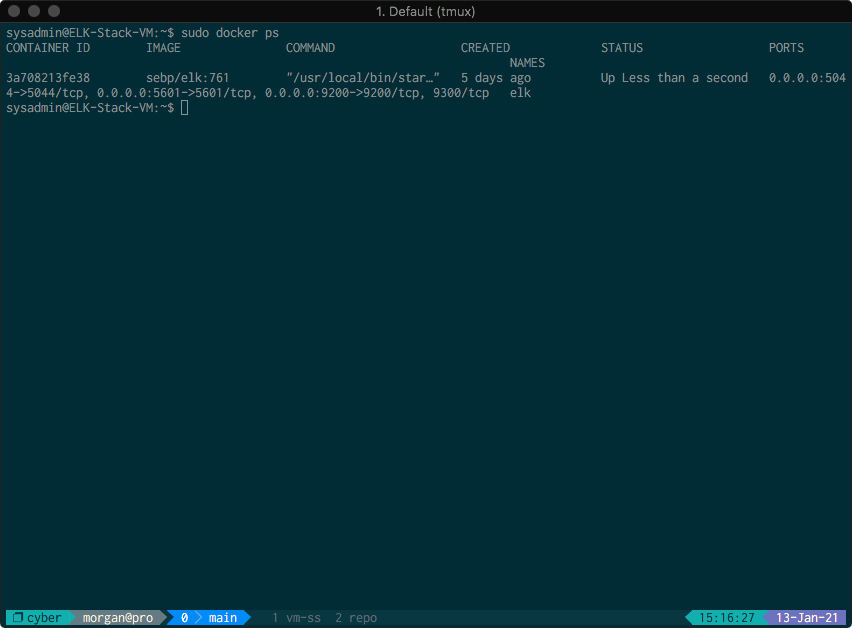
The following screenshot displays the result of running docker ps after
successfully configuring the ELK instance.
This ELK server is configured to monitor the following machines:
- Web-1
- Web-2
- Web-3
We have installed the following Beats on these machines:
- Filebeat
- Metricbeat
These Beats allow us to collect the following information from each machine:
Filebeatcollects system logs, allowing us to view a variety of information, including successful and failed login attempts, failed processes, errors that occur in running processes, etc.Metricbeatcollects metric information on each system, allowing us to view CPU load, network I/O, CPU usage, and memory pressure, among other things.
In order to use the playbooks, you will need to have an Ansible control node already configured. Assuming you have such a control node provisioned:
SSH into the control node and follow the below steps:
- Copy the three playbook files (
install-elk.yml,filebeat-playbook.yml, andmetricbeat-playbook.yml) to the/etc/ansible/rolesdirectory on your control node. - Update the
/etc/ansible/hostsfile. You will need to include a group calledelkserverswhich contains the IP address of the server you wish to install the ELK stack on. Additionally, you will need to create a group calledwebserverswith the IP addresses of the target machines you wish to monitor. An example configuration has been provided below:[webservers] 10.1.0.5 ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3 10.1.0.6 ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3 10.1.0.9 ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3 [elkservers] 10.0.0.4 ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
- Run the playbook, and navigate to
http://[PUBLIC IP OF ELK SERVER]:5601to confirm that the installation worked as expected.
Example commands are shown below. Note that the exact commands may differ based on your exact configuration.
From the Ansible control node:
# Clone this repository
$ git clone https://github.com/baberthal/CSBC-Elk-Stack
# NOTE: `sudo` may be required for the following commands, depending on your
# exact configuration
# Ensure the destination directories exist
$ mkdir -p /etc/ansible/roles/files
# Copy the playbooks to the expected locations
$ cp CSBC-Elk-Stack/ansible/roles/install-elk.yml /etc/ansible/roles
$ cp CSBC-Elk-Stack/ansible/roles/filebeat-playbook.yml /etc/ansible/roles
$ cp CSBC-Elk-Stack/ansible/roles/metricbeat-playbook.yml /etc/ansible/roles
# Copy the filebeat and metricbeat configurations to the expected location
$ cp CSBC-Elk-Stack/ansible/roles/files/filebeat-config.yml /etc/ansible/roles/files
$ cp CSBC-Elk-Stack/ansible/roles/files/metricbeat-config.yml /etc/ansible/roles/files
# Update the /etc/ansible/hosts file with appropriate configuration
$ vi /etc/ansible/hosts
# Run the ELK installation playbook
$ ansible-playbook /etc/ansible/roles/install-elk.yml
# Run the Filebeat installation playbook
$ ansible-playbook /etc/ansible/roles/filebeat-playbook.yml
# Run the Metricbeat installation playbook
$ ansible-playbook /etc/ansible/roles/metricbeat-playbook.yml