BubbleOS is an operating system for personal educational purposes, aimed at providing insight into the fundamentals of operating system development.
This project serves as a practical learning resource for those interested in understanding the essentials of OS development. It offers page memory management, preemptive/cooperative multitasking, trap(interrupts and exception handling), timer, spin lock, and system call.
In the future, BubbleOS will undergo a major overhaul and transition to Rust programming language. This transition will introduce advanced features including Virtual Memory support, File Systems implementation, and Network components integration.
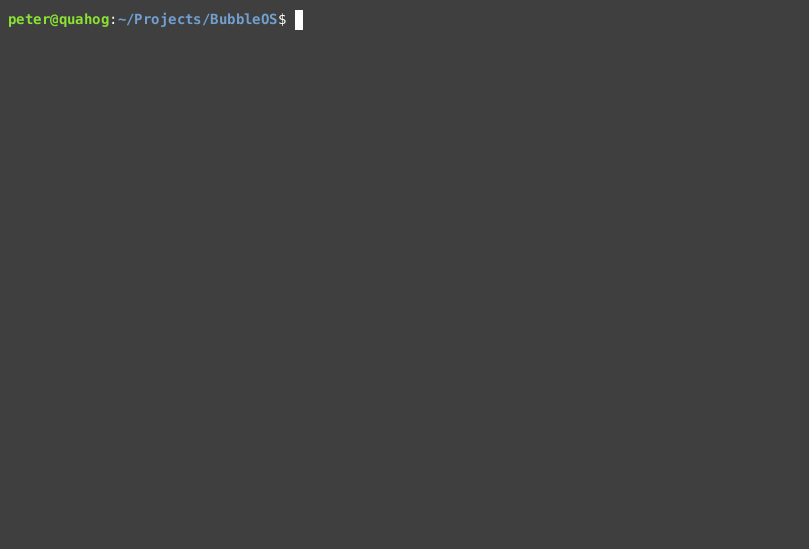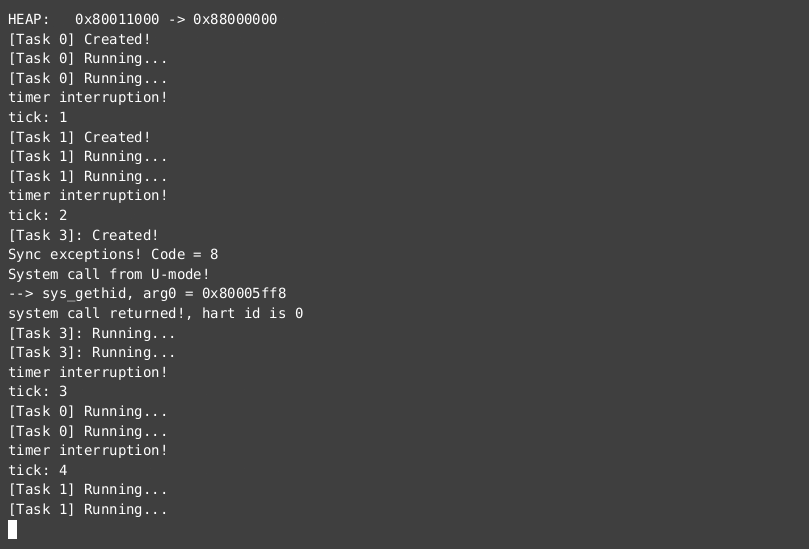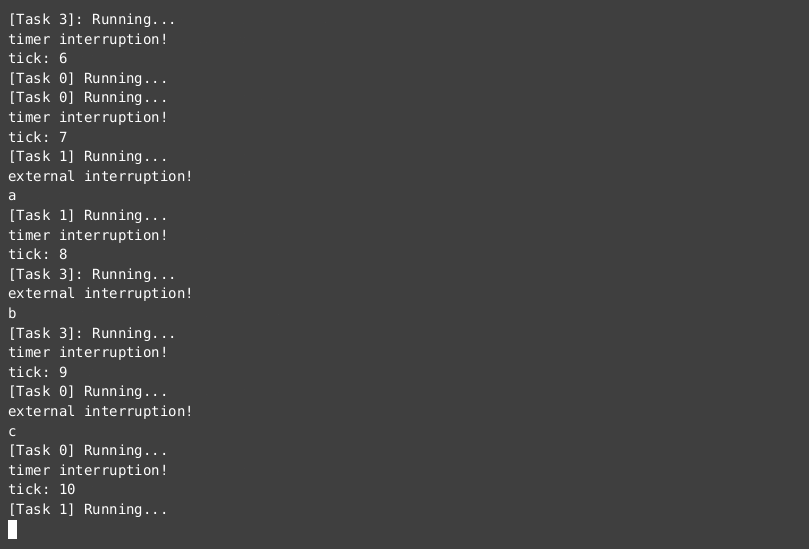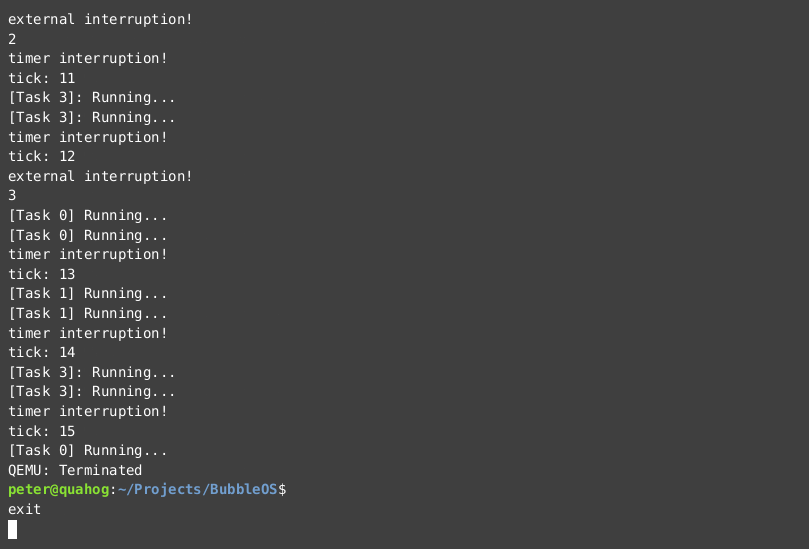
The length of Memory is 128M = 8 managment pages * 4096 bytes * 4096 page size
BubbleOS utilizes a page-based memory management system. The first 8 pages are dedicated to management, followed by real pages for data storage. Each byte within the management pages stores a flag, where the last two bits represent PAGE_LAST (indicating if the page is the last page of an allocation) and PAGE_TAKEN (indicating if the page is currently in use).
For example, a flag value of 0x0000_0001 signifies that the page is currently in use and is not the last page of an allocation.
In Cooperative Multitasking, before a new task can be executed, the current one must voluntarily give up the CPU.
mscratch: A register in Machine mode to point current contextra(x1): General register to save the return addressret: jump back toracall: will also store the next address of instruction intora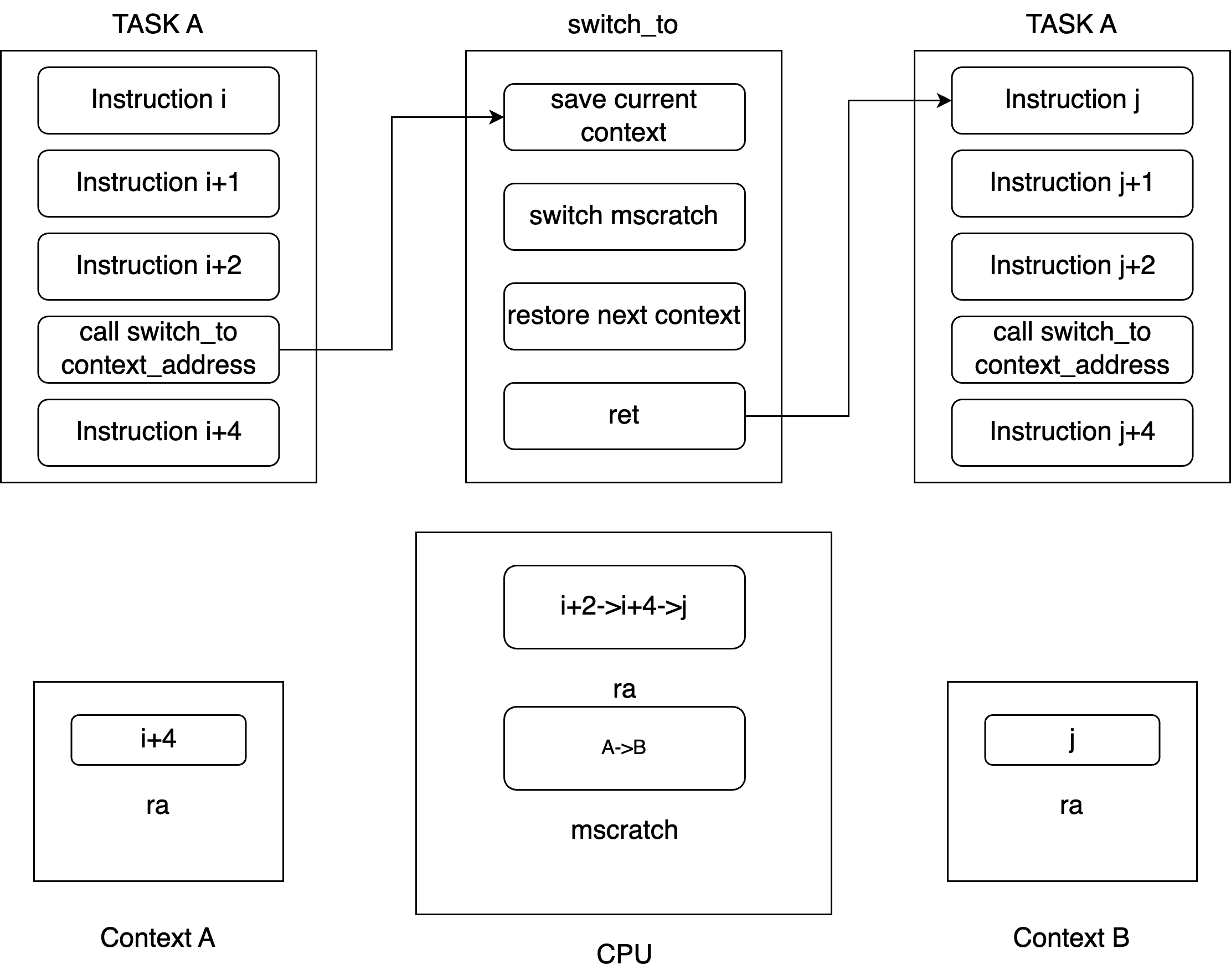 There are two tasks, A and B. Task A is running on the CPU. When it calls
There are two tasks, A and B. Task A is running on the CPU. When it calls switch_toto switch to task B, it stores the address of the next instruction of task A in theraregister before entering theswitch_tofunction in BubbleOS. Insideswitch_to, it saves the context of task A into memory, then restores the context of task B from memory on top of that in order to execute the instructions for task B itret(jump to the instruction in B).
Trap is Exceptional Control Flow(ECF) in RISC-V.
Trap initialize -> Top Half(Hardware, cannot be controled) -> Bottom Half(Our logic) -> Return
- setting BASE address by
mtvecregister
- copy MIE in
mstatusto MPIE and clean MIE to close interrupt - setting
mepcandmtvec,mepcwill be set to the address of next command if trap is caused by interrupt. if trap is caused by Exception,mepcwill be set to the address of current command. - setting
mcauseandmtval - save previous priviledge to MPP in
mstatusand change the current priviledge to Machine
- save context
- call function
trap_handler - return
- restore context
- execute MRET to restore trap status
- current privilidge of hart = mstatus.MPP
- mstatus.MPP = U or M
- mstatus.MIE = mstatus.MPIE
- mstatus,MPIE = 1
- pc = mepc
-
Interrupt
- Local interrupt
- software interrupt
- timer interrupt
- Global interrupt
- externrl interrupt
- Local interrupt
-
interrupt steps:
- Copy MIE from
mstatusto MPIE and clean MIE to disable interrupt - Copy next instruction address to
mepc - Set PC =
mtvec - Set
mcauseandmtval - Copy previous to MPP in
mstatusand Set current to M
- Copy MIE from
Because every hart only has one external interrupt pin, we need a hub to control all interruptions -- PLIC
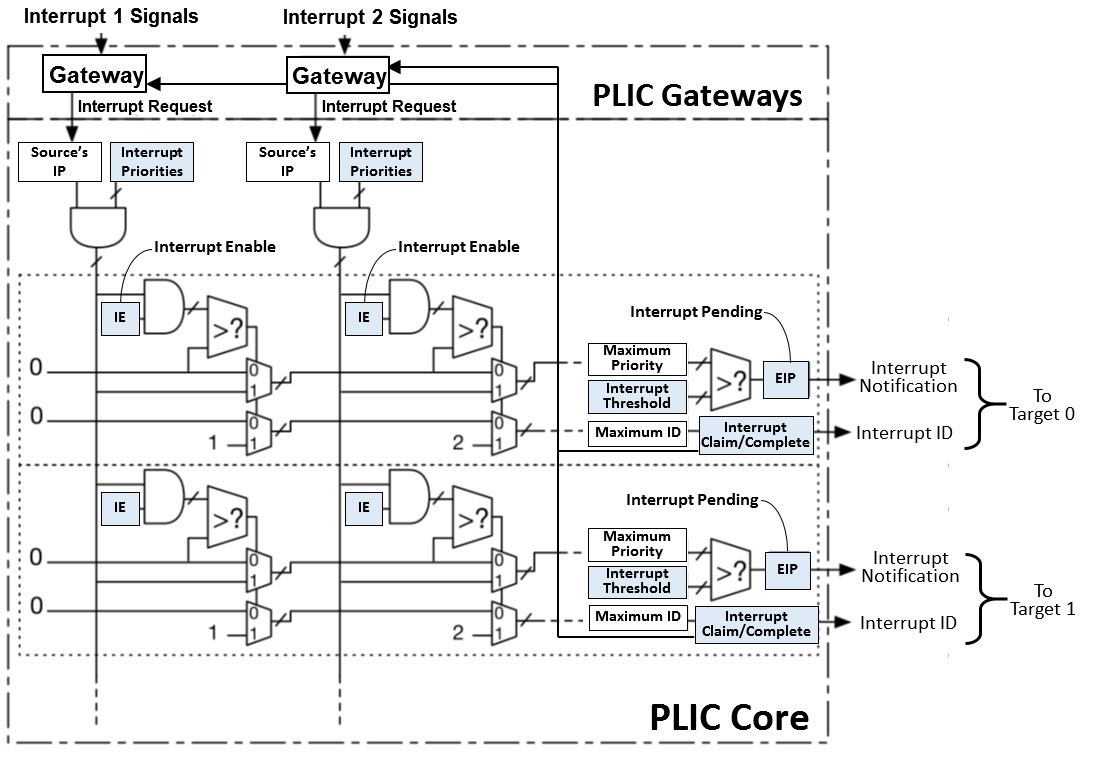
It is a local interrupt cause by CLINT(Core Local Interrupt)
- mtime = 0 and mtiomcmp += INTERVAL
- wait for timer interrupt
- excute interrupt steps and set mtimecmp += INTERVAL