Microarchitecture determines the implementation of a microprocessor. Designing a microarchitecture to achieve better performance, power, and area (PPA) trade-off has been increasingly difficult. Previous data-driven methodologies hold inappropriate assumptions and failed to tightly couple with expert knowledge. In this repo., we release a novel reinforcement learning-based (RL) solution that addresses these limitations. With the integration of microarchitecture scaling graph, PPA preference space embedding, and proposed lightweight environment in RL, experiments using commercial electronic design automation (EDA) tools show that our method achieves an average PPA trade-off improvement of 16.03% than previous state-of-the-art approaches with 4.07× higher efficiency. The solution qualities also outperform human implementations by at most 2.03× in the PPA trade-off.
The folder tree is shown below.
rl-explorer
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── __init__.py
├── baselines
│ ├── boom_explorer
│ │ ├── LICENSE
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ ├── algo
│ │ │ ├── boom_explorer.py
│ │ │ ├── dkl_gp.py
│ │ │ └── problem.py
│ │ ├── configs
│ │ │ ├── README.md
│ │ │ └── boom-explorer.yml
│ │ ├── main.py
│ │ └── util
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── exception.py
│ │ ├── sample.py
│ │ └── util.py
│ ├── dac16
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── dac16.py
│ └── isca14
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── boom.txt
│ ├── configs
│ │ └── isca14.yml
│ ├── isca14.py
├── data
│ ├── boom
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ ├── boom.txt
│ │ └── dataset.txt
│ └── rocket
│ ├── dataset.txt
│ └── rocket.txt
├── dse
│ ├── algo
│ │ └── a3c
│ │ ├── a3c.py
│ │ ├── agent
│ │ │ ├── agent.py
│ │ │ ├── boom.py
│ │ │ └── rocket.py
│ │ ├── buffer.py
│ │ ├── functions.py
│ │ ├── model.py
│ │ └── preference.py
│ └── env
│ ├── base_design_space.py
│ ├── boom
│ │ ├── design_space.py
│ │ └── env.py
│ └── rocket
│ ├── design_space.py
│ └── env.py
├── main
│ ├── configs
│ │ ├── example.yml
│ │ ├── giga.yaml
│ │ ├── medium.yaml
│ │ ├── mega.yaml
│ │ ├── rocket.yaml
│ │ └── small.yaml
│ └── main.py
├── simulation
│ ├── base_simulation.py
│ ├── boom
│ │ └── simulation.py
│ └── rocket
│ └── simulation.py
├── tools
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── calib.py
│ ├── gem5-mcpat-parser.py
│ ├── mcpat-research
│ │ └── ... # mcpat-research project
│ ├── models
│ │ ├── boom
│ │ │ ├── boom-area.pt
│ │ │ ├── boom-perf.pt
│ │ │ ├── boom-power.pt
│ │ └── rocket
│ │ ├── rocket-area.pt
│ │ ├── rocket-perf.pt
│ │ └── rocket-power.pt
│ └── template
│ ├── boom.xml
│ ├── rocket.xml
│ └── template.xml
├── requirements.txt
└── utils
├── exceptions.py
├── handle_data.py
├── thread.py
├── utils.py
└── visualizer.pyKey folders where we implement critical functions.
-
dse: implement our RL-based solution framework, including episode design with microarchitecture scaling graph, PPA preference space, and conditioned actor-critic network design. -
simulationandtools: implement our lightweight environment. -
baselines: implement our baselines.
Currently, we do not provide the Docker environment (we will provide Docker environment in the future work).
So, users need to install the required software packages.
The software requirements are listed in requirements.txt.
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txtUsers need to purchase commercial EDA tools licenses to reproduce PPA values reported in the manuscript. Otherwise, users only obtain PPA values from lightweight PPA models, and these values are inaccurate compared to estimations from commercial EDA tools. However, users can still experience our algorithm flow if commercial EDA tools are not presented on users' machines.
The commercial EDA tools are:
-
Synopsys VCS M-2017.03: More information can be found in link.
-
Synopsys PrimeTime PX R-2020.09-SP1: More information can be found in link
-
Cadence Genus 18.12-e012 1: More information can be found in link
A high-performance server-class machine is preferred since our repo. includes parallel compilations and simulations, which demonstrates very large workloads for machines. In our experiments, we use 80 Quad Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E7-4820 V3 cores with a 1 TB main memory.
- Environment setup
$ cd /path/to/rl-explorer
$ export PYTHONPATH=`pwd` # `. ./tools/settings.sh` is also OK for you
$ pushd tools/mcpat-research && make -j`nproc` && popd
$ vim main/configs/example-boom.yaml # main/configs/example-rocket.yaml is used for Rocket experimentsIn `main/configs/example.yaml`, several absolute paths needs to be configurated correctly.
They are:
-
chipyard-research-root: set the path to point tochipyar-research(Please see TODO). -
gem5-research-root: set the path to point togem5-research(Please see TODO). -
dataset: set the path to point torl-explorer/data/boom/boom.txt. -
calib-dataset: set the path to point torl-explorer/data/boom/dataset.txt. -
ppa-model: set the path to point torl-explorer/tools/models/boom.
NOTICE: chipyard-research-root & gem5-research-root are the other two private repositories. These two repositories are too large to be anonymous. We will open-source them to the public after the anonymous stage.
- RL training
$ cd main
$ python3 main.py -c configs/example.yml- Check outputs after the training
$ cd logsThe training logs include the following folder organizations.
train-small-SonicBOOM-example-user-example-machine-2023-08-18-23-59 is an example folder name.
train-small-SonicBOOM-example-user-example-machine-2023-08-18-23-59
├── example.yaml # users' YAML configuration file
├── log-2023-08-18-23-59.log # users' RL training log
├── models
│ └── log-2023-05-09-15-10.pt # users' saved RL agents
└── summary-logs
└── train-small-SonicBOOM-example-user-example-machine-2023-08-18-23-59
└── log-2023-08-18-23-59.log
├── episode_action_BP_a1 # action probability visualization, e.g., 1st branch predictor
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_BP_a2
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_BP_a3
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_D$_a1 # action probability visualization, e.g., 1st d-cache structure
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_D$_a2
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_D$_a3
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_D$_a4
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_I$_a1
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_IFU_a1
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_IFU_a2
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_IFU_a3
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_IFU_a4
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_IFU_a5
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ISU_a1
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ISU_a2
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ISU_a3
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ISU_a4
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ISU_a5
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_LSU_a1
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_LSU_a2
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_LSU_a3
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_LSU_a4
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_PRF_a1
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_PRF_a2
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_PRF_a3
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_PRF_a4
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_PRF_a5
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ROB_a1
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ROB_a2
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ROB_a3
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_ROB_a4
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_maxBrCount_a1
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_maxBrCount_a2
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_maxBrCount_a3
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_action_maxBrCount_a4
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_area_area
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_learning-rate_learning-rate
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_loss_actor-loss
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_loss_critic-loss
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_loss_entropy
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_loss_total-loss
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_perf_perf
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_power_power
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_preference_area-performance
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_preference_perf-preference
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_preference_power-preference
│ └── events.out.tfevents
├── episode_reward_reward
│ └── events.out.tfevents
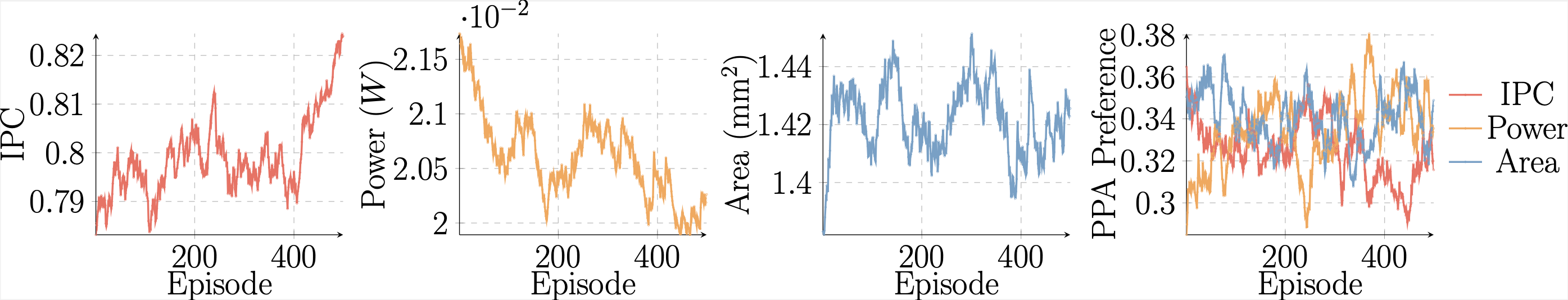
└── events.out.tfevents- Example training curves
- RL design space exploration (DSE)
$ cd main # Assume you are not in the `main` directory
$ vim configs/example.ymlIn main/configs/example.yaml, make some revisions to start DSE.
-
change
mode: traintomode: test. -
rl-model: set with the saved RL agents' absolute path, e.g.,/path/to/train-small-SonicBOOM-example-user-example-machine-2023-08-18-23-59/models/log-2023-05-09-15-10.pt
We start DSE by executing the following instructions:
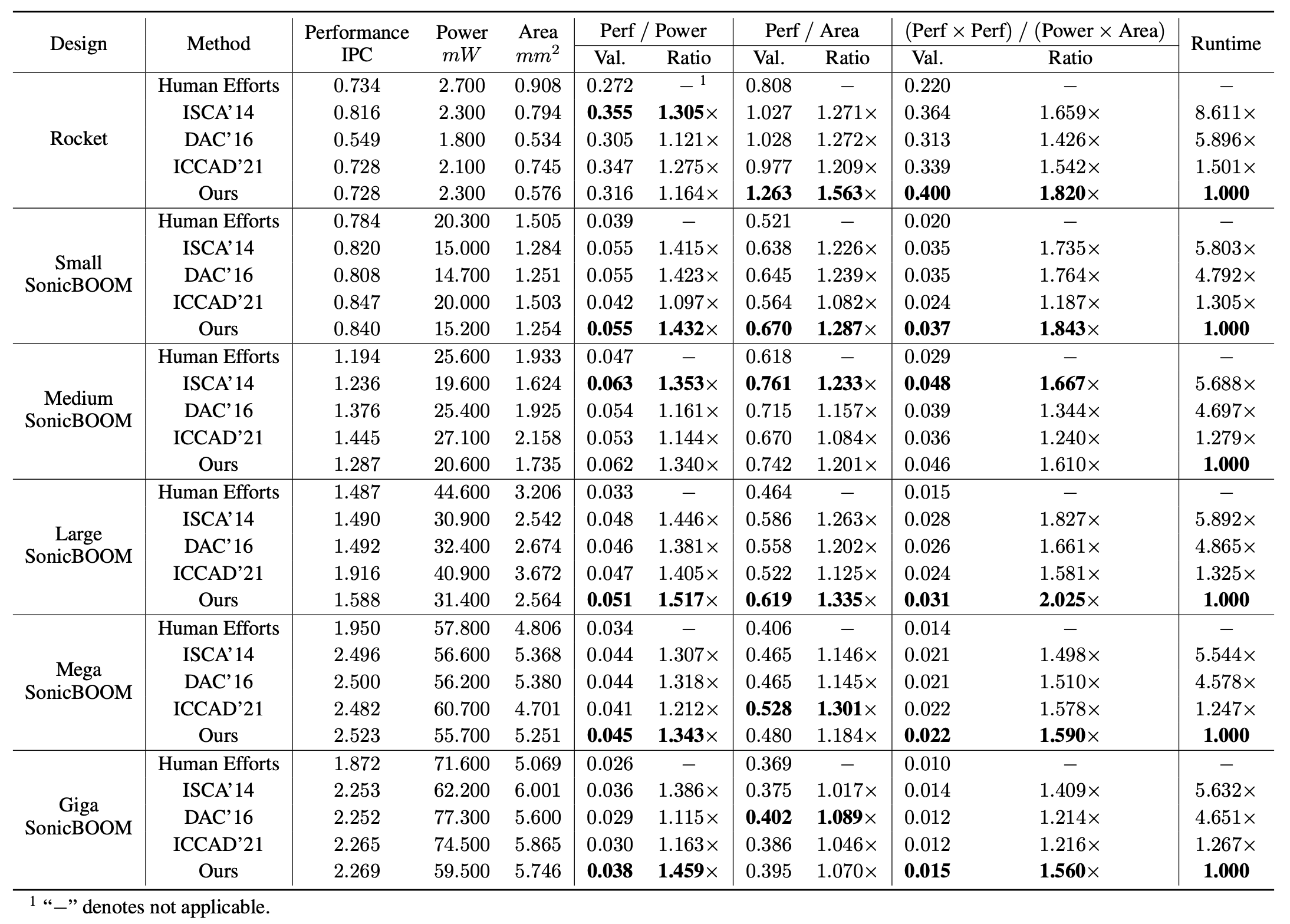
$ python3 main.py -c configs/example-boom.ymlThe main results evaluated with commercial EDA tools are reported below.
- Open source part of
chipyard-researchforrl-explorer. - Open source
gem5-researchforrl-explorer.