LSP4IntelliJ - Language Server Protocol Support for JetBrains Plugins
LSP4IntelliJ is a client library that enables Language Server Protocol (LSP) support for IntelliJ IDEA and other JetBrains IDEs.
Designed for plugin developers, it facilitates integration with LSP-based features and supports language-specific extensions via the JSON-RPC protocol.
Follow the below steps to integrate LSP4IntelliJ into your custom language plugin.
Include lsp4intellij in your project's build file. Instructions for popular build tools are available at jitpack/lsp4intellij.
Supported build tools:
- Gradle
- Maven
- SBT
Info: Maven Central publishing is a work in progress. Support for Maven Central will be available soon.
Define the required configurations in your plugin.xml file.
deprecated "components"-based setup
1. Add `IntellijLanguageClient` as an application component. ```xml org.wso2.lsp4intellij.IntellijLanguageClient ```-
Add the following extensions to get the relevant features as listed below.
- Code completion (You can replace the
languageattribute if you already have your own custom language implementations)<extensions defaultExtensionNs="com.intellij"> <completion.contributor implementationClass="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.contributors.LSPCompletionContributor" id="LSPCompletionContributor" language="any"/> </extensions>
- Code Formatting
<actions> <action class="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.actions.LSPReformatAction" id="ReformatCode" use-shortcut-of="ReformatCode" overrides="true" text="Reformat Code"/> <action class="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.actions.LSPShowReformatDialogAction" id="ShowReformatFileDialog" use-shortcut-of="ShowReformatFileDialog" overrides="true" text="Show Reformat File Dialog"/> </actions>
- Diagnostics and code actions (You can replace the
languageattribute if you already have your own custom language implementations)<extensions defaultExtensionNs="com.intellij"> <externalAnnotator id="LSPAnnotator" language="TEXT" implementationClass="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.contributors.annotator.LSPAnnotator"/> </extensions>
- Find Usages
<actions> <action class="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.actions.LSPReferencesAction" id="LSPFindUsages"> <keyboard-shortcut first-keystroke="shift alt F7" keymap="$default"/> </action> </actions>
- Workspace symbols
<extensions defaultExtensionNs="com.intellij"> <gotoSymbolContributor implementation="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.contributors.symbol.LSPSymbolContributor" id="LSPSymbolContributor"/> </extensions>
- Renaming Support
<extensions defaultExtensionNs="com.intellij"> <renameHandler implementation="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.contributors.rename.LSPRenameHandler" id="LSPRenameHandler" order="first"/> <renamePsiElementProcessor implementation="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.contributors.rename .LSPRenameProcessor" id="LSPRenameProcessor" order="first"/> </extensions>
- Signature Help
<extensions defaultExtensionNs="com.intellij"> <typedHandler implementation="org.wso2.lsp4intellij.listeners.LSPTypedHandler" id="LSPTypedHandler"/> </extensions>
- Code completion (You can replace the
Note: You do not need any additional configurations for the other features.
Copy the example plugin.xml file from resources/plugin.xml.example, place it under src/resources/META-INF, and adjust it as needed.
Add a preloading activity to initialize and configure LSP support:
public class BallerinaPreloadingActivity extends PreloadingActivity {
@Override
public void preload(ProgressIndicator indicator) {
IntellijLanguageClient.addServerDefinition(new RawCommandServerDefinition("bal", new String[]{"path/to/launcher-script.sh"}));
}
}Update your plugin.xml to include the preloading activity:
<extensions defaultExtensionNs="com.intellij">
<preloadingActivity implementation="io.ballerina.plugins.idea.preloading.BallerinaPreloadingActivity"
id="io.ballerina.plugins.idea.preloading.BallerinaPreloadingActivity" />
</extensions>Tip: For other options you can use instead of implementing a preloading activity, go to InteliJ Plugin initialization on startup
After successfully connecting to the language server, a green icon will appear in the bottom-right corner of your IDE. Clicking on the icon will display connection details and timeouts.
In addition to RawCommandServerDefinition, several classes implement LanguageServerDefinition, allowing you to connect to a language server in different ways. Below are the available options:
You can specify multiple extensions for a server by separating them with a comma (e.g., "ts,js").
If you want to bind your language server definition only with a specific set of files, you can use that specific file pattern as a regex expression instead of binding with the file extension (e.g., "application*.properties").
Example Usage:
new RawCommandServerDefinition("bal", new String[]{"path/to/launcher-script.sh"});String[] command = new String[]{"java", "-jar", "path/to/language-server.jar"};
new RawCommandServerDefinition("bsl,os", command);This definition is an extended form of the RawCommandServerDefinition, which accepts
java.lang.ProcessBuilder instances so that the users will have more controllability over the language
server
process to be created.
You can specify multiple extensions for a server by separating them with a comma (e.g., "ts,js").
If you want to bind your language server definition only with a specific set of files, you can use that specific file pattern as a regex expression instead of binding with the file extension (e.g., "application*.properties").
Example Usage:
ProcessBuilder process = new ProcessBuilder("path/to/launcher-script.sh");
new ProcessBuilderServerDefinition("bal", process);ProcessBuilder process = new ProcessBuilder("java", "-jar", "path/to/language-server.jar");
new ProcessBuilderServerDefinition("bsl,os", process);If your language server requires custom initialization options, you can extend ProcessBuilderServerDefinition or RawCommandServerDefinition and override the customizeInitializeParams method to modify the initialization parameters.
public class MyServerDefinition extends ProcessBuilderServerDefinition {
public MyServerDefinition(String ext, ProcessBuilder process) {
super(ext, process);
}
@Override
public void customizeInitializeParams(InitializeParams params) {
params.clientInfo = new ClientInfo("MyName", "MyVersion");
}
}Finally, assign your class as a ServerDefinition:
ProcessBuilder process = new ProcessBuilder("path/to/launcher-script.sh");
IntellijLanguageClient.addServerDefinition(new MyServerDefinition("xxx", processBuilder));You can refer to #311 for more details.
Note: All implementations use stdin/stdout for server communication.
Tip: A green icon in the IDE's bottom-right corner indicates successful connection to the language server. Clicking on the icon will display connection details and timeouts.
Press the CTRL+SPACE keys to see the completion items list, which depends on your cursor position.(Code completion items
will also pop-up automatically based on your language-server-specific trigger characters.)
For Code Snippets, you can use TAB/ENTER to navigate to the next place holder position or ESC to apply the code snippets with the default values.
Navigate to Code->Reformat Code and you will get a dialog to choose whether to format the whole file or the selected range.
To see diagnostics (errors, warnings etc.), hover over them to view the message.
Hover over any diagnostic highlight to view and apply related code actions using the light bulb that pops up as
shown below.
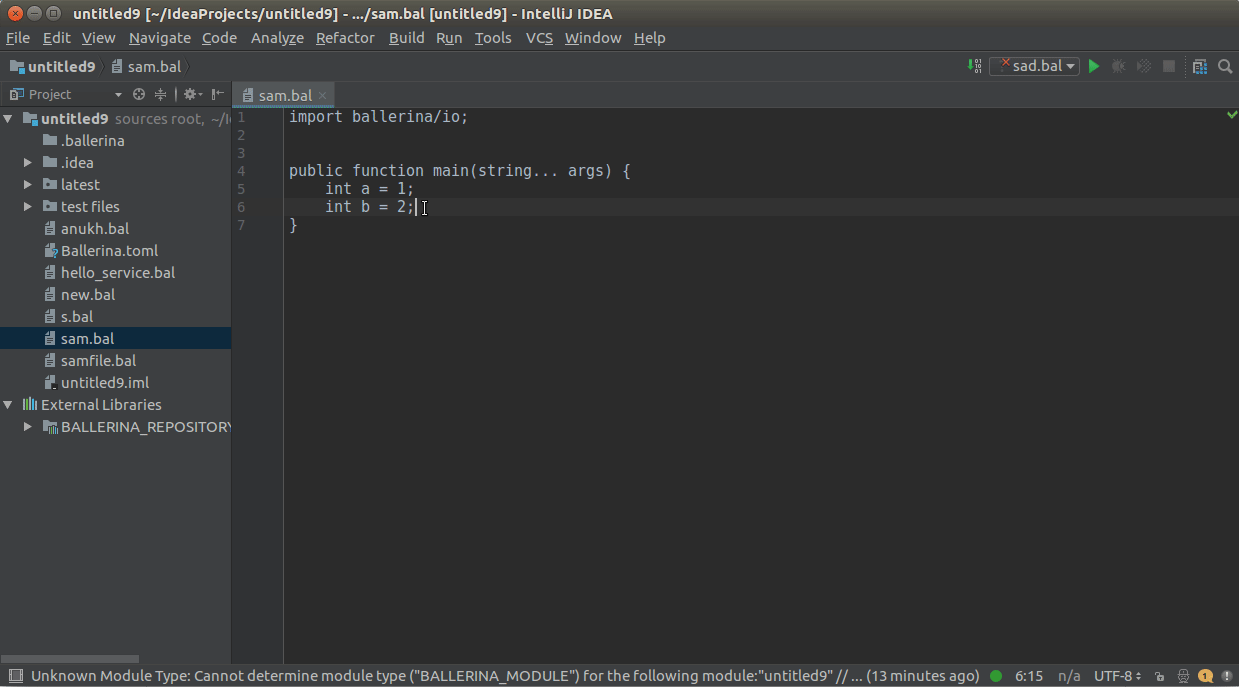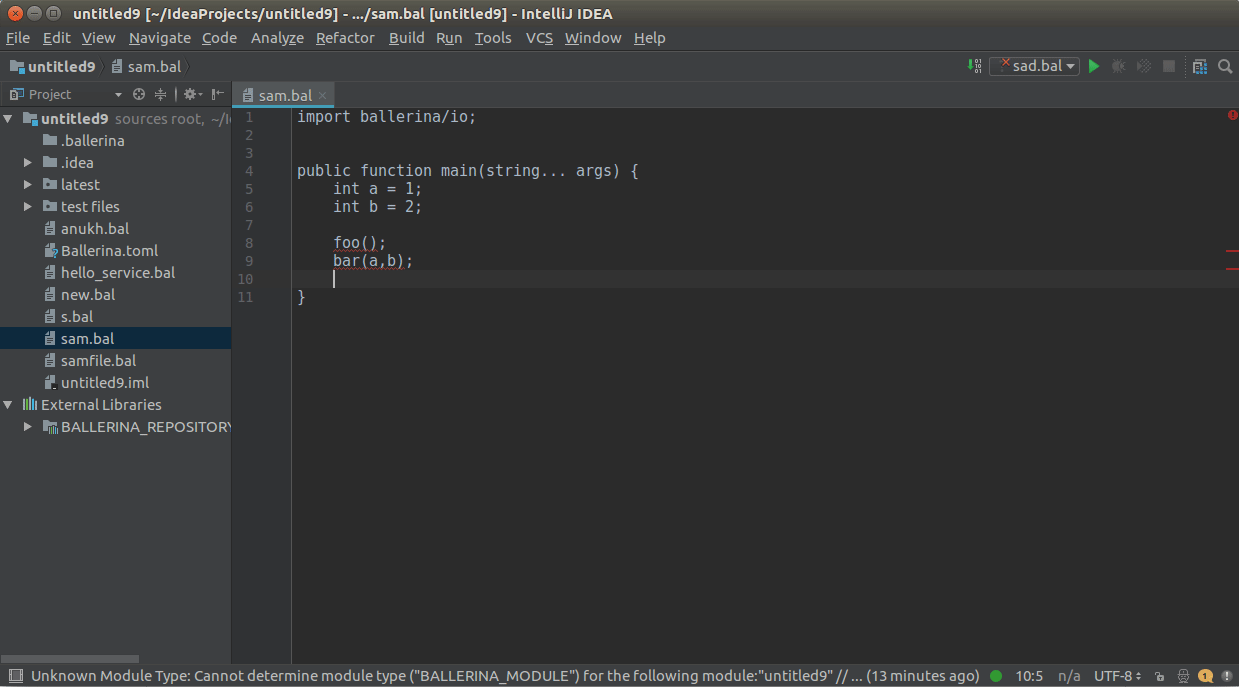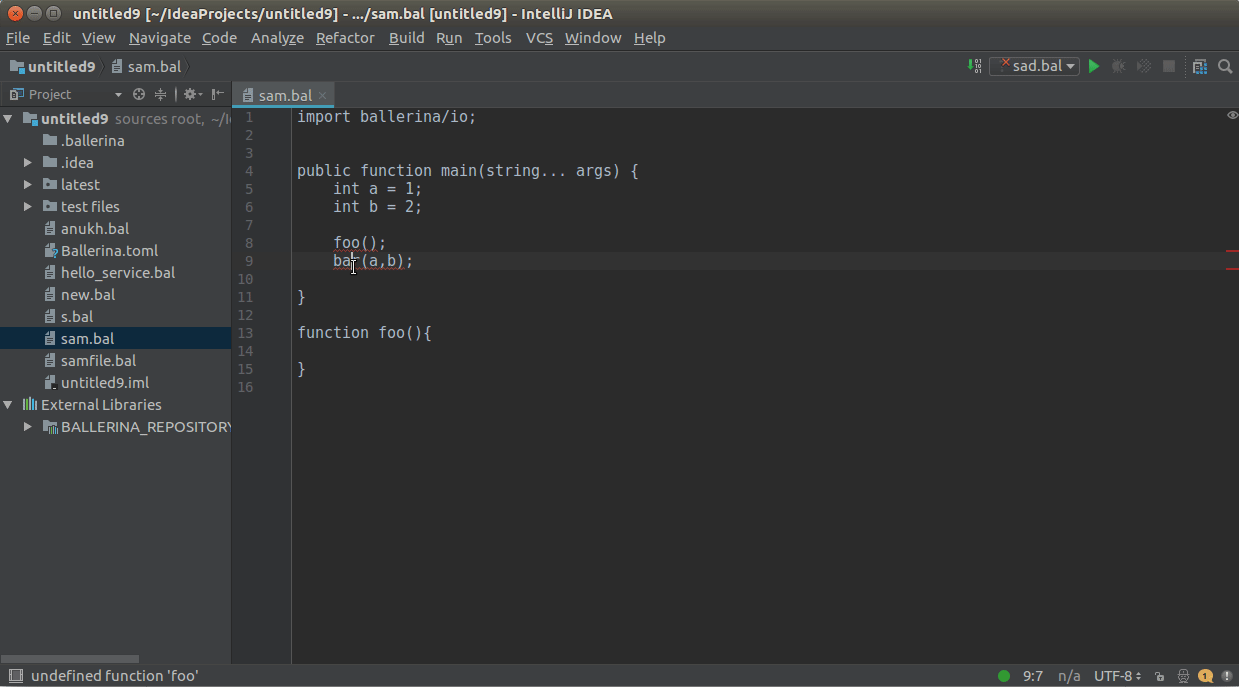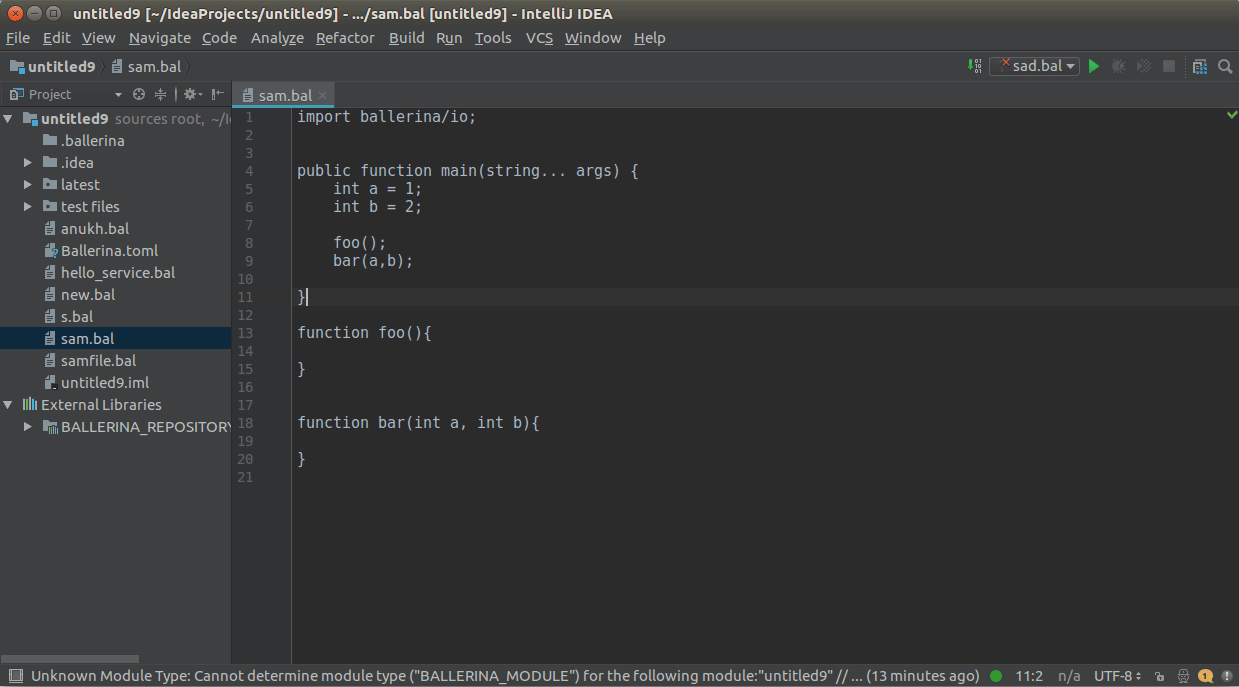
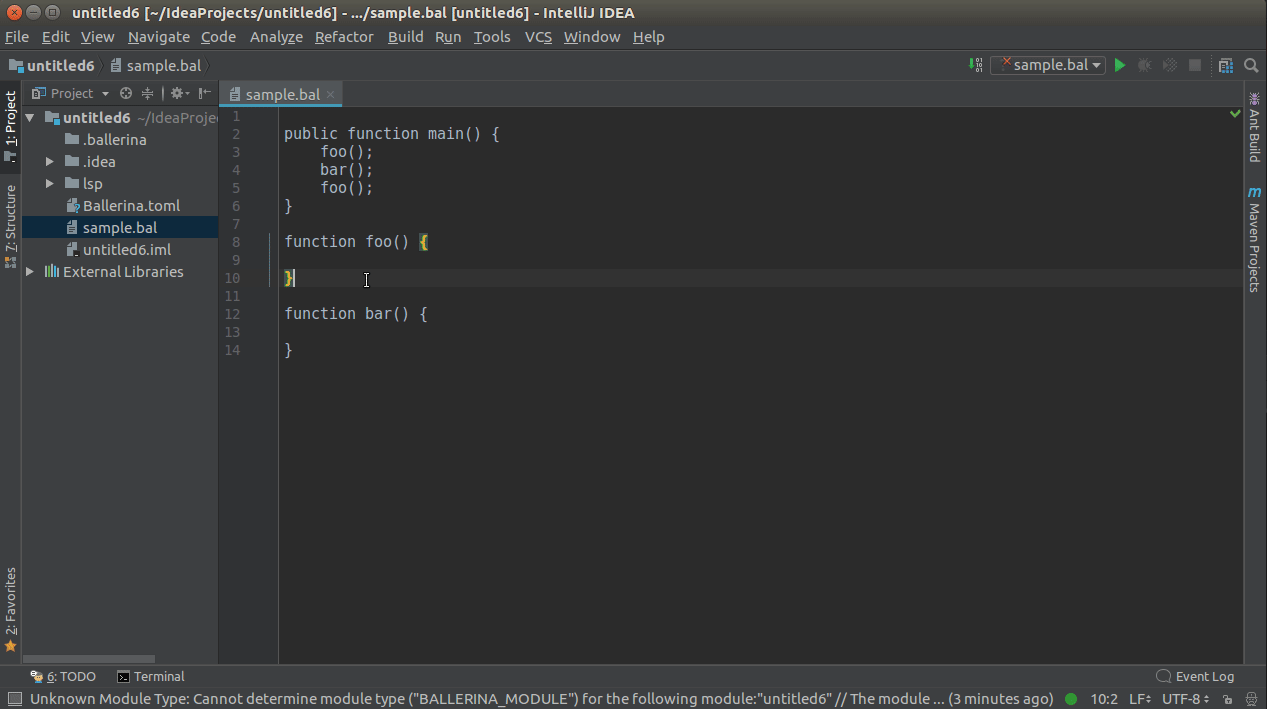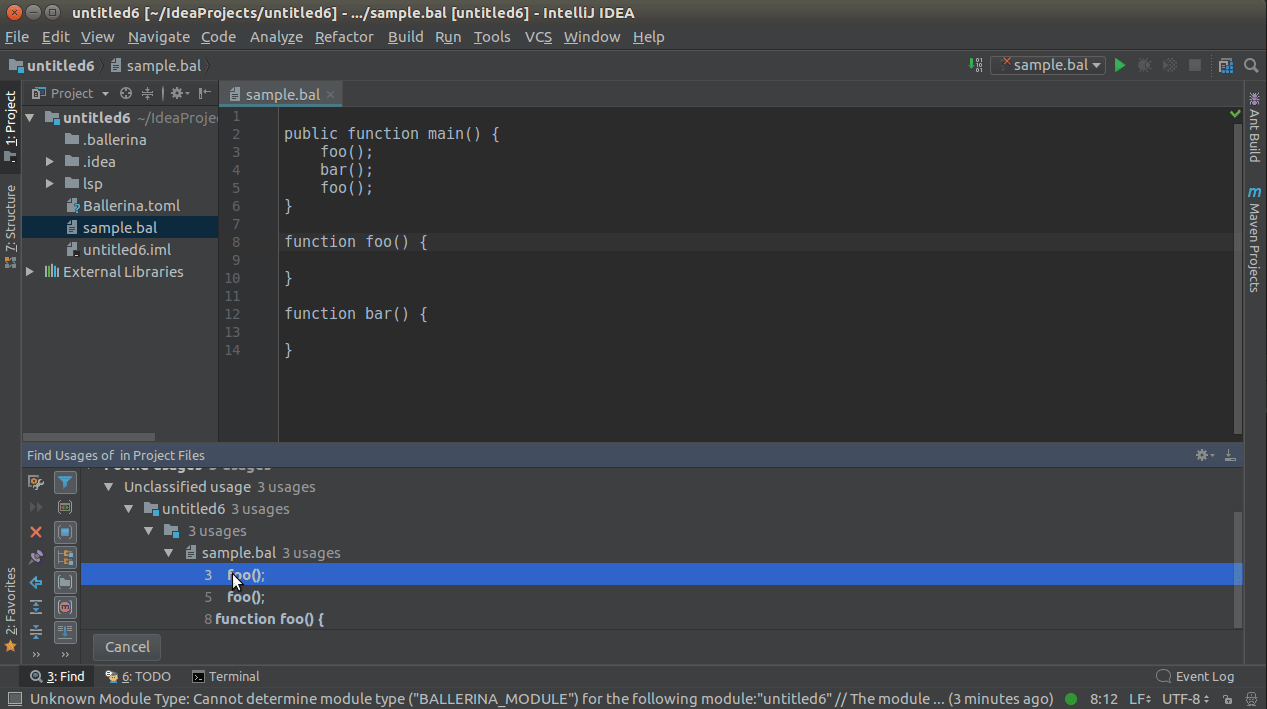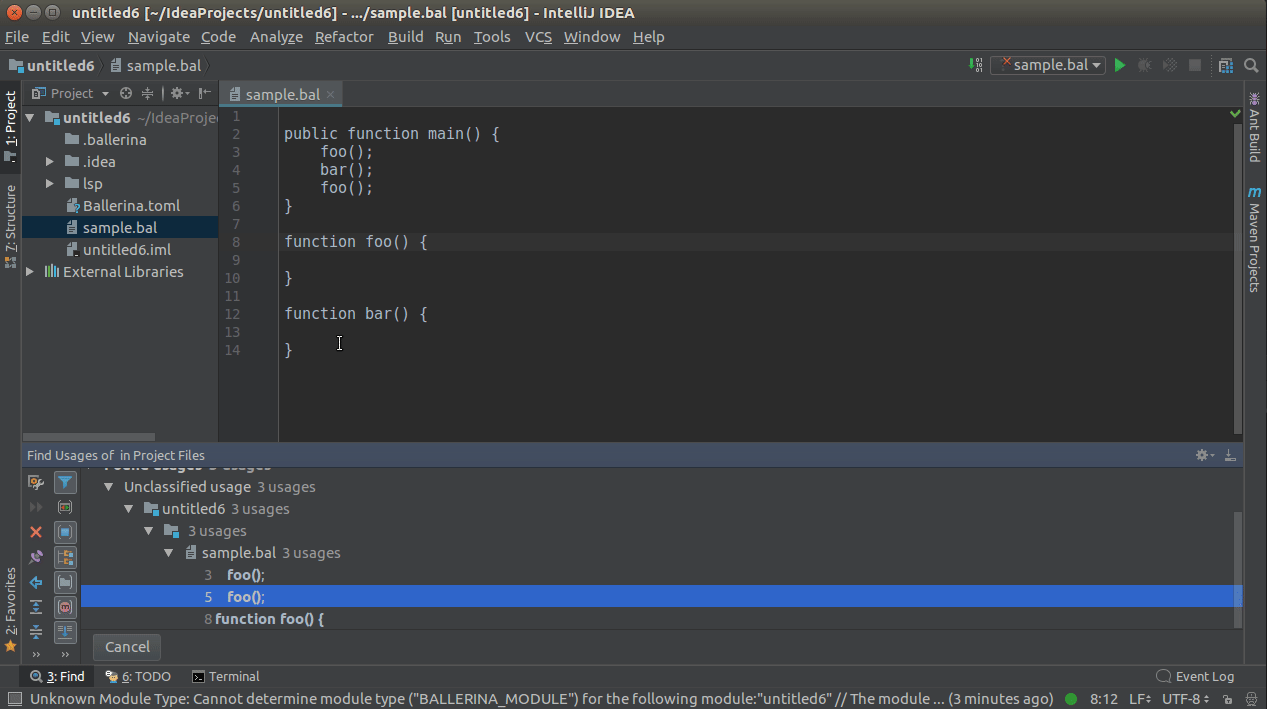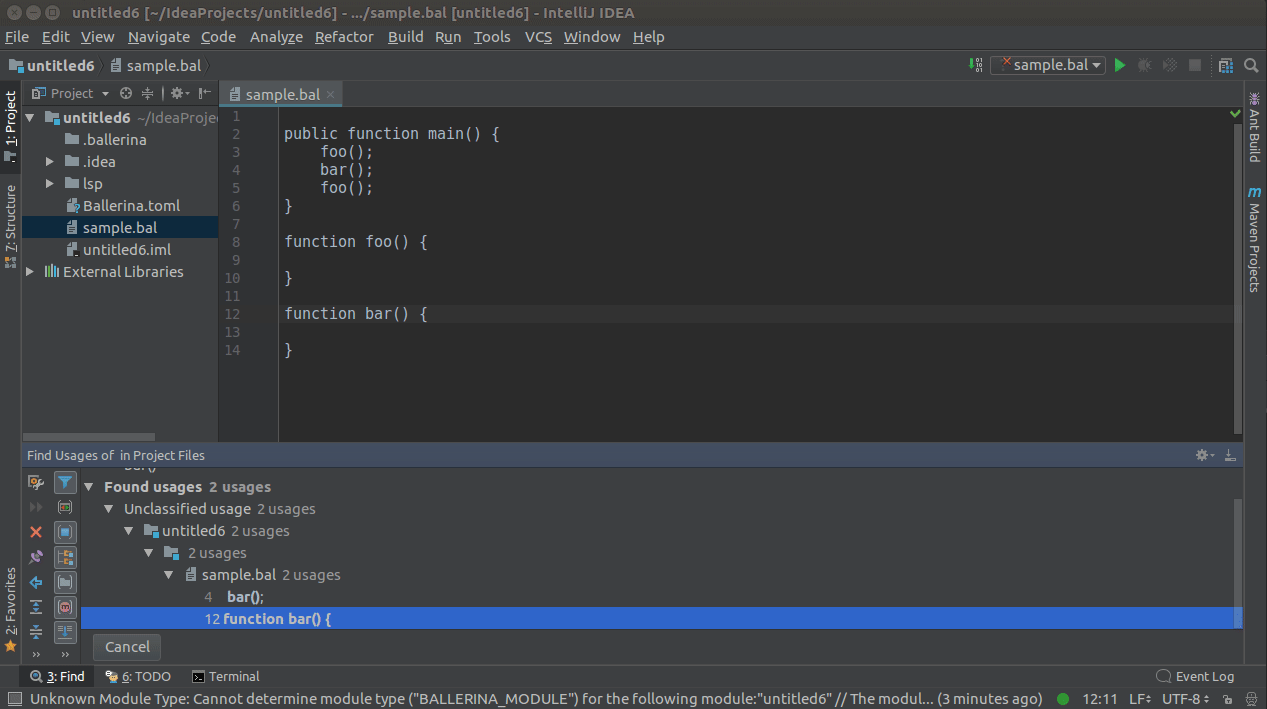
You can use CTRL+CLICK(COMMAND+CLICK in MacOS) to navigate to its definition.
You can use CTRL+CLICK(COMMAND+CLICK in MacOS) or SHIFT+ALT+F7 for a symbol to view the list of its references/usages.
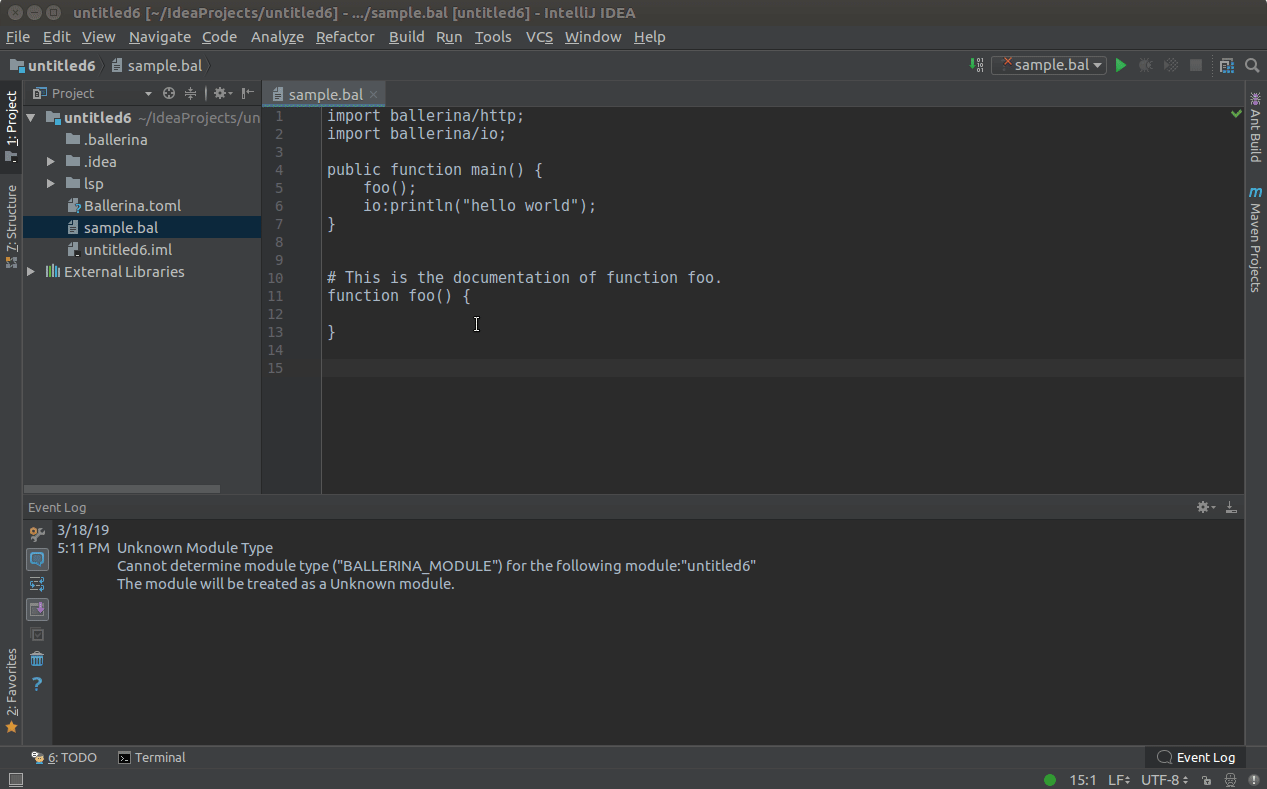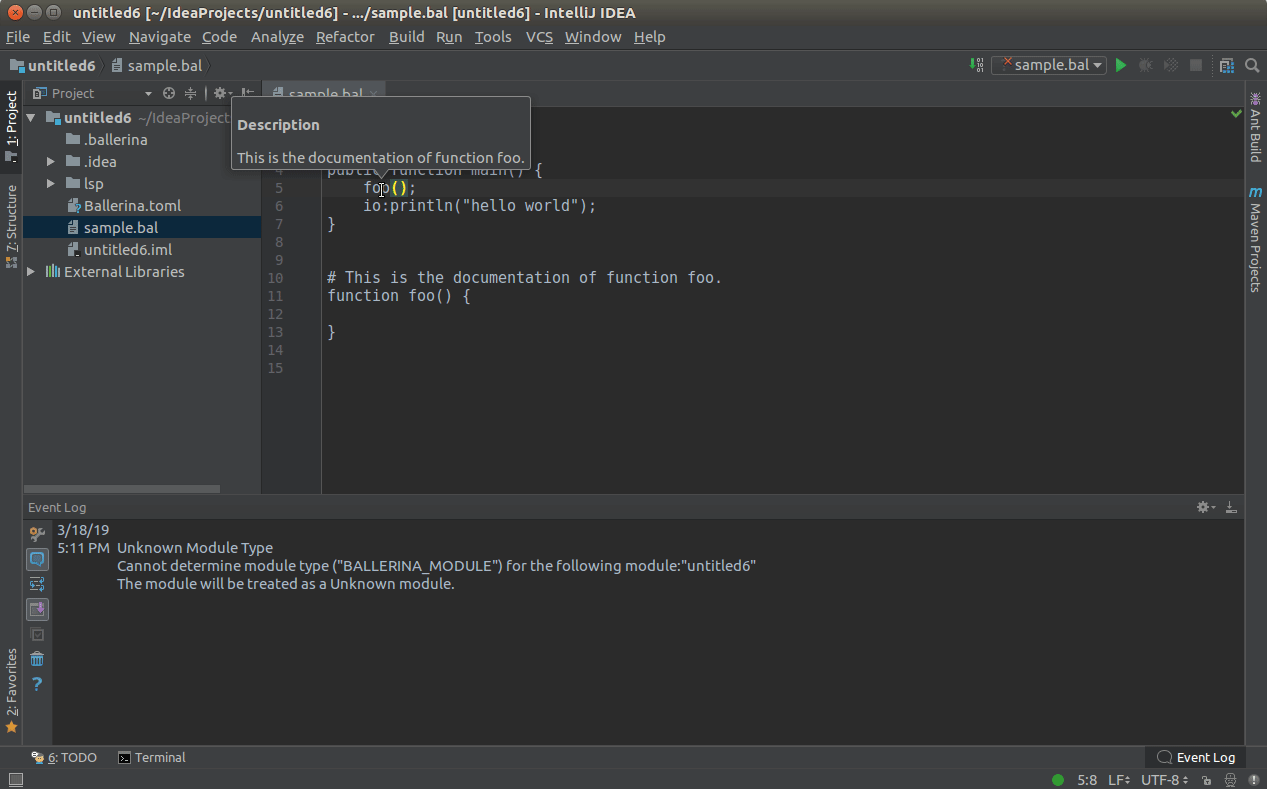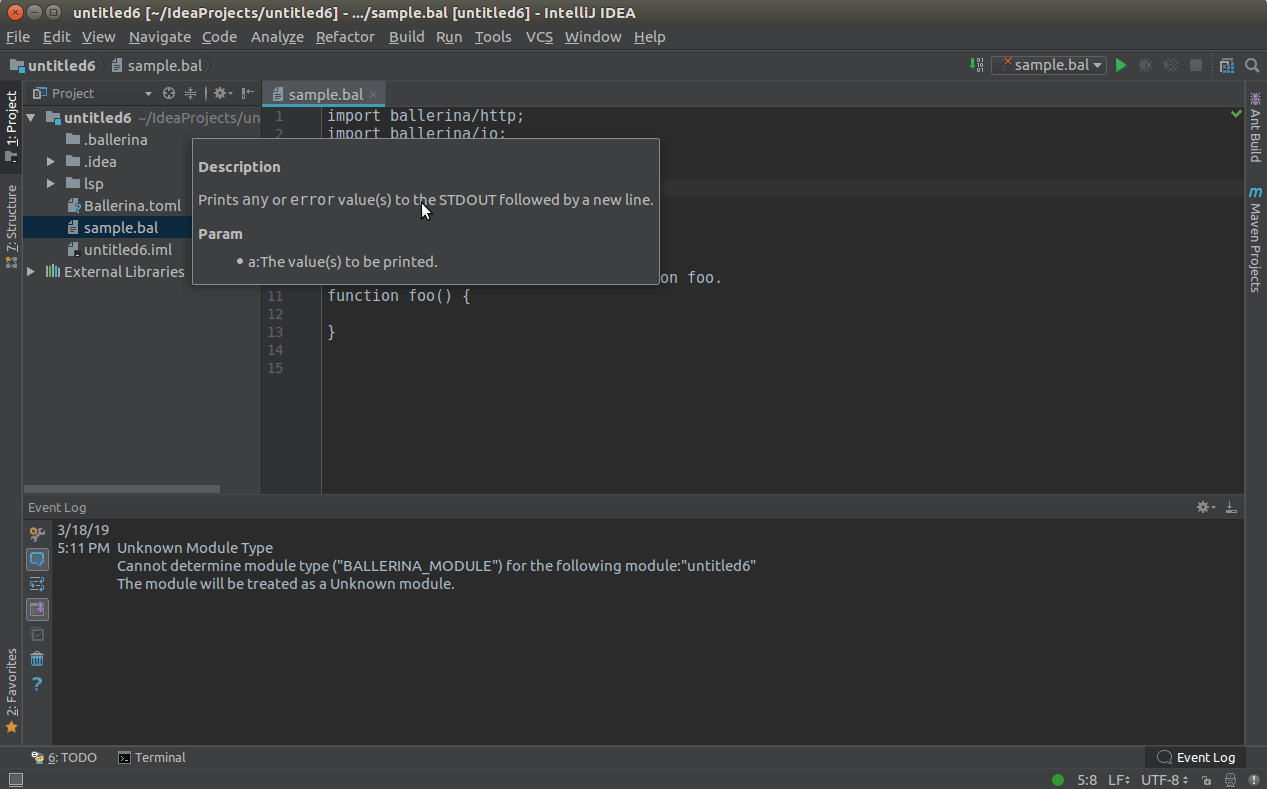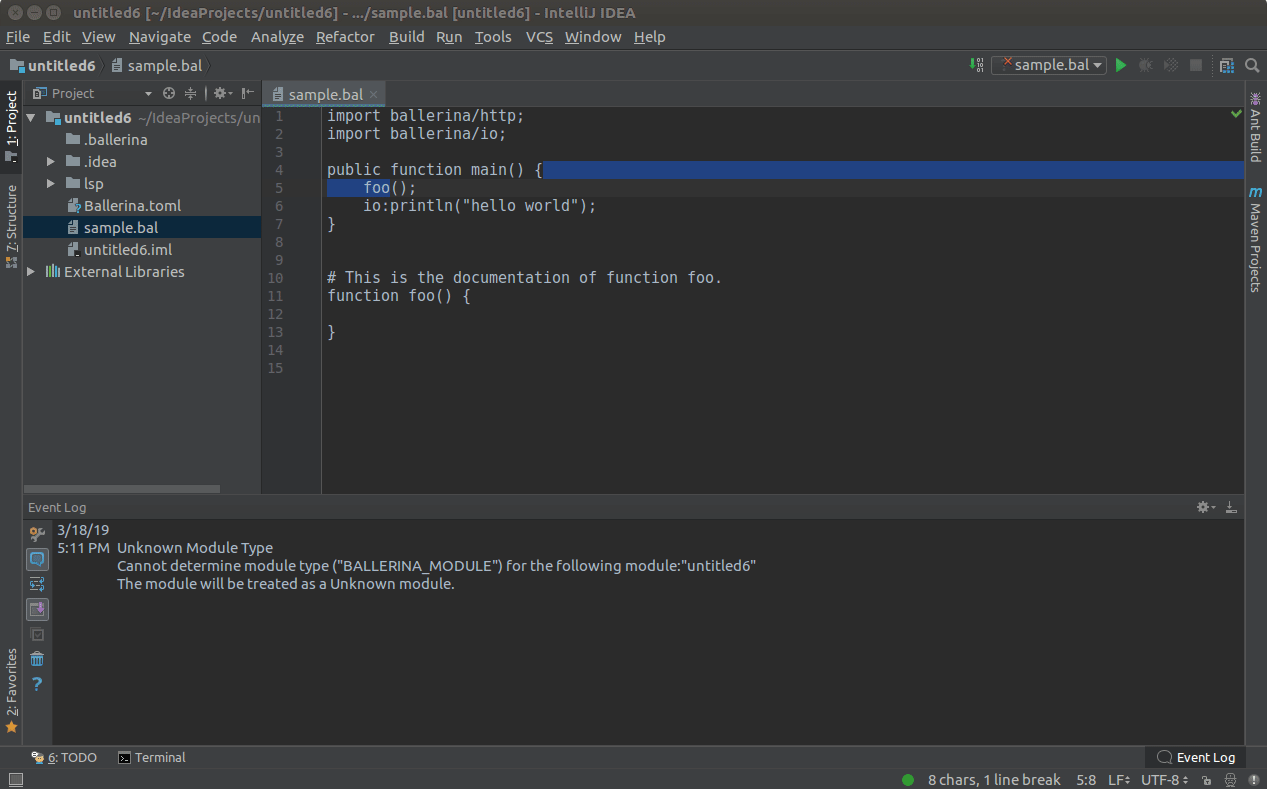
You can hover over an element while pressing the CTRL(COMMAND in MacOS) key to view its documentation if available.
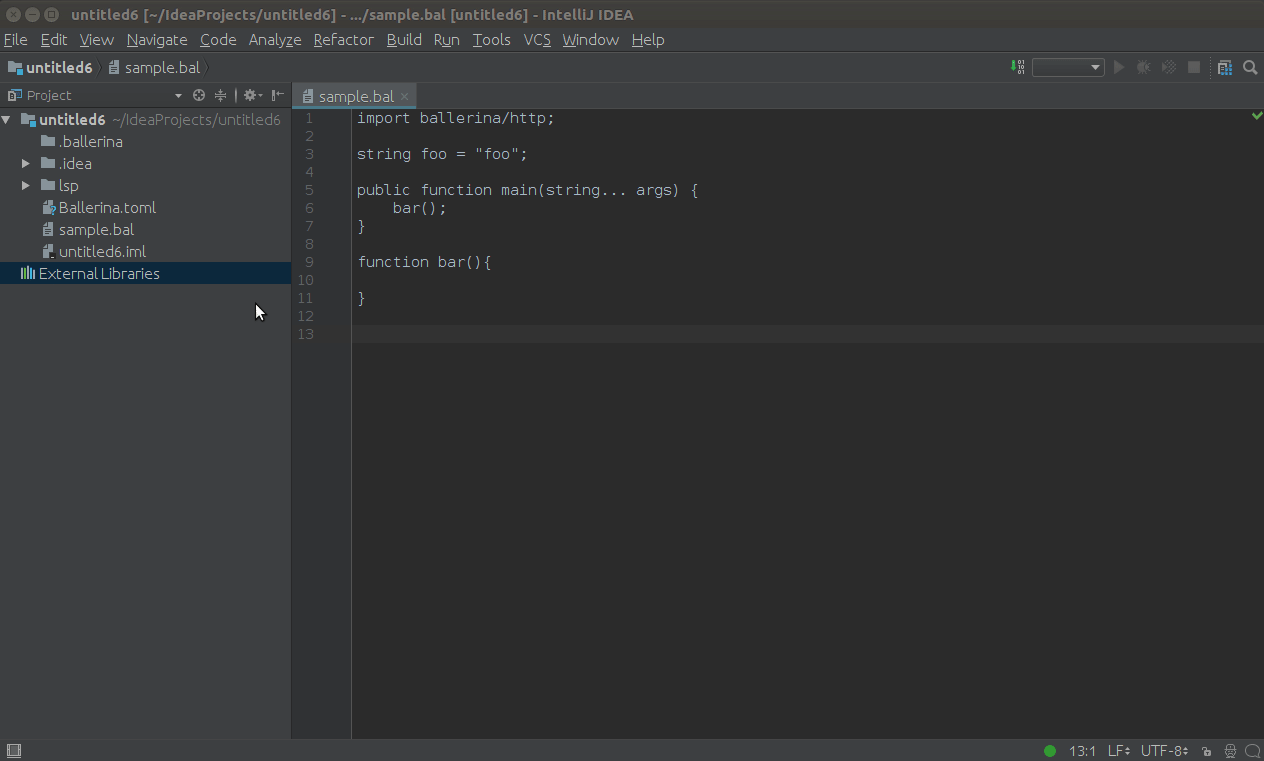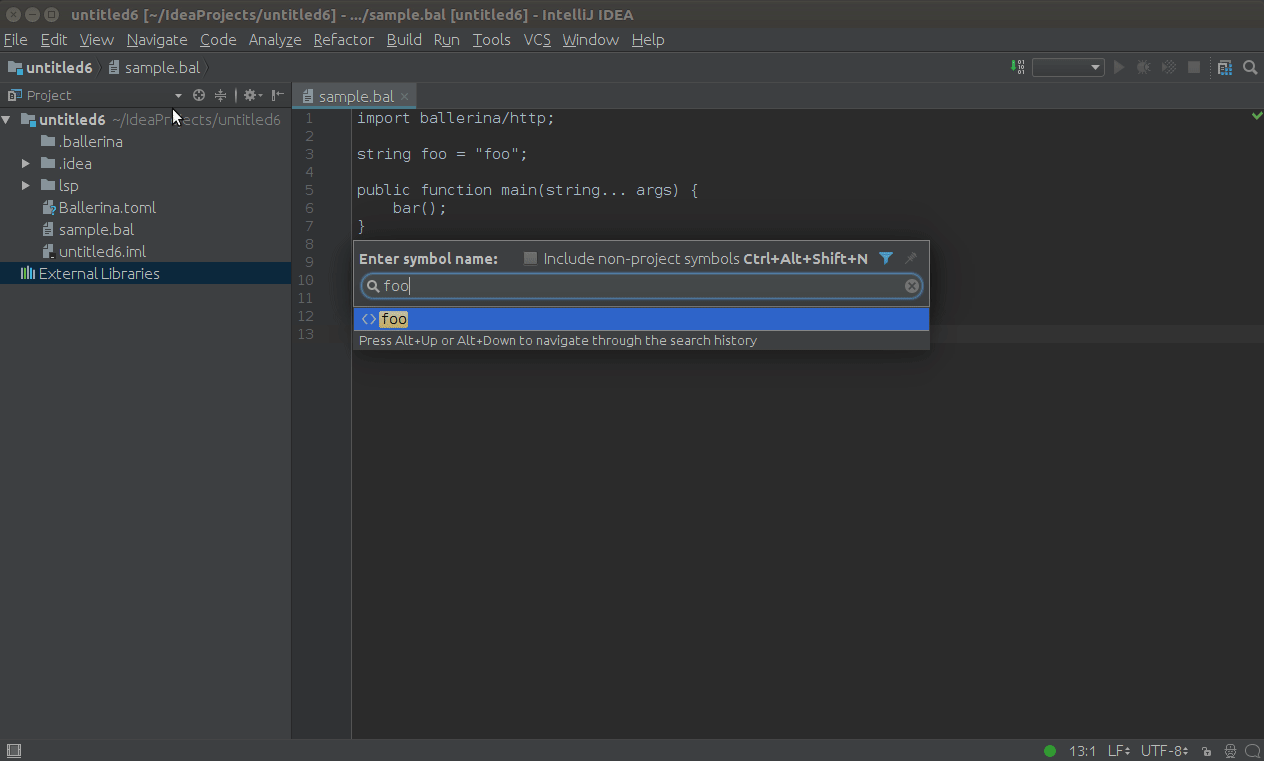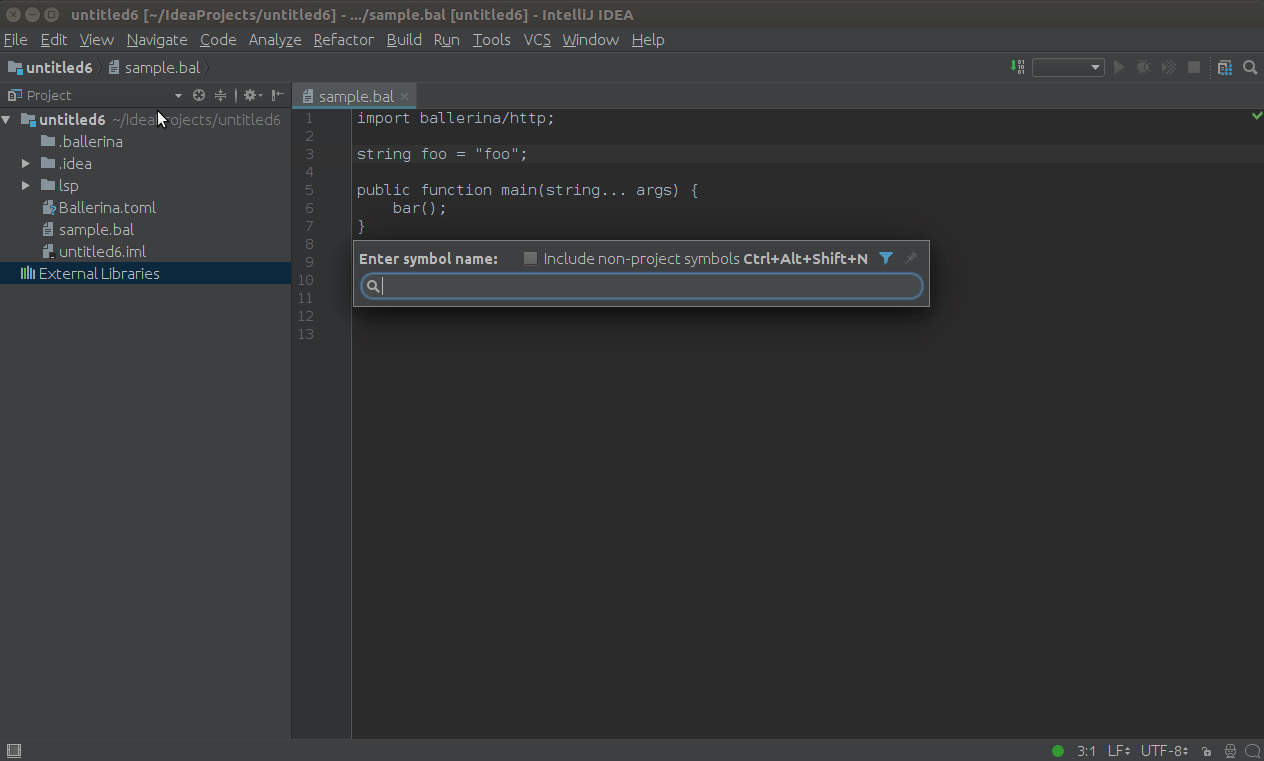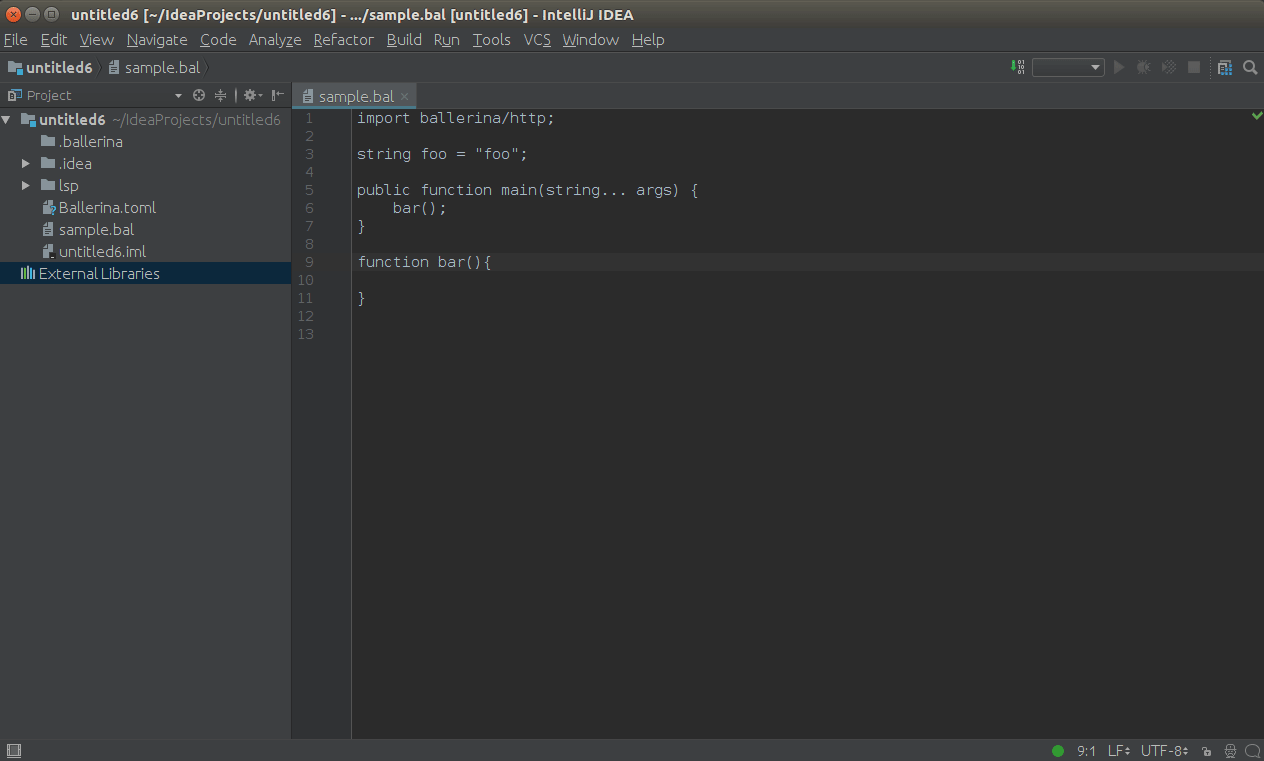
Click Navigate in the top menu, then click Symbol..., and enter the name of the symbol you want to search in the search box that pops up.
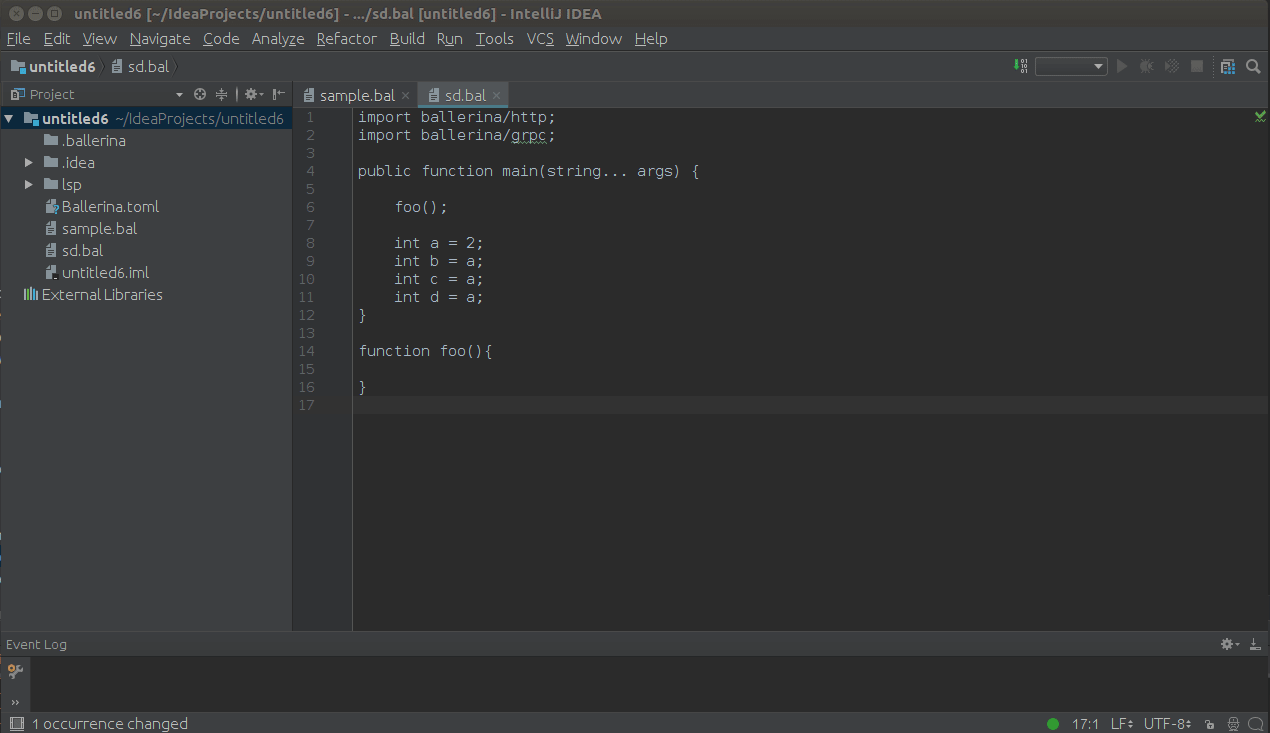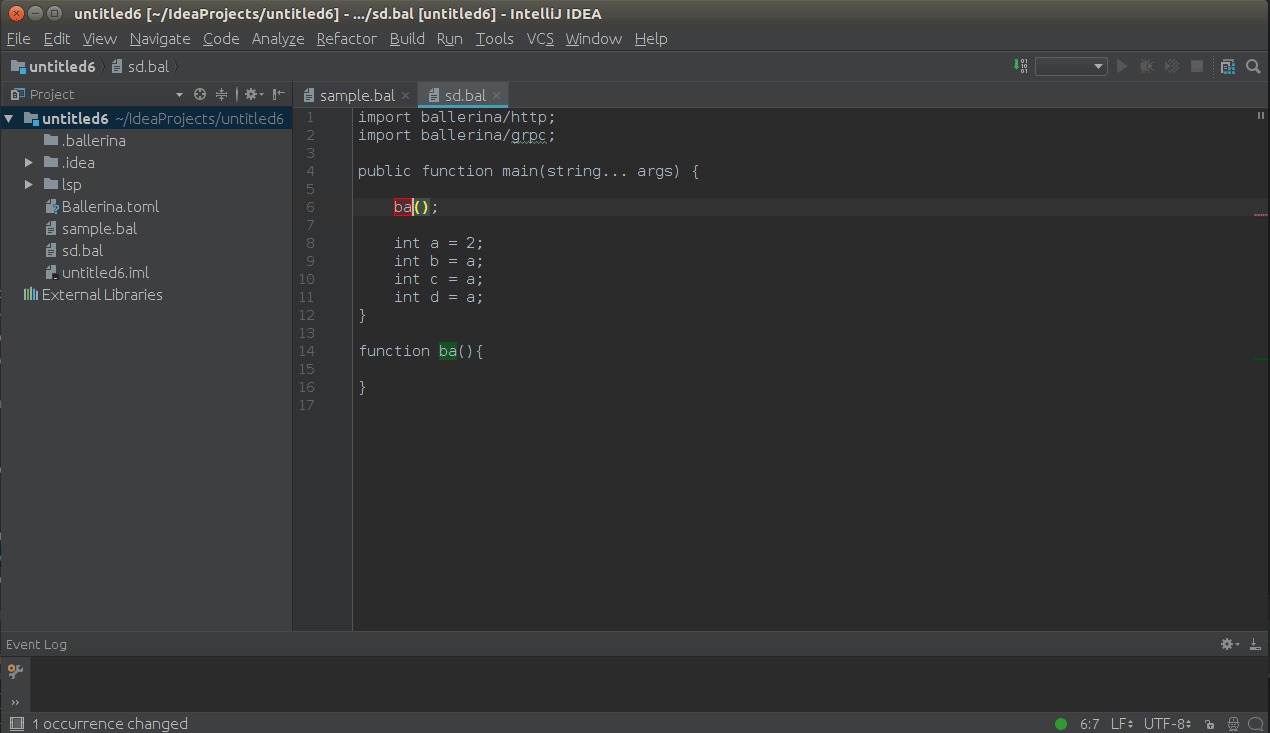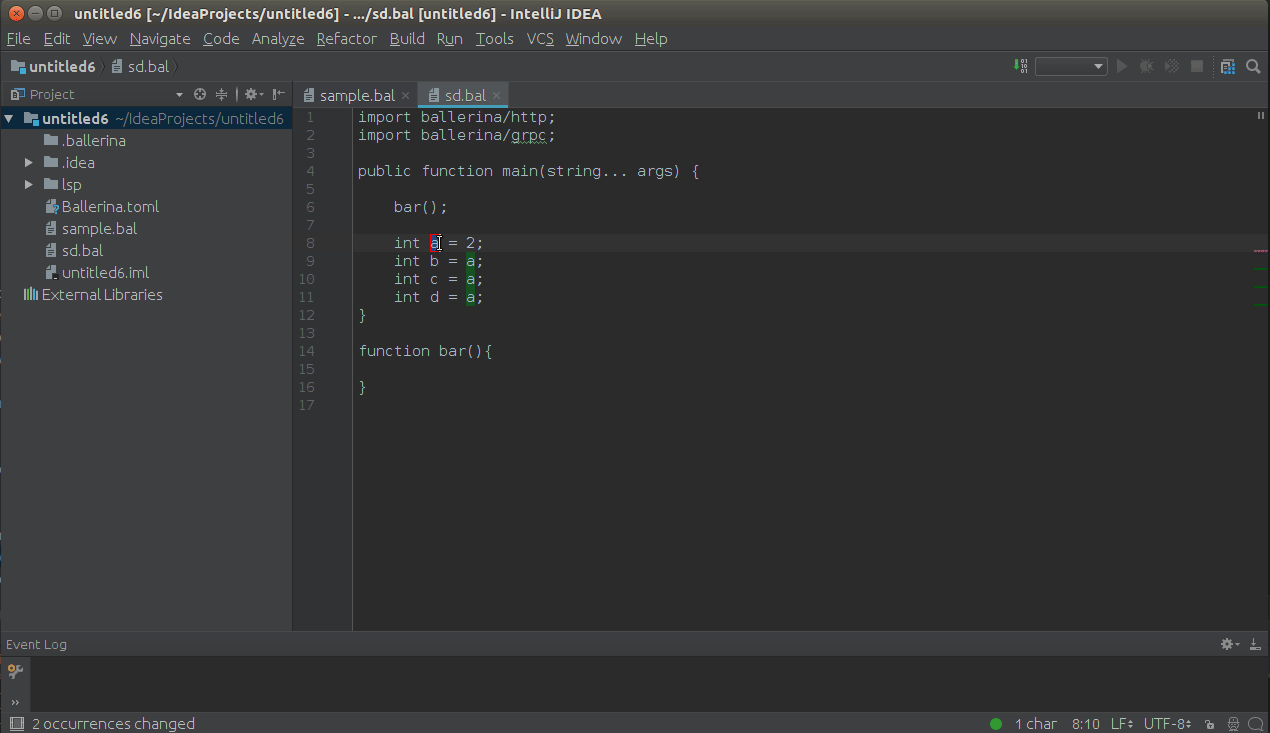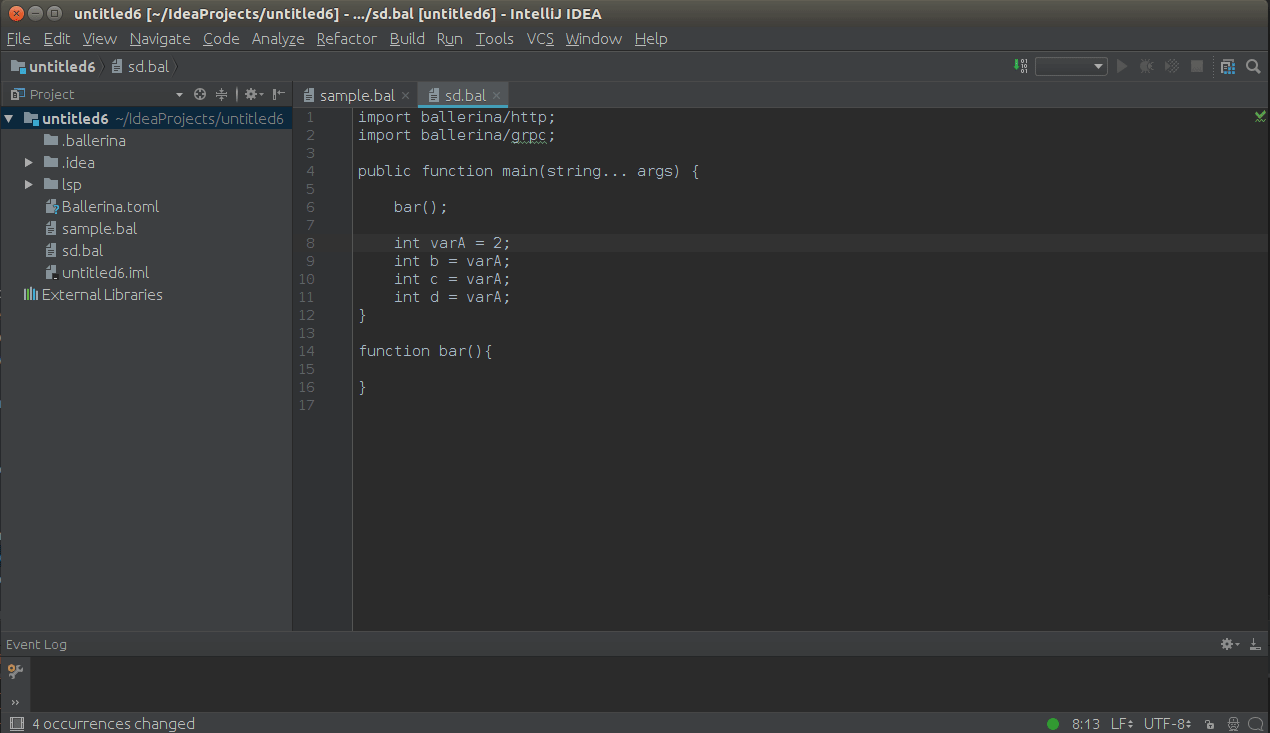
Set the courser to the element which needs to renamed and press SHIFT+F6 to trigger the in-place renaming as shown
below.
Note - Above features are currently tested only with IntelliJ IDEA and the Ballerina Language Server.
WIP Features
- Signature Help
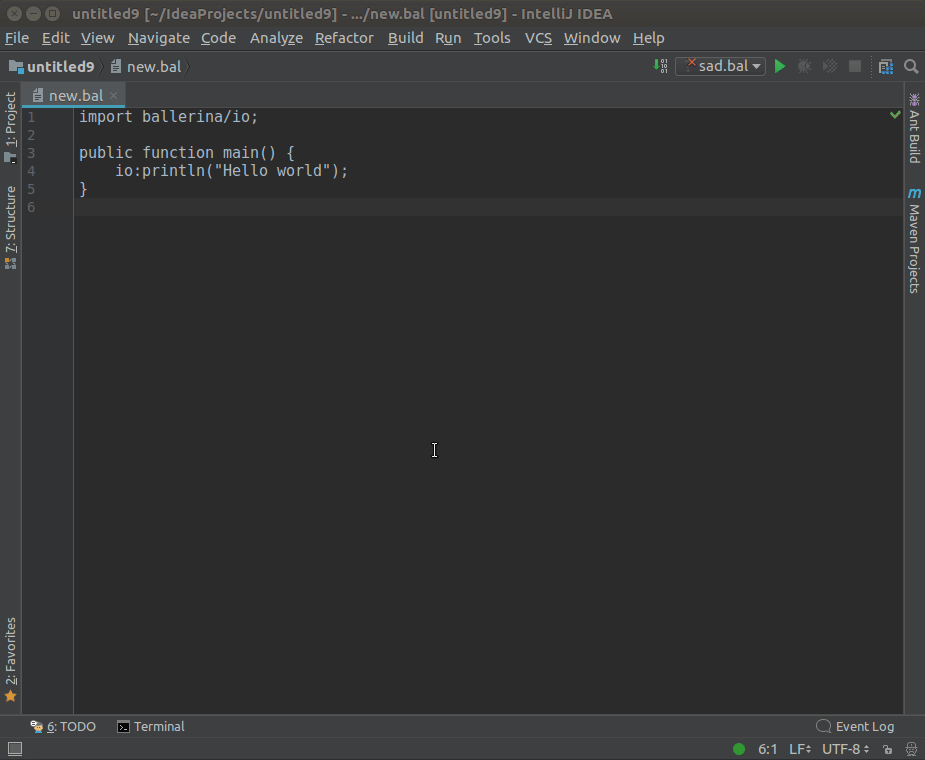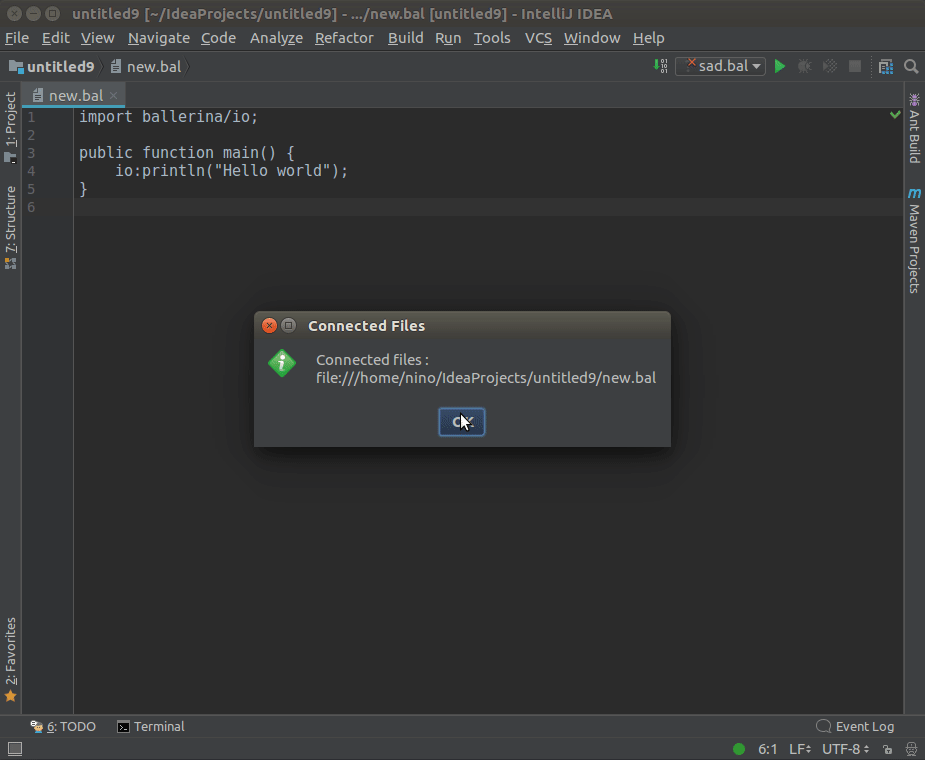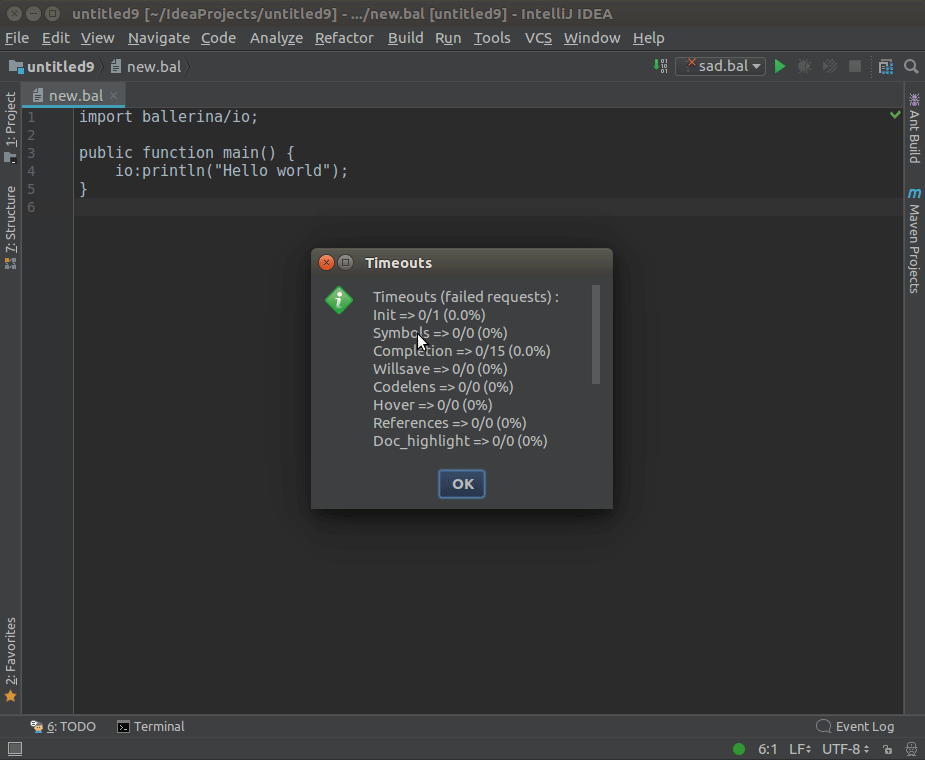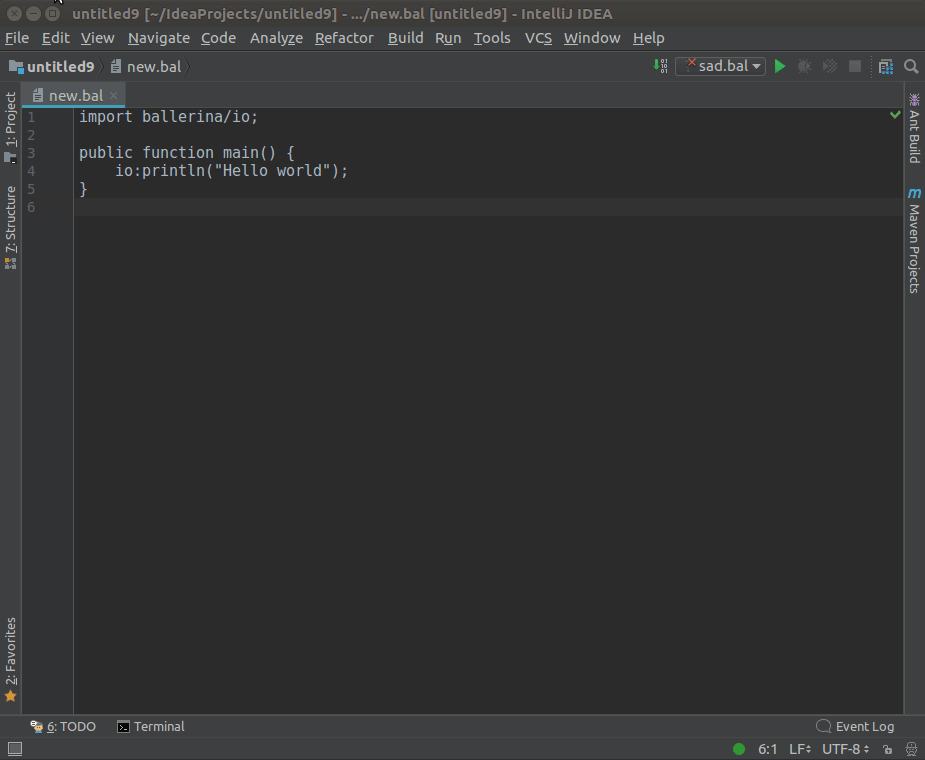
The Lsp4IntelliJ language client has default timeout values for LSP-based requests as shown below.
| Type | Default timeout value(in milliseconds) |
|---|---|
| Code Actions | 2000 |
| Completion | 1000 |
| Goto Definition | 2000 |
| Execute Command | 2000 |
| Formatting | 2000 |
| Hover Support | 2000 |
| Initialization | 10000 |
| References | 2000 |
| Shutdown | 5000 |
| WillSave | 2000 |
The LspIntelliJ language client provides following methods related to timeout configurations.
-
getTimeouts() - Returns the current timeout values (in milliseconds).
Example:
Map<Timeouts, Integer> timeouts = IntelliJLnaguageClient.getTimeouts();
-
getTimeout(Timeouts timeoutType) - Returns the current timeout value of a given timeout type (in milliseconds).
Example
int timeout = IntellijLanguageClient.getTimeout(Timeouts.INIT);
-
setTimeouts(Map<Timeouts, Integer> newTimeouts)) - Overrides the default timeout values with a given set of timeout values.
Example
Map<Timeouts,Integer> newTimeouts = new HashMap<>(); newTimeouts.put(Timeouts.INIT,15000); newTimeouts.put(Timeouts.COMPLETION,1000); IntellijLanguageClient.setTimeouts(newTimeouts);
-
setTimeout(Timeouts timeout, int value) - Overrides a specific timeout value with a new one.
Example
IntellijLanguageClient.setTimeout(Timeouts.INIT, 15000);
The LSP4Intellij code is distributed under the Apache license 2.0.
Lsp4IntelliJ is heavily inspired by the intellij-lsp plugin community.
Credits should go to the original author for his astounding work.
A huge thanks to all the amazing contributors! 🚀