Our study explores the relation between the stock market, its volatility, and behavior versus weather conditions, environmental factors, and natural disasters. The objective is to establish correlations between such factors and the value of stocks and volume traded, so as to enable accurate modeling and interpretation based on the data.
- ZEPL US Stock Market Data for Data Science
- yfinance API
- Knoema Environmental Data Atlas
- NOAA Climate Data Online
From our environmental data-set, we first analyze the factors that can affect stocks or the other way: companies have an effect on these factors.
For example, the following environmental factors were present in our data-set, among others:
Use of potash
Methane emissions
CO2 emissions
Terrestrial and marine protected areas
CO2 emissions from gaseous fuel consumption
CO2 intensity
Use of nitrogen
We considered all these environmental factors and some example stocks.
We plotted the yearly average open prices of these stocks. We also plotted the yearly value of these environmental factors.
Along with the plots, we also found out the value of correlation between the average yearly opening prices and the yearly value for the environmental factors.
where rxy is the value of correlation (or the correlation coefficient) between x and y.
Here are the results:
Here, we have normalized values of Open, Close and Volume of several stocks contrasted with normalized values of several environmental factors, meant to depict whether there is any sign of possible correlation.
Some of the correlation values were extremely low (including negative values). And some of the values were very high.
Strong Correlations
High values of correlation usually mean that there is an interdependence (Strong Correlation) between a stock and an environmental factor.
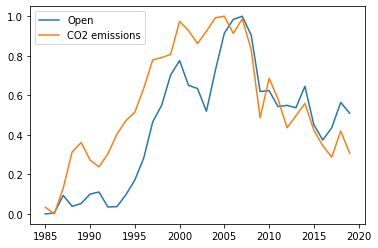
Consider the stock BP (British petroleum Company) and the factor CO2 emissions:
These have a high correlation value of 0.8159. We know that BP is an oil and gas company. Hence, it is very sensible reasoning that the company's production has a direct effect on the CO2 emission.
Hence, we can infer that CO2 emission values are affected by BP's stock.
Causation not equal to Correlation.
It is not always true that a high value of correlation means that there is an interdependence between the stocks.
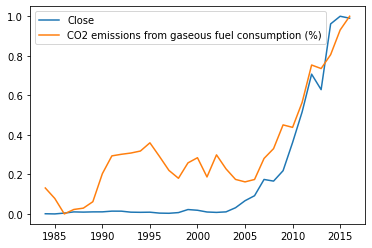
Consider the stock AAPL (Apple) ****and the factor CO2 emissions from gaseous fuel consumption:
These two have a high correlation of 0.93.
We know that Apple (a tech company), is obviously not dependent on CO2 emissions from gaseous fuel consumption. In spite of that, it has a high correlation with that factor. This is not a result of dependence between the two things. The high correlation is simply a coincidence as CO2 emissions from gaseous fuels are rising because of the rapid population growth and because nuclear and other clean energy sources are not very prevalent.
Hence Correlation is not always a result of Causation.
Hidden Correlations
Sometimes, a stock and a factor that seem unrelated have a high correlation.
There are two possible explanations for this:
- It is a coincidence (as shown above)
- Or it has a hidden correlation
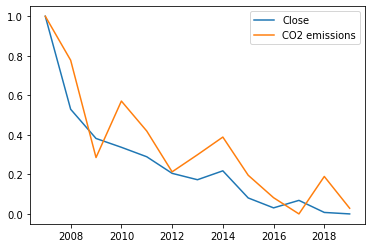
Consider the stock EOD (Wells Fargo Global) and the factor CO2 emissions:
This has a high correlation value of 0.927.
On first thought, it seems like Well Fargo Global, a finance company is unrelated to CO2 emissions.
However, it is likely that there are hidden correlations due to dependencies of carbon emissions on an industry which also determines whether the prices of companies that own/invest in the same.
This means large companies such as large banks and firms.
Hence, this high correlation is very likely not a result of coincidence but a result of purposeful investing/decisions taken by the company.
Low Positive Correlations
A low positive correlation usually means that the stock and the environmental factor in consideration are independent of each other.
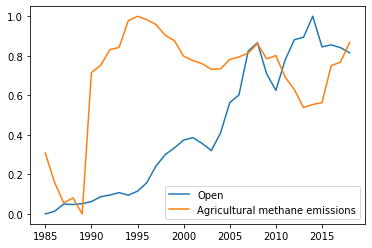
Consider XOM and Agricultural Methane Emissions.
This has a low correlation of 0.234
Hence, we can most of the time conclude that these two are independent of each other.
In rare cases though, they could be dependent and still have a low correlation.
Highly Negative Correlations
Highly negative values of correlation usually imply an inverse effect between the company's production/success and the factor in consideration.
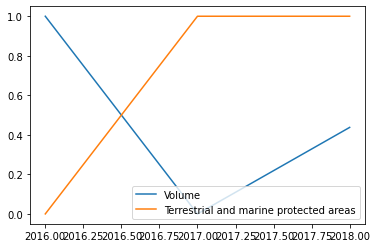
Consider the volume of the stock CVX (Chevron Corporation) ****and the factor Terrestrial and marine protected areas.
This has a highly negative correlation of -0.899
It is fair to assume that when the number of terrestrial and marine protected areas increases, the volume of the stock CVX, which is an energy industry decreases.
Hence, a highly negative correlation value means inverse dependence.
The global emission levels are predicted to be stranded due to growing awareness about climate change and a noticeable switch to renewable sources as primary energy sources.
As we earlier saw the high correlation between the carbon emission levels and the stock price of BP, it can be analyzed that in coming times the stock price of BP and other large oil companies will begin to fall. This also means that there will be a rise in the stock prices of companies that provide an alternative source of fuels such as solar panels and windmills.
We will also explore what kind of effect Natural Disasters have on stock values.
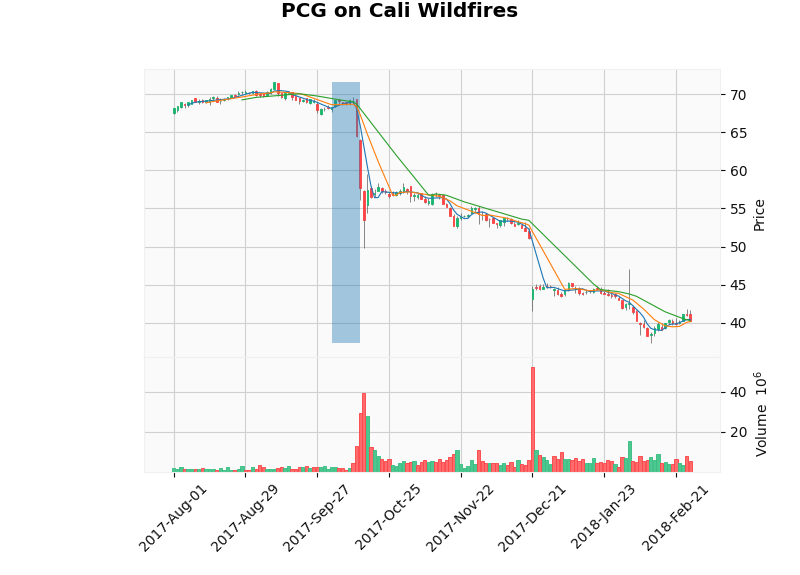
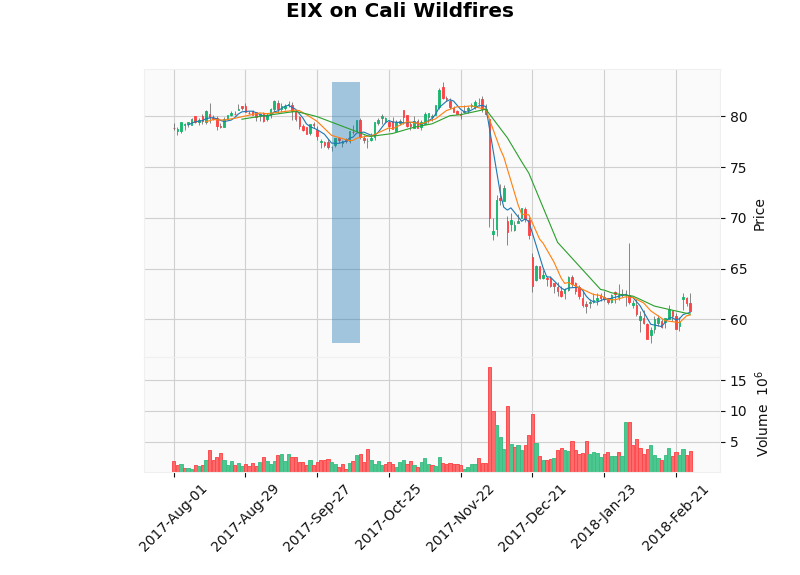
It is interesting how some companies are dependent on each other. Consider the California fires:
The stock of PCG which is a gas and electric company was affected right after the disaster took place. But now consider EIX. Its stock fell sharply sometime after PCG's. We know that EIX depends on PCG for its production. This is also evident through the graph as its stock was not affected directly after the wildfires but a few days later.
This gives clear information about the dependence of companies on each other. The blue line is the duration of the disaster.
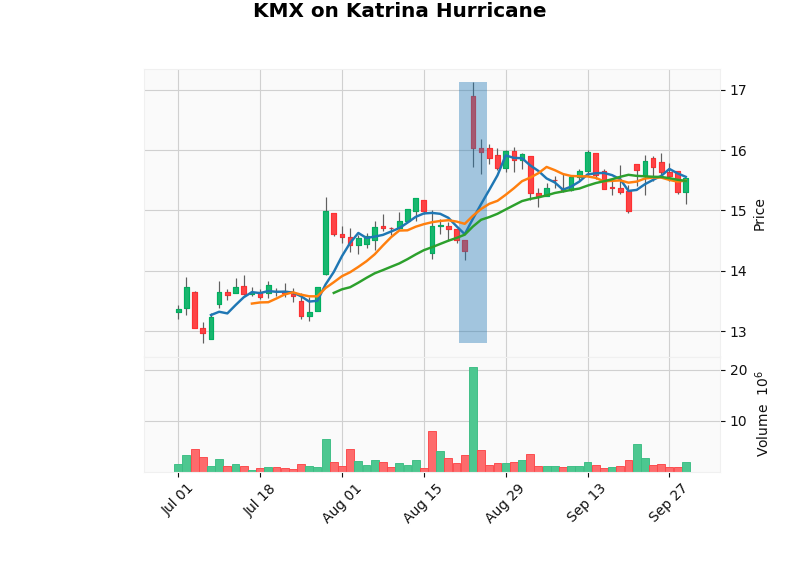
In August 2005, Katrina was a category 5 Atlantic hurricane that caused over 1,800 deaths and $125 billion in damage. This damage was mainly focused on New Orleans and the surrounding areas.
Large transportation companies such as C.H. Robinson had to face a heavy loss due to denial of services. Since hurricanes leave a relatively smaller effect on companies, they are able to resume their services. so the loss is made back.
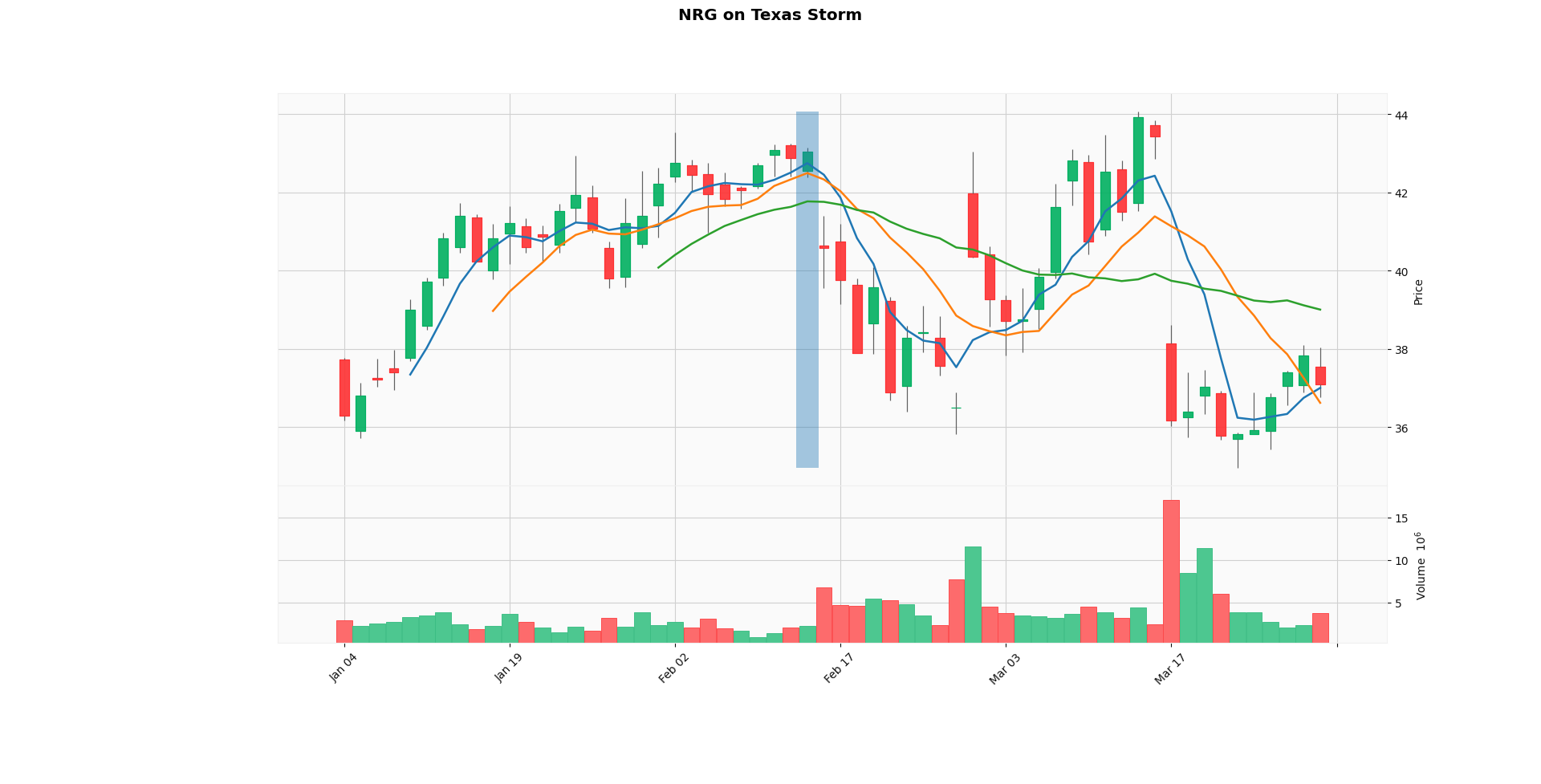
In February 2021, the state of Texas suffered a major power crisis, which came about as a result of three severe winter storms sweeping across the United States. The storms caused a massive electricity generation failure in the entire state leading to shortages of water, food, and heat.
More than 4.5 million homes and businesses were left without power, at least 210 people were killed directly or indirectly with some estimates going as high as 702.
The Texas Grid failure was majorly caused by the inadequately winterized natural gas equipment.
NRG suffered the most as can be seen in the following plots. It can also be emphasized that the analysis has to be done on a small time scale as companies often bounce back from such losses over a longer period of time such as a year.
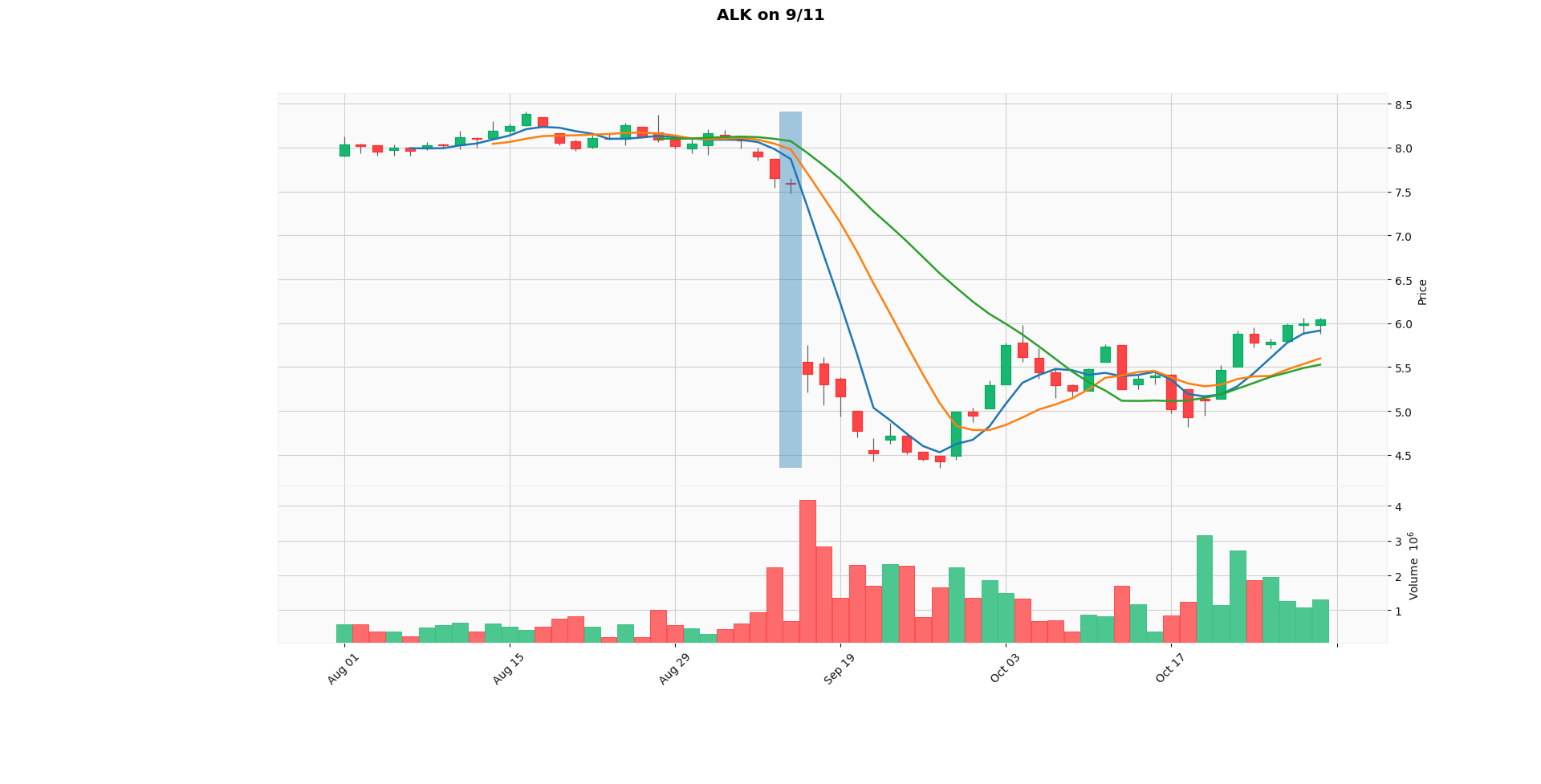
Although 9/11 is not a natural disaster, it is worth considering how it affected the stock market. The effect is very visible on the entire stock market due to direct or indirect loss. As seen in the bottom graphs, the prices go down relatively fast after the event took place.
Due to its surprising nature, the impact's nature and magnitude were no less than a natural disaster over the country.
For all these disasters, stocks of companies that seemed related to those events were taken into consideration. In agreement with our hypothesis, the stocks of those companies suffered a heavy hit after those events.
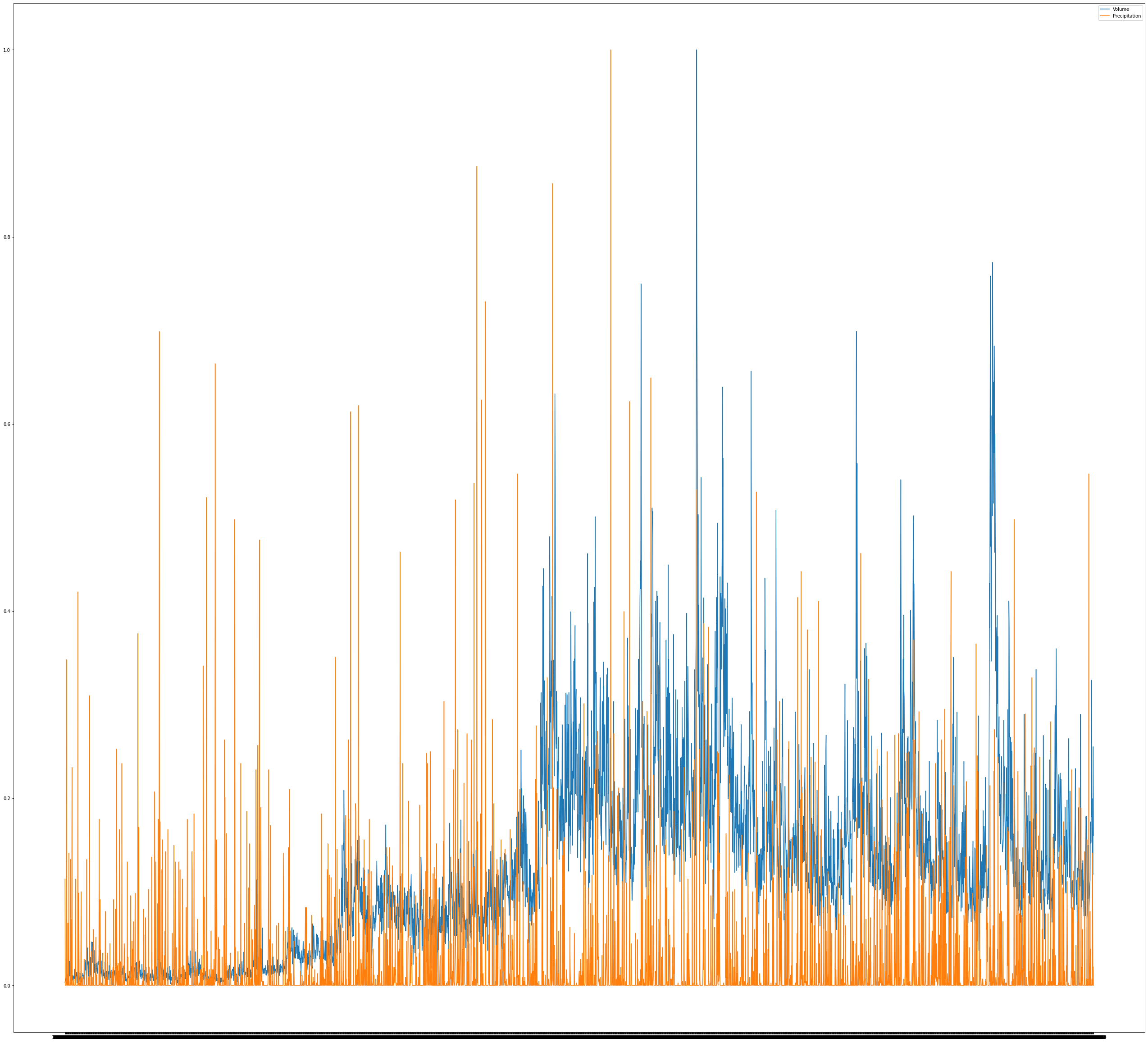
Precipitation and Volume were plotted over a very large period.
These two have a correlation of
It can be seen that there is no correlation between volume and precipitation. Due to the availability of the stock market electronically, trades can be made from anywhere. This pattern is new, but before the availability of the stock market on electronics, the trades had to be done in a building to which people traveled.
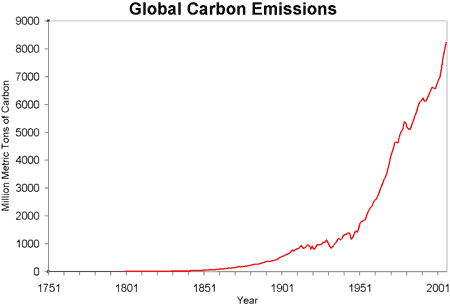
The example of correlation and not causation can further be understood by considering the rise in the population and workforce. The rise in population meant more consumption of energy and since we lack any large source of energy other than fossil fuels it means that there will be a rise in the pollution levels.
If the stock history of the industrial revolution times along with the carbon emission levels of the same was available, it can be seen that the rising workforce and demand directly meant a rise in carbon levels. This is a correlation due to common sources of the rise.
The data has been analyzed so far which has us given some insights, it can be used to build upon for prediction and more analysis for determining the effect of stocks on future natural events.
Once the prediction model has been built, it can be used to analyze environmental factors. For example, when we compare the predicted value of a stock to its actual value, and there is a big difference at some point, it implies that some kind of environmental factor affected that stock at that point.
Events such as hurricanes and heatwaves recur periodically. Due to rising climate change, they will only become more frequent. This means that past analysis on such events will help us determine the kind of impact it will happen on the companies it had an impact on.
This analysis has revealed that there are correlations underlying between the stock value and the environmental factors such as weather and natural disasters. Further, major events which were unpredictable but aren't natural causes also have a heavy effect on the market. It can also be seen that the increase in supply and demand had a direct impact on the market stock, along with which there was an impact on environmental factors such as carbon emissions.
There are cases that have been explained where the impact of a natural disaster first hit the company which had a direct link to the resources that were lost followed by a loss in the companies that depended upon the primary companies after a delay.
The data can be understood and analyzed with graphs and other tools, predictions can be made with the help of machine learning models which could be trained on used in a case such events are repeated again.