GitLab Branch Source Plugin
To be fully able to run a Jenkins Continuous Integration on a GitLab repository or project, you require the following plugins:
-
GitLab API Plugin - Wraps GitLab Java API
-
GitLab Branch Source Plugin:
Contains two packages:
-
io.jenkins.plugins.gitlabserverconfig- Manages server configuration and web hooks management. Ideally should reside inside another plugin with nameGitLab Plugin. In future, this package will be moved into a new plugin. -
io.jenkins.plugins.gitlabbranchsource- Adds GitLab Branch Source for Multi-branch Pipeline Jobs (including Merge Requests) and Folder organisation.
-
Jenkins and GitLab Integration:
This section contains information about Jenkins CI support for GitLab.
Present State
-
FreeStyle Job and Pipeline(Single Branch) Job are fully supported.
-
Multi-branch Pipeline Job is partially supported (no MRs detection).
-
GitLab Folder Organisation is not supported.
Issues
-
The GitLab Java APIs are written within the plugin itself when it should be a different plugin.
-
Multi-branch Pipeline support is missing.
-
GitLab Folder Organisation for GitLab Projects is missing.
-
Convention for 3 separate plugin is not followed (e.g. - github-api-plugin, github-plugin, github-branch-source-plugin).
Goals of this project
-
Implement a lightweight GitLab Plugin that depends on GitLab API Plugin.
-
Follow convention of 3 separate plugins i.e.
GitLab Plugin,GitLab API Plugin,GitLab Branch Source Plugin. -
Implement GitLab Branch Source Plugin with support for Multi-branch Pipeline Jobs.
-
Support new Jenkins features such as Jenkins Code as Configuration (JCasC), Incremental Tools.
-
Provide rich user experience.
-
Support all SCM Trait APIs.
-
Support Java 8 and above.
Building the plugin
No binaries are available for this plugin as the plugin is in the very early alpha stage, and not ready for the general public quite yet. If you want to jump in early, you can try building it yourself from source.
Installation:
-
Checkout out source code to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/baymac/gitlab-branch-source-plugin.git\ cd gitlab-branch-source-plugin -
Install the plugin:
mvn clean install
or
mvn clean install -DskipTests # to skip tests -
Run the Plugin:
mvn hpi:run # runs a Jenkins instance at localhost:8080or
mvn hpi:run -Djetty.port={port} # to run on your desired port numberIf you want to test it with your Jenkins server, after
mvn clean installfollow these steps in your Jenkins instance:-
Select
Manage Jenkins -
Select
Manage Plugins -
Select
Advancedtab -
In
Upload Pluginsection, selectChoose file -
Select
${root_dir}/target/gitlab-branch-source.hpi -
Select
Upload -
Select
Install without restart
-
Getting Started
Jenkins is an open source, self hosting automation server for continuous integration and continuous delivery. The source code of the core Jenkins and its plugins are written in Java. There have been development on a modern Jenkins Server (see: Blueocean Plugin) using React and other modern front end tools to provide rich user experience.
For more Jenkins related information, see documentation.
Extending Jenkins
Jenkins has more than a 1000 plugins so a vast set of functionality has already been implemented and this can be used
to leverage new plugins. Jenkins has an extensibility feature that allows plugin to use other plugins or core features
simply by extending their classes. To define or create an extension in Jenkins,we use the @Extension annotation
type. This annotation is picked up by Jenkins, and the new extension will be added to an ExtensionList object, where
the extension can then be found via ExtensionFinder.
Running your Jenkins server:
Here are a few ways to setup your own Jenkins server:
-
Using a Jenkins docker:
i. Download docker image from here.
ii. Open up a terminal/command prompt window to the download directory.
iii. Run command:
docker run \ -u root \ --rm \ -d \ -p 8080:8080 \ -p 50000:50000 \ -v jenkins-data:/var/jenkins_home \ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ --name jenkins \ jenkinsci/blueocean
iv. Browse to
http://localhost:8080.If you need more information about docker commands, see here.
-
Using a Jenkins Web application Archive (WAR):
i. Download latest stable Jenkins WAR file.
ii. Open up a terminal/command prompt window to the download directory.
iii. Run command:
java -jar jenkins.war
iv. Browse to
http://localhost:8080/jenkins. -
Using a Azure Jenkins solution:
Refer to Azure docs.
-
Using a Bitnami Jenkins Stack:
Refer to Bitnami docs.
Post installation:
-
Unlock your Jenkins instance:
i. From the Jenkins console log output, copy the automatically-generated alphanumeric password.
ii. On the Unlock Jenkins page, paste this password into the Administrator password field and click
Continue. -
Customizing Jenkins with plugins
Click one of the two options shown:
i.
Install suggested plugins- to install the recommended set of plugins, which are based on most common use cases.ii.
Select plugins to install- to choose which set of plugins to initially install. When you first access the plugin selection page, the suggested plugins are selected by default. -
Create an admin user
i. When the Create First Admin User page appears, specify the details for your administrator user in the respective fields and click Save and Finish.
ii. When the Jenkins is ready page appears, click Start using Jenkins.
iii. If required, log in to Jenkins with the credentials of the user you just created and you are ready to start using Jenkins!
Usage
Assuming plugin installation has been done already.
Setting up GitLab Server Configuration on Jenkins
-
On jenkins, select
Manage Jenkins -
Select
Configure System -
Scroll down to find the
GitLabsection -
Select
Add GitLab Server| SelectGitLab Server -
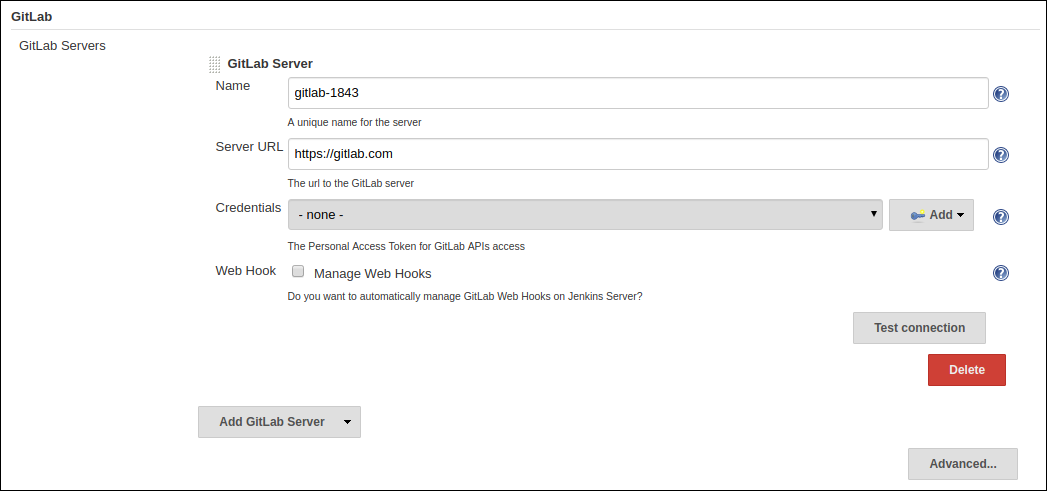
Now you will now see the GitLab Server Configuration options
There are 4 fields that needs to be configured:
i.
Name- Plugin automatically generates an unique server name for you. User may want to configure this field to suit their needs but should make sure it is sufficiently unique. We recommend to keep it as it is.ii.
Server URL- Contains the URL to your GitLab Server. By default it is set to "https://gitlab.com". User can modify it to enter their GitLab Server URL e.g. https://gitlab.gnome.org/, http://gitlab.example.com:7990. etc.iii.
Credentials- Contains a list of credentials entries that are of type GitLab Personal Access Token. When no credential has been added it shows "-none-". User can add a credential by clicking "Add" button.iv.
Web Hook- This field is a checkbox. If you want the plugin to setup a webhook on your GitLab project(s) related jobs, check this box. The plugin listens to a URL for the concerned GitLab project(s) and when an event occurs in the GitLab Server, the server sends an event trigger to the URL where the web hook is setup. If you want continuous integration (or continuous delivery) on your GitLab project then you may want to automatically set it up. -
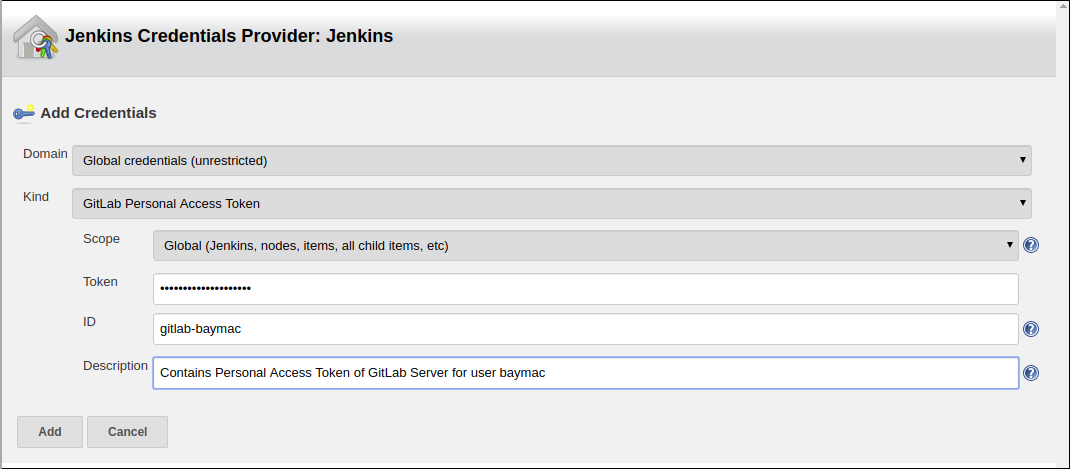
Adding a Personal Access Token Credentials:
This is a manual setup. To automatically generate Personal Access Token see next section.
i. User is required to add a
GitLab Personal Access Tokentype credentials entry to securely persist the token inside Jenkins.ii. Generate a
Personal Access Tokenon your GitLab Server:a. Select profile dropdown menu from top-right corner b. Select `Settings` c. Select `Access Token` from left column d. Enter a name | Set Scope to `api`,`read_user`, `read_repository` e. Select `Create Personal Access Token` f. Copy the token generatediii. Return to Jenkins | Select
Addin Credentials field | SelectJenkinsiv. Set
Kindto GitLab Personal Access Tokenv. Enter
Tokenvi. Enter a unique id in
IDvii. Enter a human readable description
viii. Select
Add -
Testing connection:
i. Select your desired token in the
Credentialsdropdownii. Select
Test Connectioniii. It should return something like
Credentials verified for user {username} -
Select
Apply(at the bottom) -
GitLab Server is now setup on Jenkins
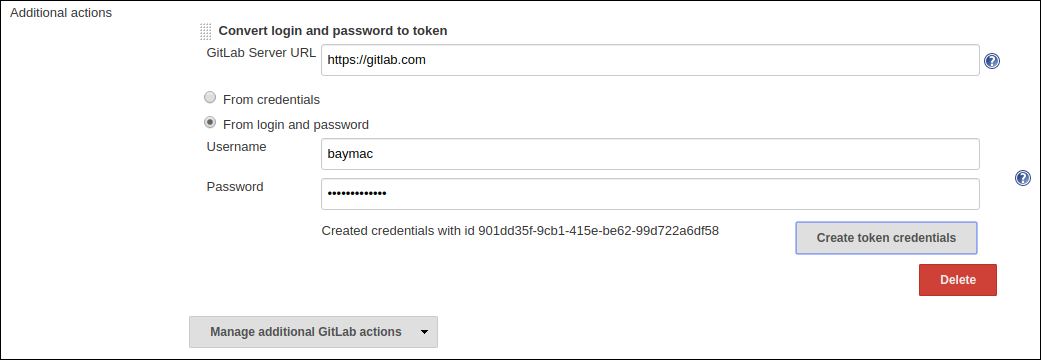
Creating Personal Access Token within Jenkins
Alternatively, users can generate a GitLab Personal Access Token within Jenkins itself and automatically add the GitLab Personal Access Token credentials to Jenkins server credentials.
-
Select
Advancedat the bottom ofGitLabSection -
Select
Manage Additional GitLab Actions -
Select
Convert login and password to token -
Set the
GitLab Server URL -
There are 2 options to generate token;
i.
From credentials- To select an already persisting Username Password Credentials or add an Username Password credential to persist it.ii.
From login and password- If this is a one time thing then you can directly enter you credentials to the text boxes and the username/password credential is not persisted. -
After setting your username/password credential, select
Create token credentials. -
The token creator will create a Personal Access Token in your GitLab Server for the given user with the required scope and also create a credentials for the same inside Jenkins server. You can go back to the GitLab Server Configuration to select the new credentials generated (select "-none-" first then new credentials will appear). For security reasons this token is not revealed as plain text rather returns an
id. It is a 128-bit long UUID-4 string (36 characters).
Configuration as Code
There is an easier way to setup GitLab Server configuration on your Jenkins server. No need for messing around in the UI.
Jenkins Configuration as Code (JCasC) or simply Configuration as Code Plugin allows you to configure Jenkins
via a yaml file. If you are a first time user, you can learn more about JCasC
here.
Prerequisite:
Installed Configuration as Code Plugin on your Jenkins instance.
Refer to Installing a new plugin in Jenkins.
Add configuration YAML:
There are multiple ways to load JCasC yaml file to configure Jenkins:
-
JCasC by default searches for a file with the name
jenkins.yamlin$JENKINS_ROOT. -
The JCasC looks for an environment variable
CASC_JENKINS_CONFIGwhich contains the path for the configurationyamlfile.-
A path to a folder containing a set of config files e.g.
/var/jenkins_home/casc_configs. -
A full path to a single file e.g.
/var/jenkins_home/casc_configs/jenkins.yaml. -
A URL pointing to a file served on the web e.g.
https://<your-domain>/jenkins.yaml.
-
-
You can also set the configuration yaml path in the UI. Go to
<your-jenkins-domain>/configuration-as-code. Enter path or URL tojenkins.yamland selectApply New Configuration.
To configure your GitLab Server in Jenkins add the following to jenkins.yaml:
credentials:
system:
domainCredentials:
- credentials:
- gitlabPersonalAccessToken:
scope: SYSTEM
id: "i<3GitLab"
token: "XfsqZvVtAx5YCph5bq3r" # gitlab personal access token
unclassified:
gitLabServers:
servers:
- credentialsId: "i<3GitLab"
manageHooks: true
name: "gitlab.com"
serverUrl: "https://gitlab.com"See handling secrets section in JCasC documentation for better security.
Setting up GitLab for jobs
This section is a Work in Progress. Will be updated upon release.
Issues
This project uses Jenkins JIRA to track issues. You can file issues under
gitlab-branch-source-plugin component.
Acknowledgements
This plugin is built and maintained by the Google Summer of Code (GSoC) Team for Multi-branch Pipeline Support for GitLab.
The team consists of:
External Support:
- Oleg (The org admin who helps with all technical issues)
- Greg (The creator of GitLab4J APIs)
- Stephen (The creator of SCM related Plugins)
Also thanks to entire Jenkins community for contributing with technical expertise and inspiration.