Library of NumPy-based and CUDA-based Image Processing functions for various types of Image Enhancement, including:
- Spatial Tone Mapping
- Local Contrast Enhencement
- Color Correction (White Balance)
- Color Saturation Adjustment
- Exposure Fusion
- get_photometric_mask(): Estimates local brightness distribution (edge-aware blurring).
- apply_local_contrast_enhancement(): Adjusts strength of local details.
- apply_spatial_tonemapping(): Adjusts brightness levels in dark and bright regions.
- transfer_graytone_to_color(): Transfers tones from a tone-mapped grayscale image to a color image.
- change_color_saturation(): Adjusts the color vibrance of an image.
- correct_colors(): Removes color casts from images.
- adjust_brightness(): Adjusts global brightness of the image.
- srgb_to_linear(): Transforms image to the linear color space.
- linear_to_srgb(): Transforms image to the gamma-corrected color space.
- enhance_image(): Applies multiple stages of enhancement to an image.
- blend_expoures(): Fuses a collection of image exposures to a single well exposed image.
├── source [Directory: Source code]
│ ├── image_enhancement.py [Main script with all the functions]
│ ├── image_enhancement_cuda.py [Script with ~most~ of the functions in CUDA]
│ ├── example_color_correction.py [Example of applying color correction]
│ ├── example_enhance_image.py [Example of combined image enhancement]
│ ├── example_local_contrast_enhancement.py [Example of applying increasing local details]
│ ├── example_blend_exposures.py [Example of blending multiple image exposures]
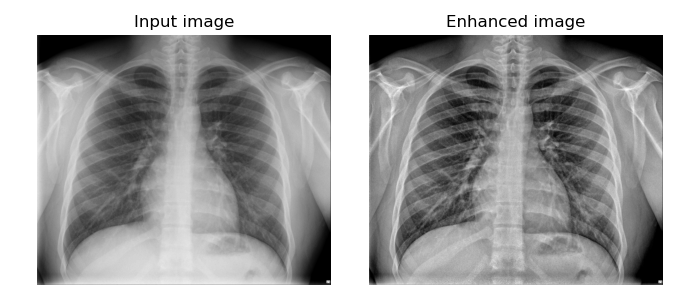
│ ├── example_medical_image.py [Example of processing medical images]
│ ├── cuda
│ │ ├── image_enhancement.cu.h [Header file for CUDA implementation]
│ │ └── image_enhancement.cu [Implementation of image enhancement in CUDA]
└── images [Directory: Sample test images]
- numpy
- imageio
- skimage (can be easily bypassed if needed)
- Pillow (optional: only needed for running
image_enhancement_cuda.py) - pycuda (optional: only needed for running
image_enhancement_cuda.py)
If you want to try this code in real-life challenging travel photos, please try the following dataset:
TM-DIED: The Most Difficult Image Enhancement Dataset
The Python code loads a compiled cuda binary (.cubin) and runs the CUDA kernels using numpy arrays. Replace [arch] in the code below to compile the CUDA code (e.g. -arch=sm_72).
nvcc --cubin -arch=[arch] -use_fast_math -O3 source/cuda/image_enhancement.cu -o source/image_enhancement.cubin
With image_enhancement.cubin in source, you can run source/image_enhancement_cuda.py to generate an enchanced version of alhambra1.jpg.
If you use this code in your research please cite the following papers:
- Vonikakis, V., Andreadis, I., & Gasteratos, A. (2008). Fast centre-surround contrast modification. IET Image processing 2(1), 19-34.
- Vonikakis, V., Winkler, S. (2016). A center-surround framework for spatial image processing. Proc. IS&T Human Vision & Electronic Imaging, (Retinex020), San Francisco, CA, Feb. 14-18.
- Vonikakis, V., Arapakis, I. & Andreadis, I. (2011).Combining Gray-World assumption, White-Point correction and power transformation for automatic white balance. International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT), 1569353295.
- Vonikakis, V., & Andreadis, I. (2008). Multi-Scale Image Contrast Enhancement. ICARCV 2008. (pp. 385-391).
- Vonikakis, V., Bouzos, O. & Andreadis, I. (2011). Multi-Exposure Image Fusion Based on Illumination Estimation, SIPA2011 (pp.135-142).