SmartChat is application for chating between two and more nodes.
This is an example of Chang Roberts Leader election algorithm.
Connections are mannaged by WebSockets.
Author is Tashpulatov Jakhongir.
First install Node.js v14.x. If you have already installed it, you can skip this step.
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejsClone it and install dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/tashpjak/smartchat.git
cd smartchat
npm installWhen downloading is done, you can launch it by enter:
$ node .
Also, you can specify a port to be listening on:
$ PORT=8080 node .
Default port is 7777
Or, you can download the package and run bash instal.sh. It will require sudo user password.
Application supports this non-trivial commands:
status
This command allows you to see information about youself and status of the network you connected to.
It shows you: your name, URL(for connecting), ID, connected nodes(previous and next) and also the leader of the network.
connect
This command allow you to connect to existing network by knowing only one member of it. Or not even member, it can be a single node.
Just type connect and it will prompt you URL for connection. Also, you can pass it as arguments. For example:
connect --host 127.0.0.1 --port 3333
disconnect
This command does just one thing - it disconnects you from existing network without damage for it. Accepts no arguments, just disconnecting you.
message
This is the most advanced, powerfull and meaningfull command in the whole application. It allows you chating. See message section for more.
export
This command allows you to export all messages to file. It will be named that way: messages_<port>_<time>.txt, where
port is a port your application is running on and time is time when you executed the command.
exit
This command allows you unexpected close the application even if you are connected to a network. In that case you don't care what will be with them. It is not your business.
Nothing. When other nodes will receive no sign from you, they repair the network. See repair section.
For connection, you will be need a host and port of at least one member of network. Or another alone node. The topology of network is ring. Every new node will be trying to join the ring. See Repair section for more.
For understanding how works connection look into diagram meaning
When node is trying to join the network, it sends handshake message and gets handshaked when joining is established. Now it can fully access all function of chat. From this moment it has a node whom it connected to(NEXT node) and node who connected to it(PREVIOUS node).
Message mode is implemented for messaging. Once you entered the mode, you can either send/receive messages or exit the mode by typing empty string and press Enter.
To send a message to all members just type it and press enter. Sooner or later your message will get all members of the network.
Simple. You send a message only to next node. When next node receive it - it checks for a stamp. Stamp can be made only by the leader.
So if the node, who receive the message is the leader it should approve it and put a stamp containing when he did it and who did it. If he is not the leader it sends the message to next node and so on. Because of circle topology sooner or later the message should get it owner. If he checks, that message has not been stamped yet, that means - the leader doesn't exist. This is the moment, when election starting.
The Chang and Roberts algorithm is a ring-based coordinator election algorithm. In our case leader is needed for creating stamps on messages.
- Initially each node in the ring is marked as non-participant.
- A node that notices a lack of leader(see message section) starts an election. It creates an election message containing its UUID (v1 for comparing). It then sends this message to next node clockwise.
- Every time a node sends or forwards an election message, the node also marks itself as a participant and saves leader's UUID.
- When a node receives an election message it compares the UUID in the message with its own UID:
- If the UUID in the election message is larger, the node unconditionally forwards the election message to next node.
- If the UUID in the election message is smaller, and the node is not yet a participant, the process replaces the UUID in the message with its own UUID, sends the updated election message to next node.
- If the UUID in the election message is smaller, and the node is already a participant (i.e., the process has already sent out an election message with a UID at least as large as its own UID), the node discards the election message.
- If the UUID in the incoming election message is the same as the UUID of the node, that node starts acting as the leader.
When a node starts acting as the leader, it begins the second stage of the algorithm:
- The leader node marks itself as non-participant and sends an elected message to next node announcing its election and UUID.
- When a node receives an elected message, it marks itself as non-participant, records the elected UID, and forwards the elected message unchanged.
- When the elected message reaches the newly elected leader, the leader discards that message, and the election is over.
Repair is algorithm for repairing network when someone leaves or joins it. Let's look. If you don't understand diagrams, look into diagram meaning
The situation: there is already a network, and you are connected to it assuming that there are N > 2 nodes.
What happens when you're leaving the network by typing disconnect or unexpectedly close application?
Thanks to WebSockets, every action you made are sent to server/client even if you're disconnecting. So, when you are leaving the NEXT and PREVIOUS nodes will know it.
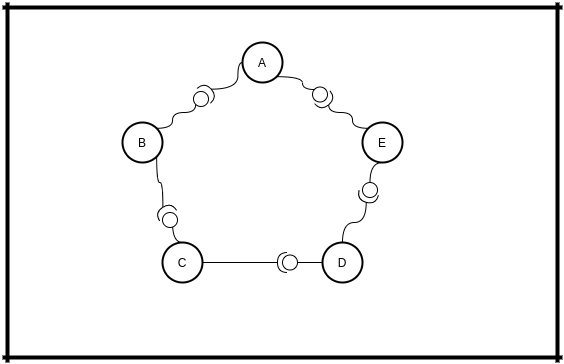
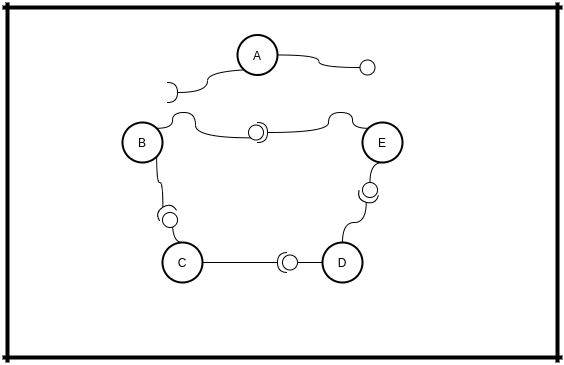
Let's assume there is a network about 5 nodes. And you're the node A.
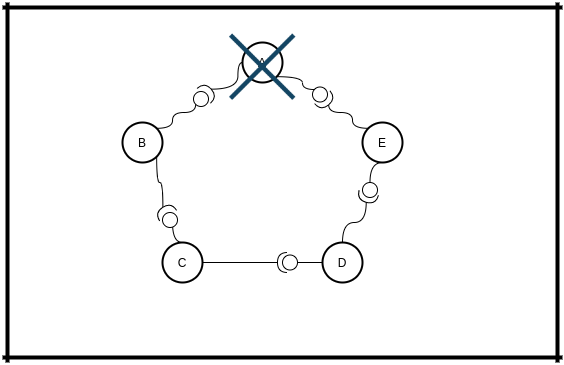
And you're disconnecting/leaving. You broke connection with NEXT and PREVIOUS nodes:
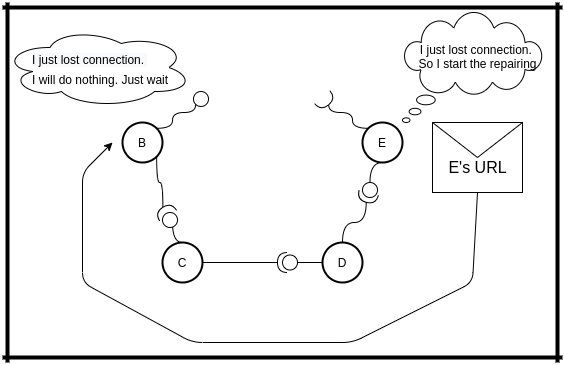
When B knows that you disconnected, it will do nothing. He is the weak node in a broken network.
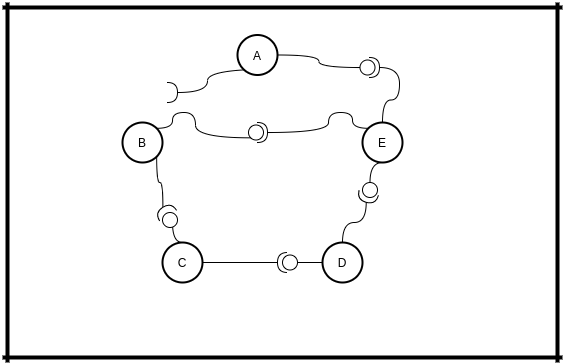
When E knows that you disconnected, it will start repairing network by sending message containing his URL to his NEXT node - D
If D has connected NEXT node, we know it has(C), it sends the message to C. And so on. they will be sending to next the message nodes until they found a node without connected client(NEXT node). That means they found the weak node.
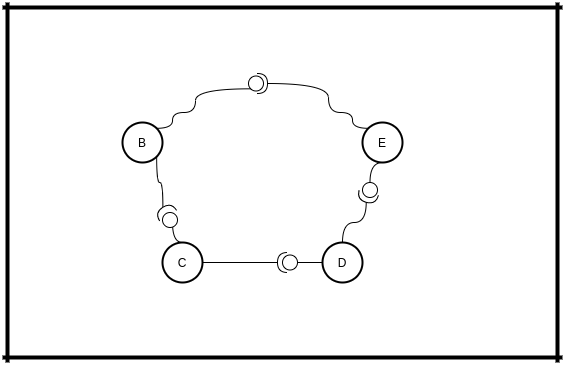
When B gets the message containing E's URL, it will connect to it. And that it is. Network is repaired
The situation: there is already a network, and you are connected to it assuming that there are 2 nodes.
Simple. When you're leaving, that means other node disconnects too, and you're both alone nodes now.
The situation: there is already a network, and you are NOT connected to it. And you want to join the network.
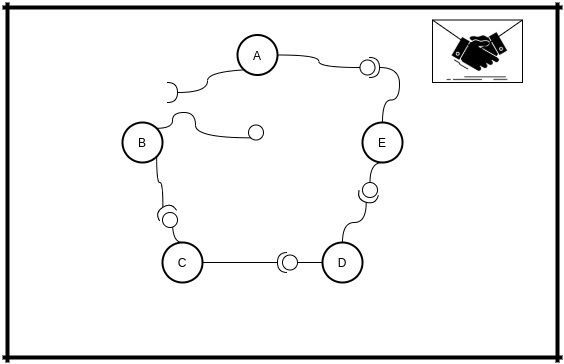
Let's assume you're node A.
You are connecting to node E, so you run connect and enter E's URL.
When E accept your connection you need to send handshake to join the network. Without it you're not a member of the
network, but just connected to E.
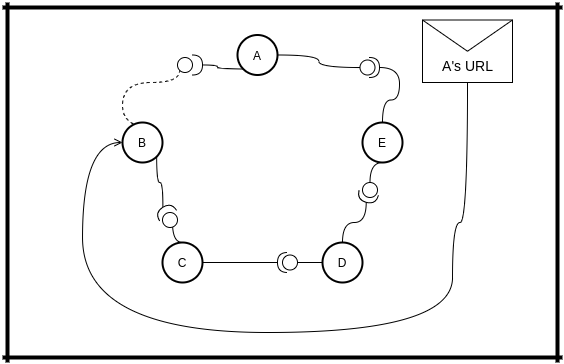
Now when E know about you, he disconnectes from B and send you hadshaked message. That means, that you're connected
to network. But as you can see now, the network is broken. There is no connection between A and B. So you have to repair
the network by sending repair message as shown in another situation(the first one)
When B gets message to repair, it will connect to you and now the network is fixed.