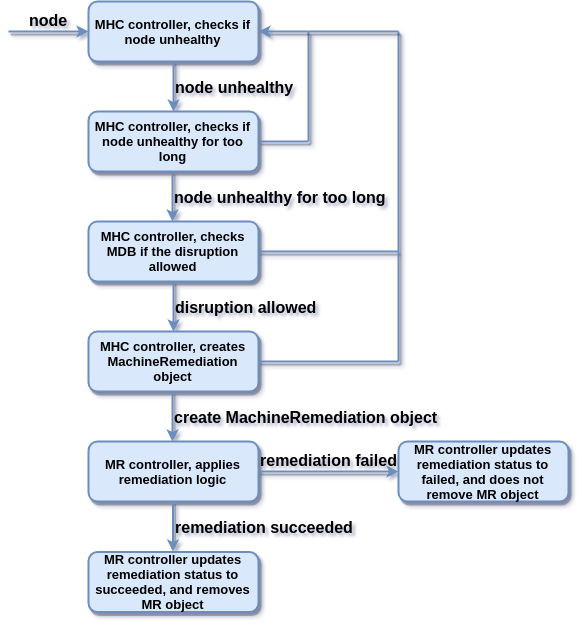
The machine remediation contains components to monitor and remediate unhealthy machines for different platforms, it works on top of machine-api-operator controllers.
It contains:
- machine-remediation controller
- node-reboot
You can check the GitHub releases to get latest yaml file, that includes CRD's, RBAC rules and deployment and apply it to your cluster.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubevirt/machine-remediation/releases/download/v0.4.3/machine-remediation.v0.4.3.yamlOnce the deployment finishes, create a MachineHealthCheck object and be sure to give it the healthchecking.openshift.io/strategy: reboot annotation that instructs the Machine Healthcheck controller to delegate remediation to us.
An example MachineHealthCheck object that covers all nodes in the cluster is as follows:
apiVersion: machine.openshift.io/v1beta1
kind: MachineHealthCheck
metadata:
name: simple-example
namespace: openshift-machine-api
annotations:
healthchecking.openshift.io/strategy: reboot
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machine-role: worker
unhealthyConditions:
- type: Ready
status: Unknown
timeout: 60sYou should have k8s or OpenShift environment with at least two worker nodes and run:
export KUBECONFIG=/dir/cluster/kubeconfig
make e2e-tests-run