Python library to trace graphql calls with Datadog.
ddtrace-graphql is tested with:
- Python versions: 3.5, 3.6, nightly
- graphql-core: 2.0, 1.1.0, latest
- ddtrace: 0.11.1, 0.10.1, latest
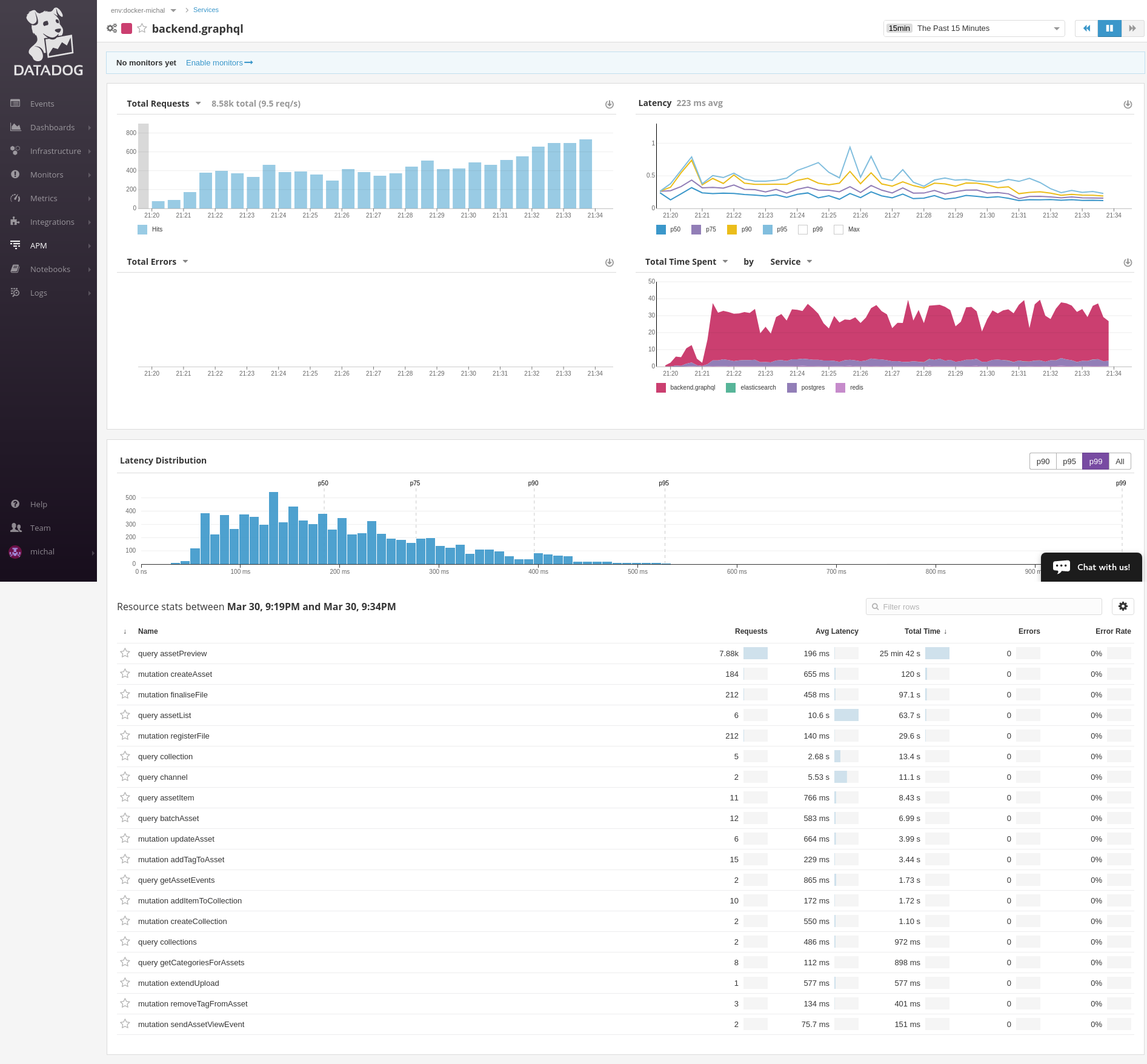
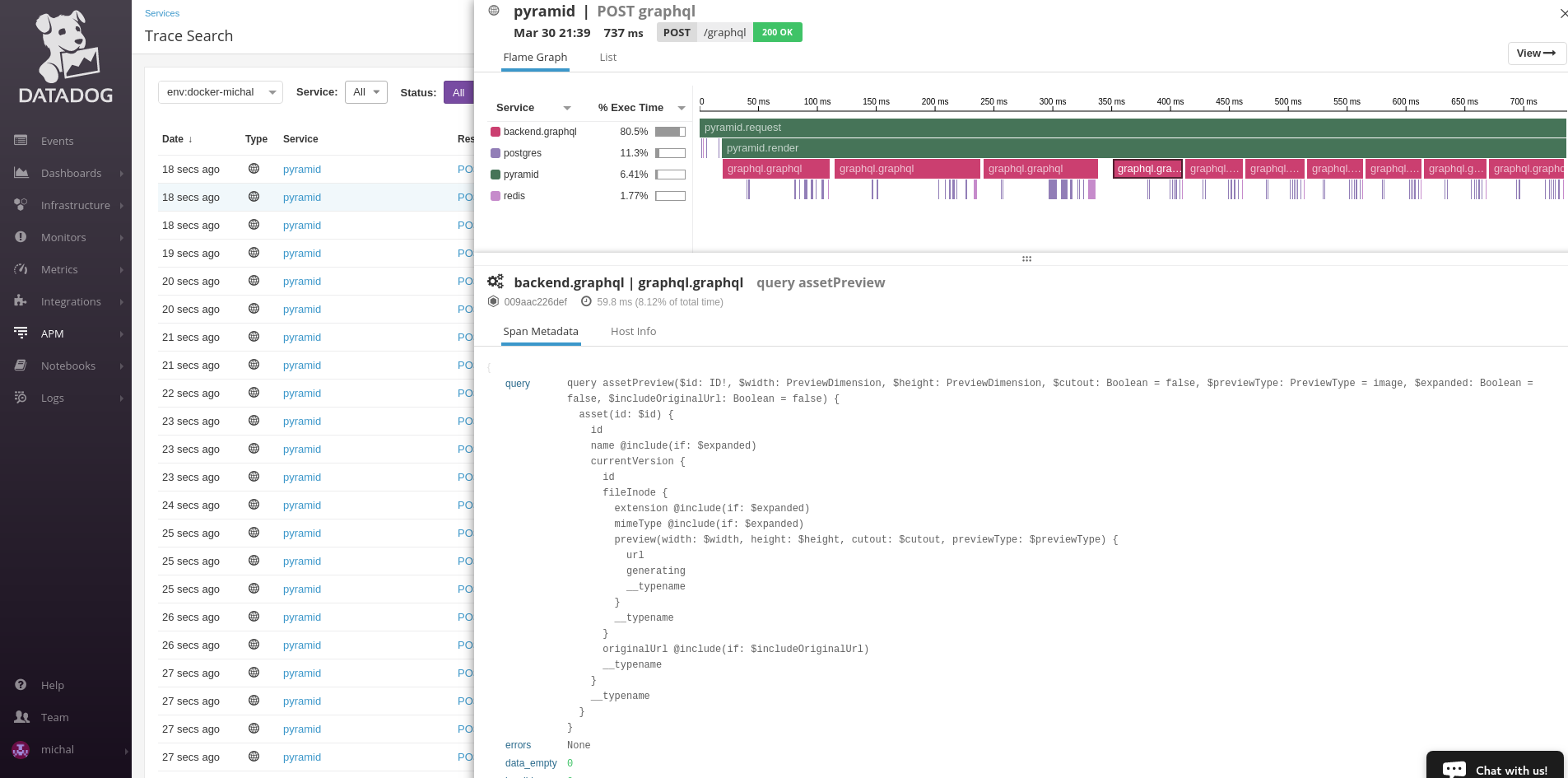
Screenshots for pyramid app serving GraphQL with tracing enabled:
GraphQL service detail. GraphQL query detail.To trace all GraphQL requests patch the library. Put this snippet to your application main entry point.
Check out the datadog trace client for all supported libraries and frameworks.
Note
For the patching to work properly, patch needs to be called before any other imports of the graphql function.
Trace only certain calls with traced_graphql function
- DDTRACE_GRAPHQL_SERVICE
Define service name under which traces are shown in Datadog. Default value is
graphql
Default arguments passed to the tracing context manager can be updated using span_kwargs argument of ddtrace_graphql.patch or ddtrace_graphql.traced_graphql functions.
Default values:
- name
Wrapped resource name. Default
graphql.graphql.- span_type
Span type. Default
graphql.- service
Service name. Defaults to
DDTRACE_GRAPHQL_SERVICEenvironment variable if present, elsegraphql.- resource
Processed resource. Defaults to query / mutation signature.
For more information visit ddtrace.Tracer.trace documentation.
In case you want to postprocess trace span you may use span_callback argument. span_callback must be function with signature def callback(result=result, span=span) where result is graphql execution result or None in case of fatal error and span is trace span object (ddtrace.span.Span).
What is it good for? Unfortunately one cannot filter/alarm on span metrics resp. meta information even if those are numeric (why Datadog?) so you can use it to send metrics based on span, result attributes.
from datadog import statsd
from ddtrace_graphql import patch, CLIENT_ERROR, INVALID
def callback(result, span):
tags = ['resource:{}'.format(span.resource.replace(' ', '_'))]
statsd.increment('{}.request'.format(span.service), tags=tags)
if span.error:
statsd.increment('{}.error'.format(span.service), tags=tags)
elif span.get_metric(CLIENT_ERROR):
statsd.increment('{}.{}'.format(span.service, CLIENT_ERROR), tags=tags)
if span.get_metric(INVALID):
statsd.increment('{}.{}'.format(span.service, INVALID), tags=tags)
patch(span_callback=callback)Some frameworks use exceptions to handle 404s etc. you may want to ignore some exceptions resp. not consider them server error. To do this you can supply ignore_exceptions argument as list of exception classes to ignore. ignore_exceptions will be used in python's isinstance thus you can ignore also using base classes.