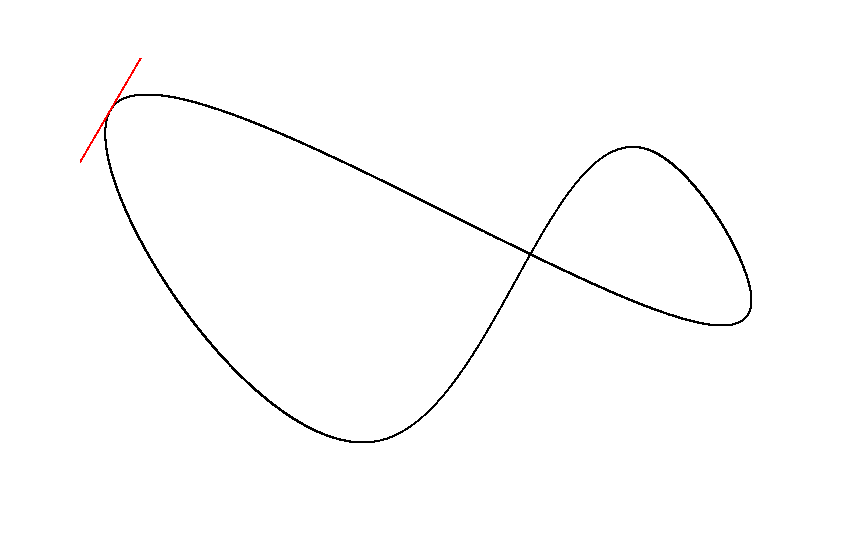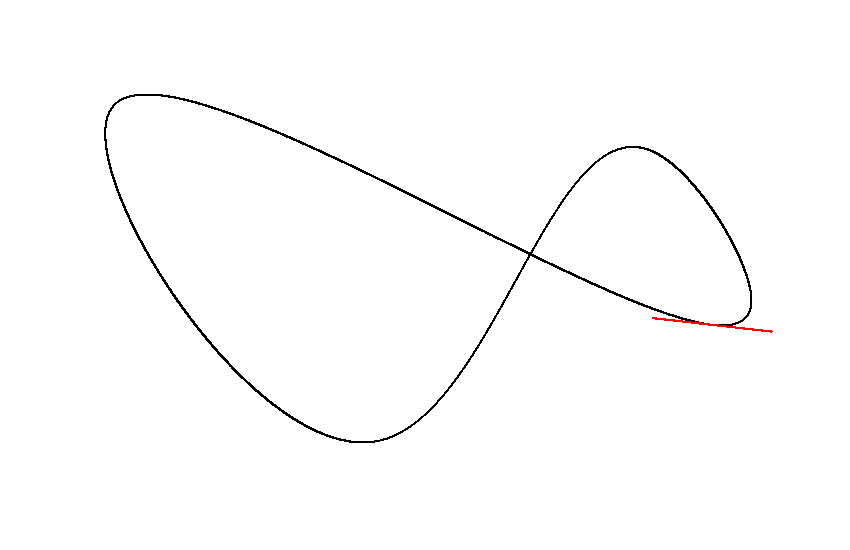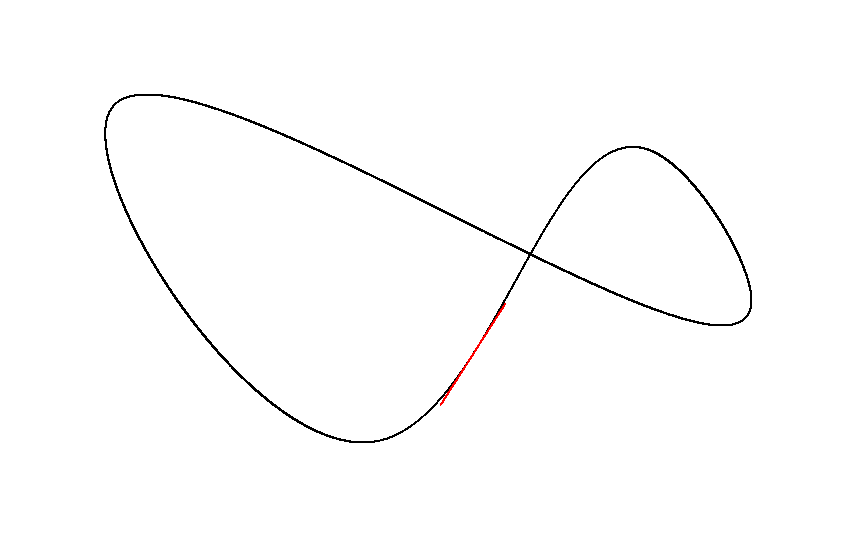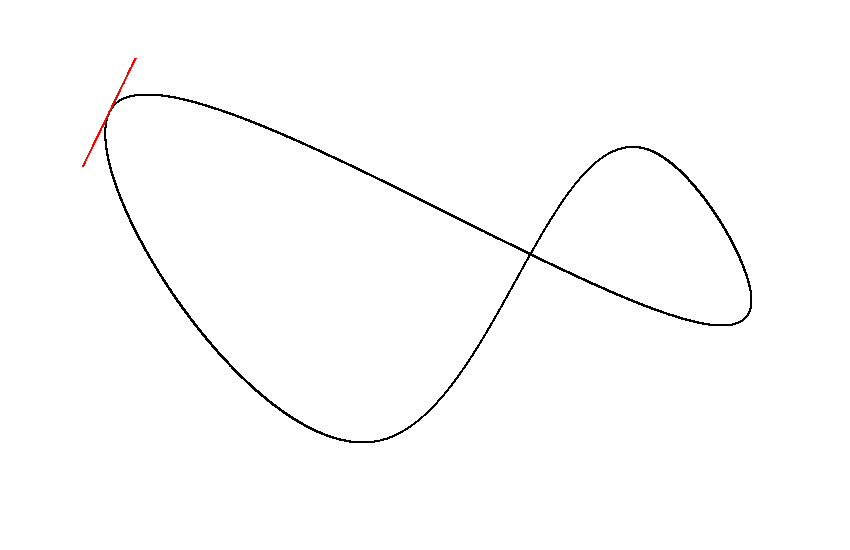A generic multi-order bezier curve and cubic bezier spline implementation for Java/Kotlin.
Note
- The calculation of bezier curve and spline lengths are implemented using estimation of variable resolution, which should be more than sufficient for most applications. Coordinates and tangents are not affected by this. If you require highly accurate measurements, consider using another library.
- There might be slightly more performant Java implementations out there. The main focus lies on being as generic as possible.
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.benedikt.math</groupId>
<artifactId>bezier-spline</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>Note: Check out the BezierSpline documentation for further options.
You can create open or closed bezier splines for any amount of dimensions using the provided FloatBezierSpline,
DoubleBezierSpline and Vector implementations. You may also create a custom bezier spline implementation.
BezierSpline<Double, Vector2D> spline = new DoubleBezierSpline<>(true);
spline.addKnots(
new Vector2D(0.06, 0.06),
new Vector2D(0.7, 0.24),
new Vector2D(0.6, 0.1),
new Vector2D(0.33, 0.39)
);
double length = spline.getLength();
Vector2D coordinates = spline.getCoordinatesAt(0.5);
Vector2D tangent = spline.getTangentAt(0.5);The required length estimation happens the first time lengths, coordinates, tangents or control points are queried. You can manually update the spline to move the workload. By default, the performance impact is negligible in most cases.
spline.compute(); // calculations happen here.
// ...
double length = spline.getLength(); // without performance impact
Vector2D coordinates = spline.getCoordinatesAt(0.5);
Vector2D tangent = spline.getTangentAt(0.5);BezierCurve<Double, Vector2D> curve = new DoubleBezierCurve(Order.CUBIC, from, to, controlPoints);
double length = curve.getLength();
Vector2D coordinates = curve.getCoordinatesAt(0.5);
Vector2D tangent = curve.getTangentAt(0.5);The required length estimation happens the first time the length is queried. You can manually update the curve to move the workload. By default, the performance impact is negligible in most cases.
curve.computeLength(); // calculations happen here.
// ...
double length = curve.getLength(); // without performance impact
Vector2D coordinates = curve.getCoordinatesAt(0.5);
Vector2D tangent = curve.getTangentAt(0.5);