Provides utilities to set up project specific git shortcuts/aliases
sudo ./install.shThis operation will copy the commands from the bin directory to /usr/local/bin and give them execution rights.
See more below.
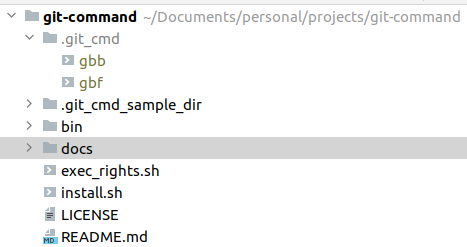
The scripts in the bin directory are the ones that will be executed from the CLI.
Please copy the contents of the bin folder into /usr/local/bin
sudo cp ./bin/* /usr/local/bin/Please add execution rights to the newly copied files.
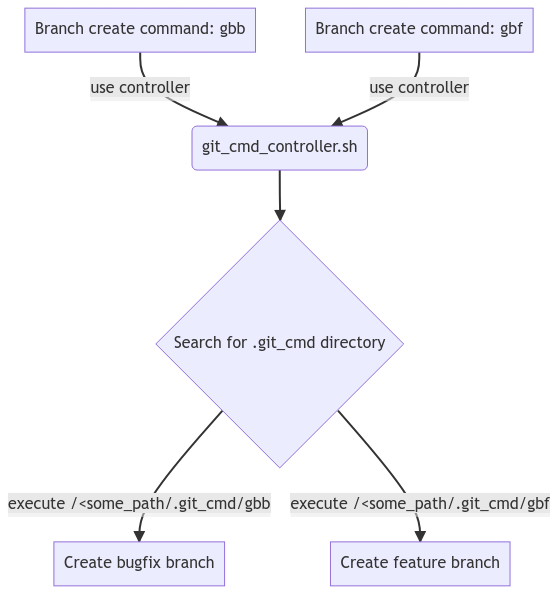
./exec_rights.shThe command scripts use the controller script, which will delegate commands to specific scripts located in a .git_cmd directory.
Place the contents of .git_cmd_sample_dir into a .git_cmd folder of your choosing.
The commands within the sample folder will create bugfix and feature branches tracking origin/main on any git project that is in a sub-directory of the location where .git_cmd was created. Feel free to modify these scripts to your project specific branching strategy.
e.g.
In the example in the image, the branch creation commands e.g. gbf will delegate the creation
to the script in .git_cmd. This directory doesn't have to be placed in your project's root path.
It can be placed anywhere above in the path, in order to re-use the same commands for multiple projects.
The branch creation commands are using this delegation pattern, because we would like to maintain 1 global
script for each operation (i.e. the commands in the bin directory, which are copied to /usr/local/bin).
In addition, leaving configurability to the user is preferred.