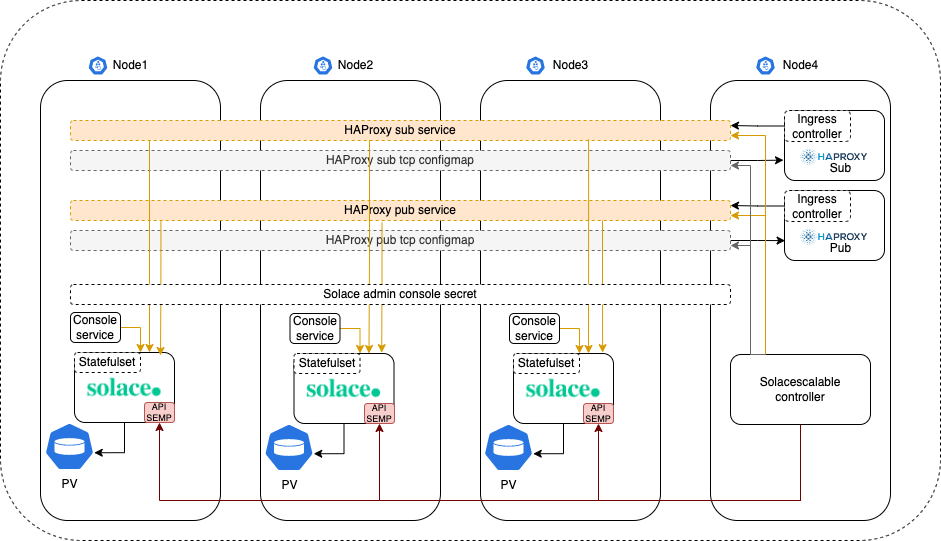
A solace operator to create a scalable solace cluster under kubernetes
The operator is used to spawn solace standalone instances using a statefulset. It listens to changes in the solace instances via it's SEMP api to make necessary openings in kubernetes.
In order to make openings, it will check for :
- Enabled message-vpn
- non null protocol ports opened in every message-vpn service
- Enabled client usernames (#client-username is ignored)
- Attributes defined in each client username (precisely, pub and sub attributes)
The operator will automatically listens for created, updated or deleted :
- message vpns
- client usernames
- clientusername attributes
The operator will create/update or delete :
- ClusterIP services
- Haproxypub and haproxysub services
- Haproxypub and haproxysub tcp configmaps
NOTE: You have to make the same provisioning in all your solace instances in order for this operator to work
You’ll need a Kubernetes cluster to run against. You can use KIND to get a local cluster for testing, or run against a remote cluster.
Note: Your controller will automatically use the current context in your kubeconfig file (i.e. whatever cluster kubectl cluster-info shows).
This operator is using haproxytech/kubernetes-ingress
Add the haproxytech/kubernetes-ingress helm repo
helm repo add haproxytech https://haproxytech.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo updateYou need to install 2 HAproxy instances:
- One for publishing
- One for subscribing.
Use below 2 helm charts with the following options
helm install --namespace ingress-controller --create-namespace --set controller.ingressClass='haproxy-pub',controller.ingressClassResource.name='haproxy-pub',controller.replicaCount=1,controller.extraArgs={'--configmap-tcp-services=solacescalable/solacescalable-pub-tcp-ingress'} haproxy-pub haproxytech/kubernetes-ingresshelm install --namespace ingress-controller --create-namespace --set controller.ingressClass='haproxy-sub',controller.ingressClassResource.name='haproxy-sub',controller.replicaCount=1,controller.extraArgs={'--configmap-tcp-services=solacescalable/solacescalable-sub-tcp-ingress'} haproxy-sub haproxytech/kubernetes-ingresskubectl create ns solacescalablekubectl create secret -n solacescalable generic solacescalable --from-literal adminPassword=<your password>
NOTE: If you run it like above, don't forget to clean your shell history
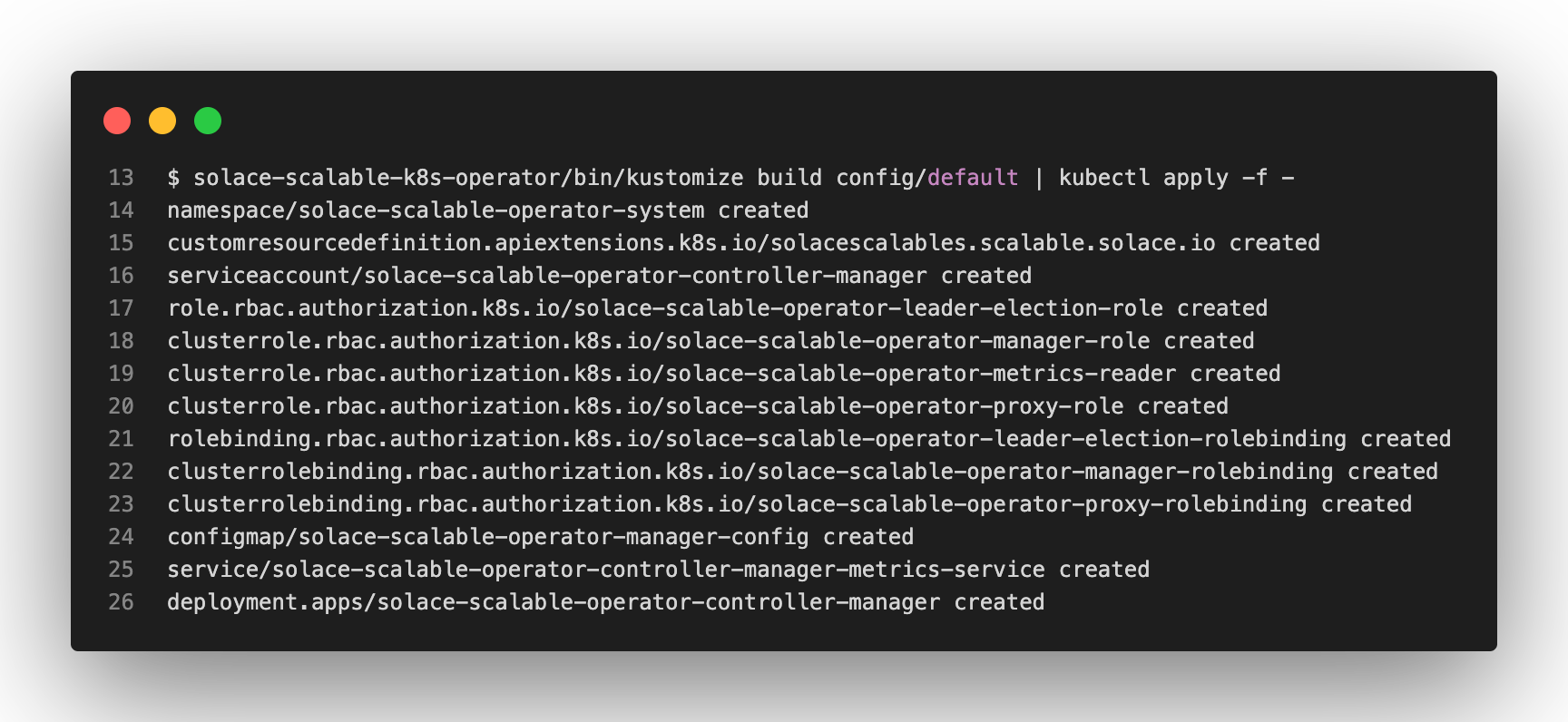
make deploy IMG=benmstm/solace-scalable-k8s-operator:latestNote: Below is the list of resources created in the cluster
Install an Instance of the Custom Resource:
kubectl apply -f config/samples/scalable_v1alpha1_solacescalable.yaml
NOTE: The Instance consist of the following yaml
apiVersion: scalable.solace.io/v1alpha1
kind: SolaceScalable
metadata:
name: solacescalable
namespace: solacescalable
spec:
replicas: 3
# Optional field can be omitted
clusterUrl: scalable.dev.gcp.digital-backbone.io
container:
name: solace
image: solace/solace-pubsub-standard:latest
volume:
name: storage
size: 50Gi
hostPath: /opt/storage
env:
- name: username_admin_globalaccesslevel
value: admin
- name: username_admin_password
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: solacescalable
key: adminPassword
optional: false
# when localManual, it will create a host path voulme in the cluster
# you can change this behaviour by selecying another pvClass
pvClass: localManual
haproxy:
namespace: ingress-controller
publish:
serviceName: haproxy-pub-kubernetes-ingress
subscribe:
serviceName: haproxy-sub-kubernetes-ingress
# Optional field can be omitted (default port allocation start at 1024)
network:
startingAvailablePorts: 1025Thats all folks :)
Build and push your image to the location specified by IMG:
make docker-build docker-push IMG=repo/img_name:tagDeploy the controller to the cluster with the image specified by IMG:
make deploy IMG=repo/img_name:tagTo delete the CRDs from the cluster:
make uninstallremove the controller from the cluster:
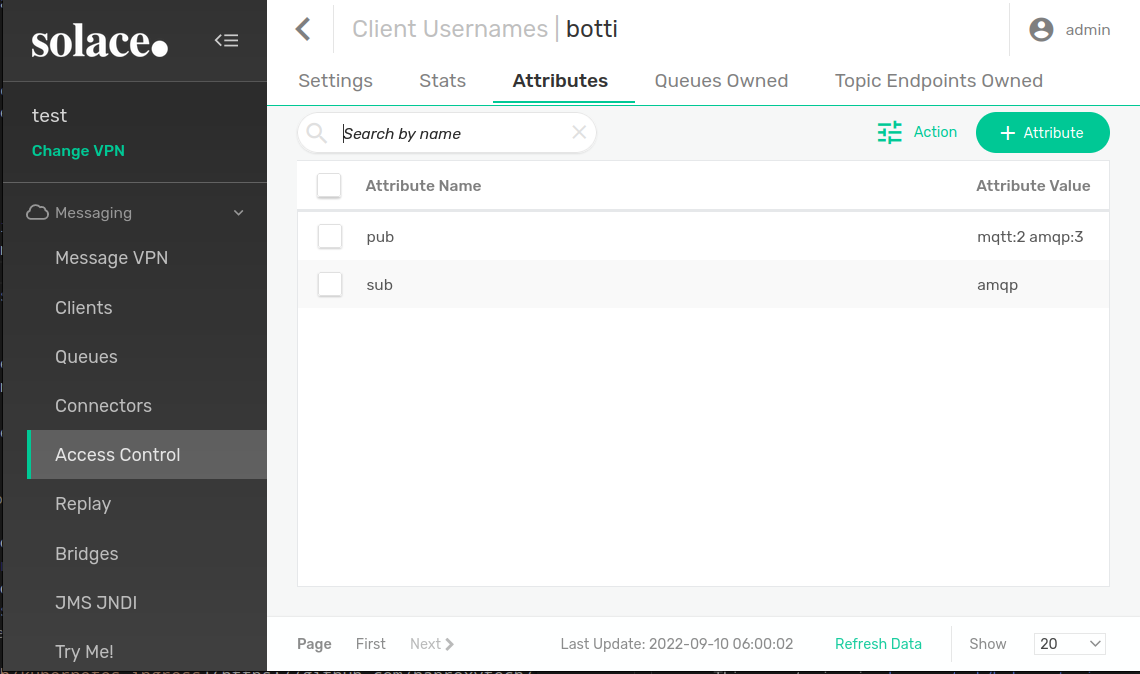
make undeployWe are using solace's client username attributes at our favour to store operator's behavioural datas
Select Message-Vpn -> Access control -> Client Usernames -> Select A client -> Attributes
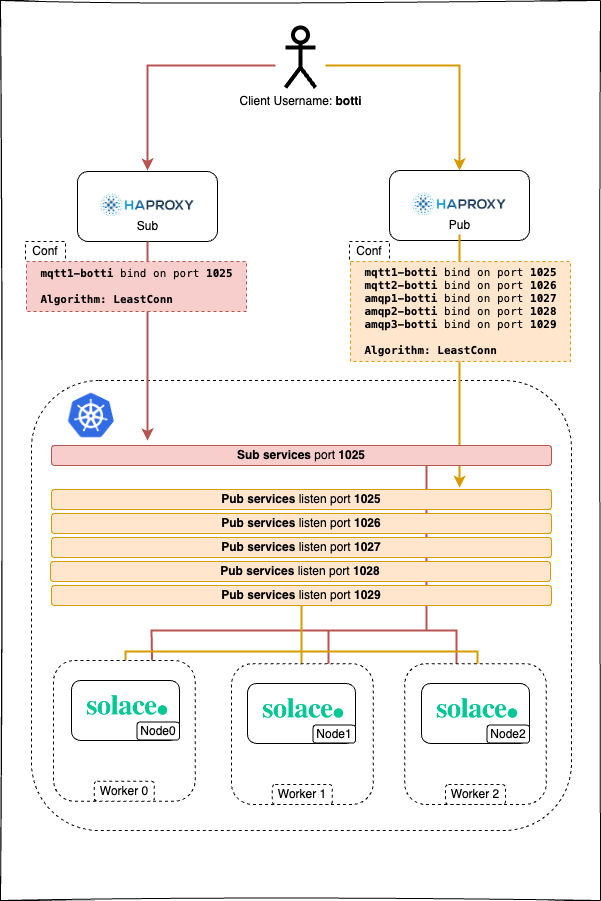
NOTE: There is the case were the client having 1 clientUsername want to publish in different topics and want the connection to be split evenly across the cluster. In this case we added a simple mecanism to spawn n ports for the same couple (clientusername/protocol), after each protocol name just add :n as mentioned in the image above.
- pub: if we want the clientusername have openings in the publish haproxy ingress
- sub: if we want the openings in subscribe haproxy
NOTE: If no pub/sub attribute are present in the clientusername, then all ports for all active protocols in the message VPN are exposed for pub/sub In the above example we will have the following openings:
| Client Username | Protocol | pub or sub | number of ports to open |
|---|---|---|---|
| botti | mqtt | pub | 2 |
| botti | amqp | pub | 3 |
| botti | amqp | sub | 1 |
Must be a list of string separated by a space. Here is the complete supported protocol list
| Solace correspondance | Protocol |
|---|---|
| ServiceAmqpPlainTextListenPort | amqp |
| ServiceAmqpTlsListenPort | amqps |
| ServiceMqttPlainTextListenPort | mqtt |
| ServiceMqttTlsListenPort | mqtts |
| ServiceMqttTlsWebSocketListenPort | mqttws |
| ServiceRestIncomingPlainTextListenPort | rest |
| ServiceRestIncomingTlsListenPort | rests |
In order to get the created pub/sub service ports in a clear manner, you can use the following kubectl ports