This repo is the source code for our ACL/IJCNLP2021 finding paper Multi-Lingual Question Generation with Language Agnostic Language Model
First of all, you should download the wikipedia dumps from https://dumps.wikimedia.org/ , basicly, there are 10 languages used in this paper for pre-training.
| Language | Short name | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Chinese | zh | 1.4G |
| English | en | 14G |
| Korean | ko | 679M |
| French | fr | 4.4G |
| Hindi | hi | 430M |
| Burmese | bu | 208M |
| German | de | 5.8G |
| Vietnam | vi | 979M |
| Japanese | Ja | 2.8G |
| Chinese Minnan | mi | 124M |
Note that the number of pre-training languages could be larger than the fine-tuning languages.
You should downloads the original wikidumps file containing the whole articles, such as jawiki-20200420-pages-articles.xml.bz2. And then using WikiExtractor to extract the paragraphs. For example:
python3 WikiExtractor.py -b 100m -o raw/ jawiki-20200420-pages-articles.xml.bz2This extract the text of japanese wikidumps into the raw directory.
Then we merge the wiki text files processed by Wikextractor into a single file, which are then used to train the sentencepiece tokenizer in [step3](###3. Train the sentencepiece tokenizer) The code we provided is preprocess/process_wiki_data.py
def check_valid_wiki_passage(txt):
if txt.startswith('<doc id'):
return False
if txt.startswith('</doc>'):
return False
if len(txt) < 10:
return False
return True
def get_all_wiki_data(language='english'):
raw_file_paths = get_dir_files('data/{}/raw'.format(language))
data = []
for one_file in tqdm(raw_file_paths):
for line in get_file_info(one_file):
if check_valid_wiki_passage(line):
data.append(line.strip())
output_filename = 'data/{}/wiki.all.txt'.format(language)
print('dump {} wiki total size is {}'.format(language, len(data)))
write_lst_to_file(data, output_filename)
print('{} done!'.format(language))Where we get the text between two xml tags and filter out the lines shorter than 10.
For each language, we use google's sentencepiece library to learn the tokenizer automatically. We use the unigram language model. And the code is preprocess/process_wiki_data.py
def train_vocab(language='english', vocab_size=30000):
sp_path = 'data/{}/wiki.all.txt'.format(language)
content = '--input=' + sp_path + ' ' \
'--model_prefix=/search/odin/bingning/data/LALM/language_slot/vocab.my_size --vocab_size=my_size ' \
'--character_coverage=0.9999 ' \
'--num_sub_iterations=2 ' \
'--max_sentencepiece_length=36 ' \
'--model_type=unigram --num_threads=40 --max_sentence_length=15000 ' \
'--input_sentence_size=2000000 '
content = content.replace('my_size', str(vocab_size))
content = content.replace('language_slot', language)
spm.SentencePieceTrainer.Train(
content
)where the language parameters are the respective language processed in previous step. The default vocabulary size is 30,000.
After processing the original wiki dumps and obtaining the tokenizer, we then pretrain the LALM.
There are two types of model we can pre-train,
- LALM_shared, where we don't discriminate any languages, and the low-level module is directly fed to the high-level module.
- LALM, we add a discriminator and adopt adversarial training to make the high-level module more language-agnostic.
Our pre-training code is provided in train/pre_train_lalm.py . And you can run the script by :
sh run_pre_train.shwhere the run_pre_train.sh is
#!bin/bash
python3 -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=4 pre_train_lalm.py \
--batch_size=24 \
--max_learning_rate==1e-4 \
--max_length==512 \
--n_embedding==128 \
--n_hidden==768 \
--n_layer==12 \
--n_head==12 \
--reload=False \
--epoch=-1 \
--type=shared \
--zh_path='data/chinese/wiki.all.txt' \
--en_path='data/chinese/wiki.all.txt' \
--ko_path='data/korean/wiki.all.txt' \
--fr_path='data/french/wiki.all.txt' \
--hi_path='data/hindi/wiki.all.txt' \
--bu_path='data/burmese/wiki.all.txt' \
--de_path='data/german/wiki.all.txt' \
--vi_path='data/vietnam/wiki.all.txt' \
--ja_path='data/japanese/wiki.all.txt' \
--mi_path='data/minnan/wiki.all.txt'Where the reload parameter means whether to reload previous pre-trained model from checkpoints, and epoch is the pre-load checkpoint's number.
type can be either shared or lalm
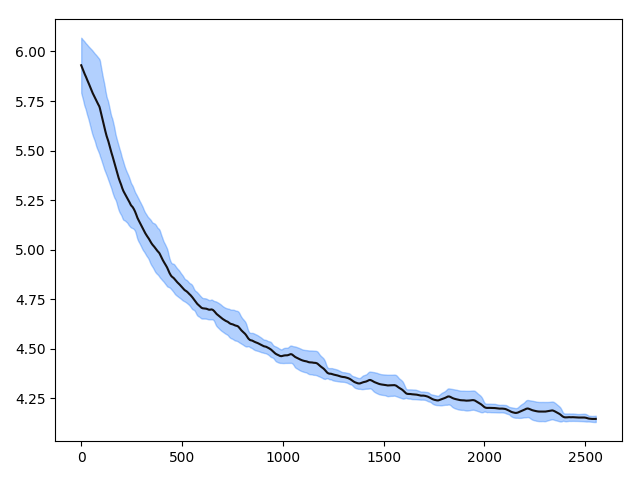
We also provid the training curve from our enviroments, where we 4 NVIDIA-V100 16Gb GPUs.
Note that the final average loss is around 3.5 for LALM_share.
First of all, we should pre-process the question answering datasets. We process the data and transform it into a list of items, where each item is [context, document_features, questions] and each question is [question, question_features]. The process script is in preprocess directory, an example of English SQuAD is shown below.
sp = spm.SentencePieceProcessor()
sp.load('../data/vocab/english.30000.model')
def one_paragraphs(paragraphs):
one_data = []
for paragraph in paragraphs["paragraphs"]:
context = paragraph['context']
doc_ids = sp.EncodeAsIds(context)
questions = []
for qa in paragraph["qas"]:
question_text = qa["question"]
question_ids = sp.EncodeAsIds(question_text)
questions.append([question_text, question_ids])
one_data.append([context, doc_ids, questions])
return one_data
def process(filename):
with open(filename) as dataset_file:
dataset_json = json.load(dataset_file)
dataset = dataset_json['data']
output = multi_process(one_paragraphs, dataset, num_cores=40)
output = [y for x in output for y in x]
if 'train' in filename:
output = [[x[1], y[1]] for x in output for y in x[2]]
print('{} proceed done, have {} samples'.format(filename, len(output)))
return output
def get_squad():
dev = process('../data/qg/english.dev.json')
dump_file(dev, '../data/qg/dev.en.obj')
train = process('../data/qg/english.train.json')
dump_file(train, '../data/qg/train.en.obj')
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_squad()Since we do not hold the licence to distribute the data, so we refer them below so you can obtain this data by yourself.
| Language | Training data size | Dev data size | url | Info |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | 87,599 | 2,067 | https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/ | english.dev.json/english.train.json, V1.1 |
| Korean | 60,407 | 964 | https://github.com/graykode/KorQuAD-beginner/tree/master/config | |
| French | 20,731 | 768 | https://fquad.illuin.tech/ | |
| Hindi | 4,000 | 2,555 | https://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~ganesh/HiQuAD/clqg/clqg_data.tar.gz | decompress the tar file into hindi directory. |
| Chinese | 180,000 | 44,962 |
todo
If you wish to use our data in your research, please cite:
@article{wangmulti,
title={Multi-Lingual Question Generation with Language Agnostic Language Model},
booktitle = "Findings of the Joint Conference of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (ACL-IJCNLP 2021)",
month = Aug,
year = "2021",
address = "Virtual",
author={Wang, Bingning and Yao, Ting and Chen, Weipeng and Xu, Jingfang and Wang, Xiaochuan}
}