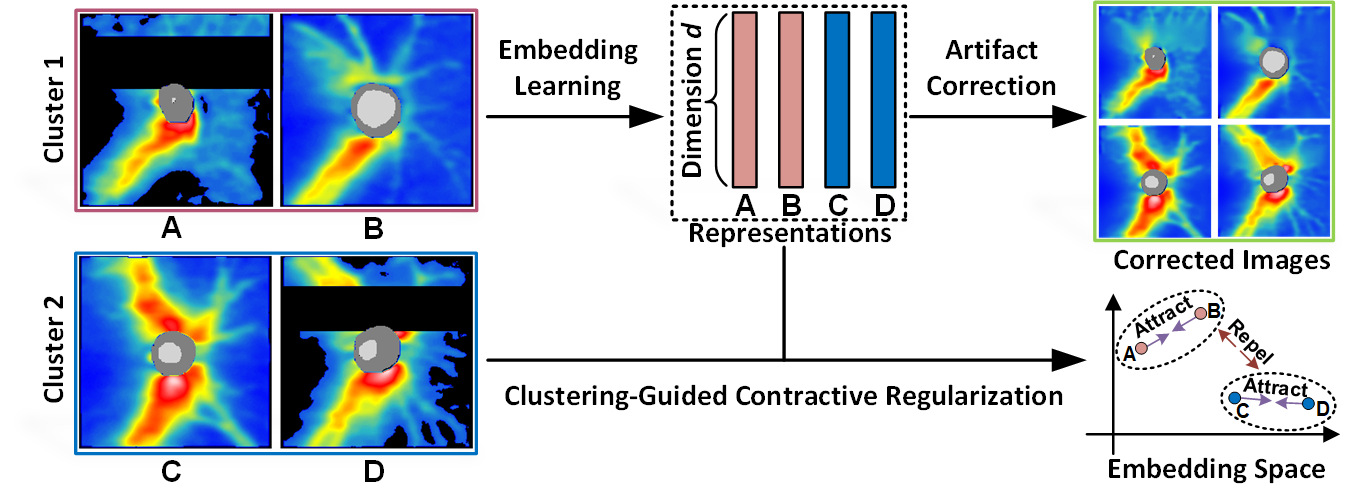
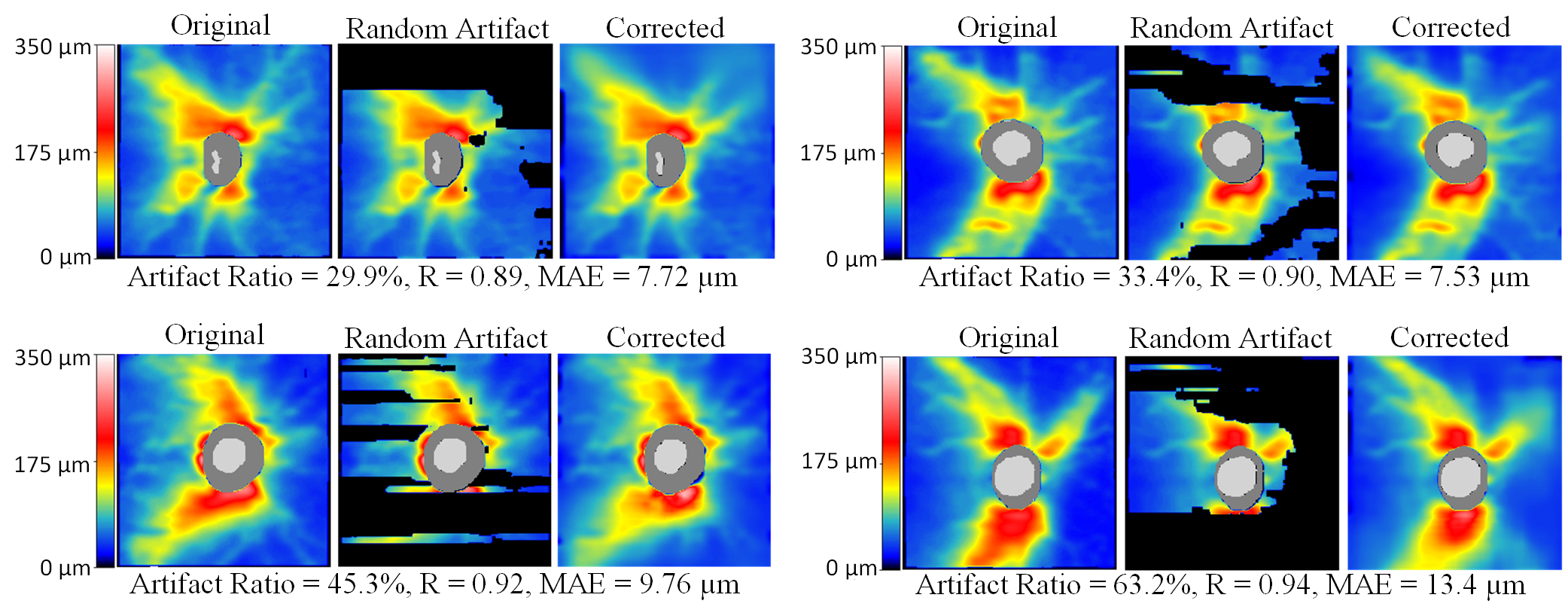
The code and dataset for the paper entitled Artifact-Tolerant Clustering-Guided Contrastive Embedding Learning for Ophthalmic Images published in the IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.
Python 3.8
tensorflow 2.4.0
opencv-python 4.5.5
The Harvard Glaucoma Detection (Harvard-GD) dataset includes 500 OCT retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (RNFLT) maps (dimension 225 x 225) from 500 unique glaucoma patients. The glaucoma label and visual field mean deviation (MD) information are also included in the data. The dataset can be accessed via this link. This dataset can only be used for non-commercial research purposes. At no time, the dataset shall be used for clinical decisions or patient care. The data use license is CC BY-NC-ND 4.0. If you have any questions, please email harvardophai@gmail.com.
Note that, the modifier word “Harvard” only indicates that our dataset is from the Department of Ophthalmology of Harvard Medical School and does not imply an endorsement, sponsorship, or assumption of responsibility by either Harvard University or Harvard Medical School as a legal identity.
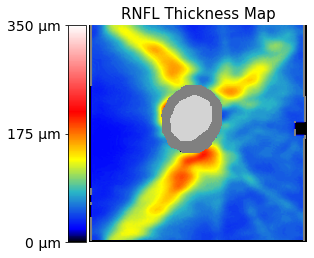
Here are sample codes to visualize the RNFLT map:
from utils.map_handler import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rnflts = np.load('dataset/rnflt_map.npy')
img = rnflts[0]
plot_2dmap(img, show_cup=True)
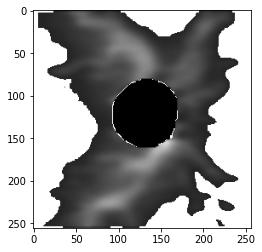
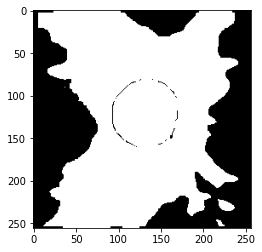
Calculate the masked RNFLT and corresponding mask image:
# RNTLT values less than the cutoff are treated as artifacts
masked_map, ori_mask, resized_map = process(img, cutoff=50)
plt.imshow(masked_map)
plt.show()
plt.imshow(ori_mask)
The model weight "EyeLearn_weights.72-0.0019.h5" trained using 10,000 samples from our larger private dataset can be downloaded via this link
from models import rnflt2vec
# load the pretrained model
eyelearn = rnflt2vec.construct_model_from_args(args)
model.load('EyeLearn_weights.72-0.0019.h5', train_bn=False, lr=0.00005)
# embedding learning model
encoder = eyelearn.model.get_layer('embed_model')
model_embed = Model(inputs=encoder.inputs,
outputs=encoder.get_layer('encoder_output').output)
# artifact correction model
model_correction = Model(inputs=[eyelearn.model.inputs[0], eyelearn.model.inputs[1]],
outputs=eyelearn.model.output[0])
# embedding inference
embeds = model_embed.predict([masked_map, ori_mask])[0]
# artifact correction
preds = model_correction.predict([masked_map, ori_mask])[0]
If you find this repository useful for your research, please consider citing our paper:
@article{10159482,
author={Shi, Min and Lokhande, Anagha and Fazli, Mojtaba S. and Sharma, Vishal and Tian, Yu and Luo, Yan and Pasquale, Louis R. and Elze, Tobias and Boland, Michael V. and Zebardast, Nazlee and Friedman, David S. and Shen, Lucy Q. and Wang, Mengyu},
journal={IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics},
title={Artifact-Tolerant Clustering-Guided Contrastive Embedding Learning for Ophthalmic Images in Glaucoma},
year={2023},
volume={27},
number={9},
pages={4329-4340},
keywords={Representation learning;Task analysis;Feature extraction;Visualization;Optical distortion;Image segmentation;Retina;Artifact correction;glaucoma;ophthalmic image;representation learning;RNFLT map},
doi={10.1109/JBHI.2023.3288830}}