This python project uses OpenStreetMap data, the python package osmnx to calculate the shortest route from getting from one coordinate to another coordinate.
OSMnx is a Python package that lets you download geospatial data from OpenStreetMap and model, project, visualize, and analyze real-world street networks and any other geospatial geometries.
1. Download street networks from OpenStreetMap as a graph.
2. Calculate the shortest paths.
3. Create the shortest route(s) service.
FastAPI is a modern, fast (high-performance), web framework for building APIs with Python 3.6+ based on standard Python type hints.
1. Create the API service users can use to interact with shortest route service.
2. Create OpenAPI swagger interface.
- We use osmnx to download road graph networks from osmnx. The downloaded graph is a networkx graph which contains nodes and edges which make solving the problem of shortest path a breeze.
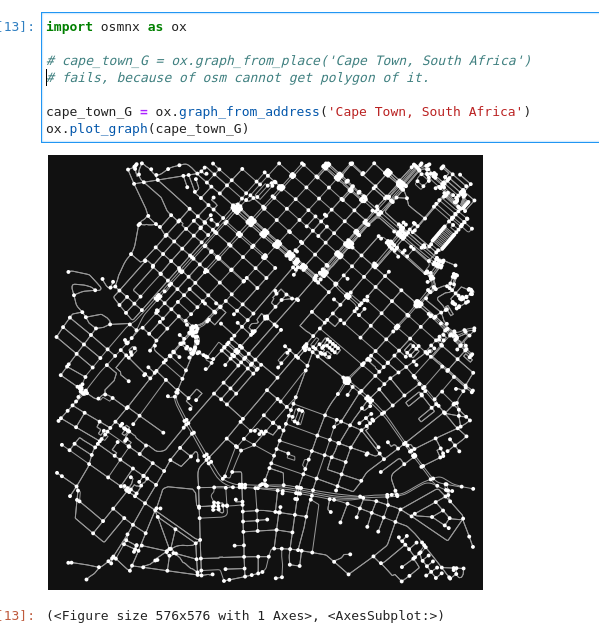
This is how to download a graph using a place name
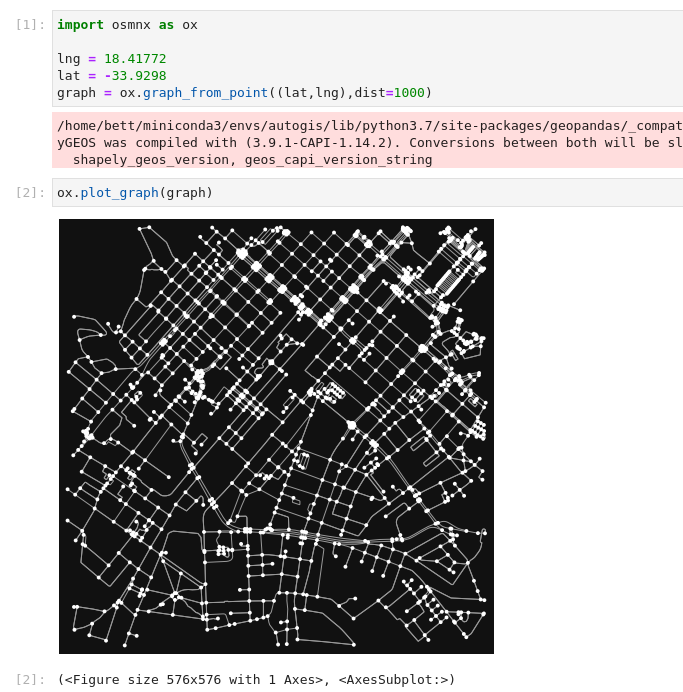
This is how to download a graph using a coordinate and distance parameter
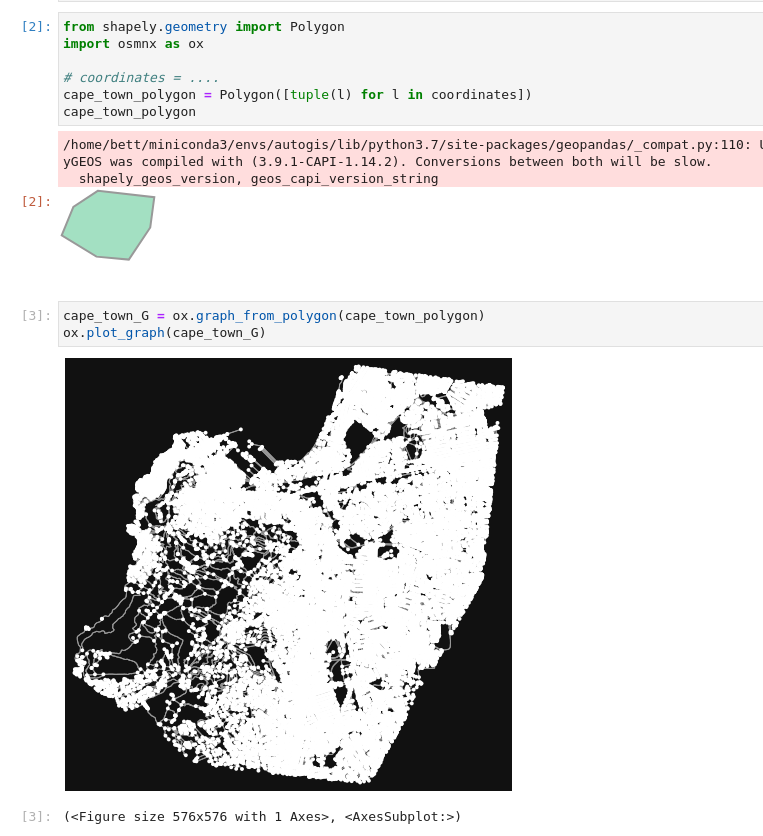
This is how to download a graph using a shapely polygon
Given an origin and destination coordinate(x,y) and a graph, to find the nearest route, we need to get the nearest graph node to the origin coordinate and the nearest graph node to the destination.
We use osmnx to get the nearest node to a point (X,Y) as
import osmnx as ox
graph = ox.graph_from_point((center_lat,center_lng),dist=4000)
orig_node = ox.nearest_nodes(graph, Y=orig_lat, X=orig_lng)
dest_node = ox.nearest_nodes(graph, Y=dest_lat, X=dest_lng)Once we have the have the origin and destination nodes, we can use osmnx to find the shortest path we can traverse to move from the origin to the destination node.
The code to query the the shortest_path to traverse from the graph is just a single line of code.
shortest_path = ox.shortest_path(graph, orig_node, dest_node)Once we get the shortest path, it contains a List[int] which is a series of nodes indexed by osmid of the node. The graph has a getter nodes which is a NodeView. When we index the nodeview using a node, we get a dictionary which contains an x and y attribute
import osmnx as ox
graph = ox.graph_from_point((center_lat,center_lng),dist=4000)
orig_node = ox.nearest_nodes(graph, Y=orig_lat, X=orig_lng)
node_value = graph.nodes[orig_node]
# returns {'y': -1.1091688, 'x': 36.6310601, 'street_count': 3}
lat = node_value['y']
lng = node_value['x']So to get the list of coordinates, we use a helper function to iterate over the graph nodes returned as shortest_path and convert it into a list of LatLng
def nodes_to_linestring(path, graph) -> List[LatLng]:
coords_list = [
LatLng(lon=graph.nodes[i]["x"], lat=graph.nodes[i]["y"]) for i in path
]
return coords_listWhen the server starts up, we download the graph and save it to an attribute called capetown_G.
import osmnx as ox
from shapely.geometry import box
# Download the graph. Change this to your Area of Interest
capetown_G = ox.graph_from_address(
"Cape Town, South Africa", dist=5000, network_type="drive"
)
# split graph into nodes and edges to get the bounds of the graph.
nodes, edges = ox.graph_to_gdfs(capetown_G)
minx, miny, maxx, maxy = nodes.total_bounds
# create polygon/envelope we'll use to check whether the point the user requests from the graph falls within our graph
graph_bounds = box(minx, miny, maxx, maxy) # Endpoint to get the shortest route. The parameters origin_lat,origin_lng,destination_lat,destination_lng will be passed in as query parameters when calling the API. We then call the
import find_route_functions
from fastapi import FastAPI, Response
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/shortest_route")
def read_shortest_route(
origin_lat: float,
origin_lng: float,
destination_lat: float,
destination_lng: float,
):
if not (
graph_bounds.contains(Point(origin_lng, origin_lat))
and graph_bounds.contains(Point(destination_lng, destination_lat))
):
return Response(
status_code=400, content="Origin or destination outside of Cape Town"
)
shortest_path = find_route_functions.shortest_path(
orig_lat=origin_lat,
orig_lng=origin_lng,
dest_lat=destination_lat,
dest_lng=destination_lng,
graph=capetown_G,
)
return linestring_to_feature(shortest_path)This works the same as read_shortest_route but takes an additional parameter k. Look into the server.py to see how it works.
- Create and activate your virtual environment
- Run
pip install -r requirements.txt - Run
uvicorn server:appto start the server. - Wait for server to start then browse the opened server address e.g
http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs/to test the server using Swagger UI.