NMT is a developing AI technology that uses deep learning to translate sentences from one language to another. Like the human brain, NMT gets smarter over time by building connections. For example, NMT can be trained to understand that the word “car” is related to “auto,” “automobile,” “vehicle,” and “cars.” Older methods of machine translation can’t build connections like this.
Before NMT came along, machine translation engines used a word-for-word approach to translation. These translations often felt stilted and robotic. NMT is smart and accurate enough to generate high-quality translations that feel more human and realistic.
This translation technology is constantly evolving, so you might be wondering if NMT will replace human translators anytime soon. Let’s explore NMT and find out.
Think about how humans comprehend language. When we want to translate ‘The girl rides the bike,’ our brain first makes a mental representation of what that looks like as a whole. Once we have a full mental picture, we can proceed to translate. Neural MT works similarly.
Neural machine translation translates entire sentences at a time, rather than word-by-word or phrase-by-phrase like older machine translation models. NMT uses the context of a sentence to come up with the most relevant translation. It then makes adjustments and rearrangements until the translation reads more like human speech with correct grammar.
Classic examples of publicly accessible NMT software are Google Translate and Baidu Translate. Many multinational corporations are utilizing NMT to help them overcome translation challenges related to their global expansion efforts.
Google Translate is the most widely used machine translation tool around the globe—translating over 140 billion words per day. The Google Neural Machine Translation System (GNMTS) significantly increases translation accuracy and fluency. The tech giant uses enormous data sets to train its translation algorithms and has an end-to-end design to boost learning over time.
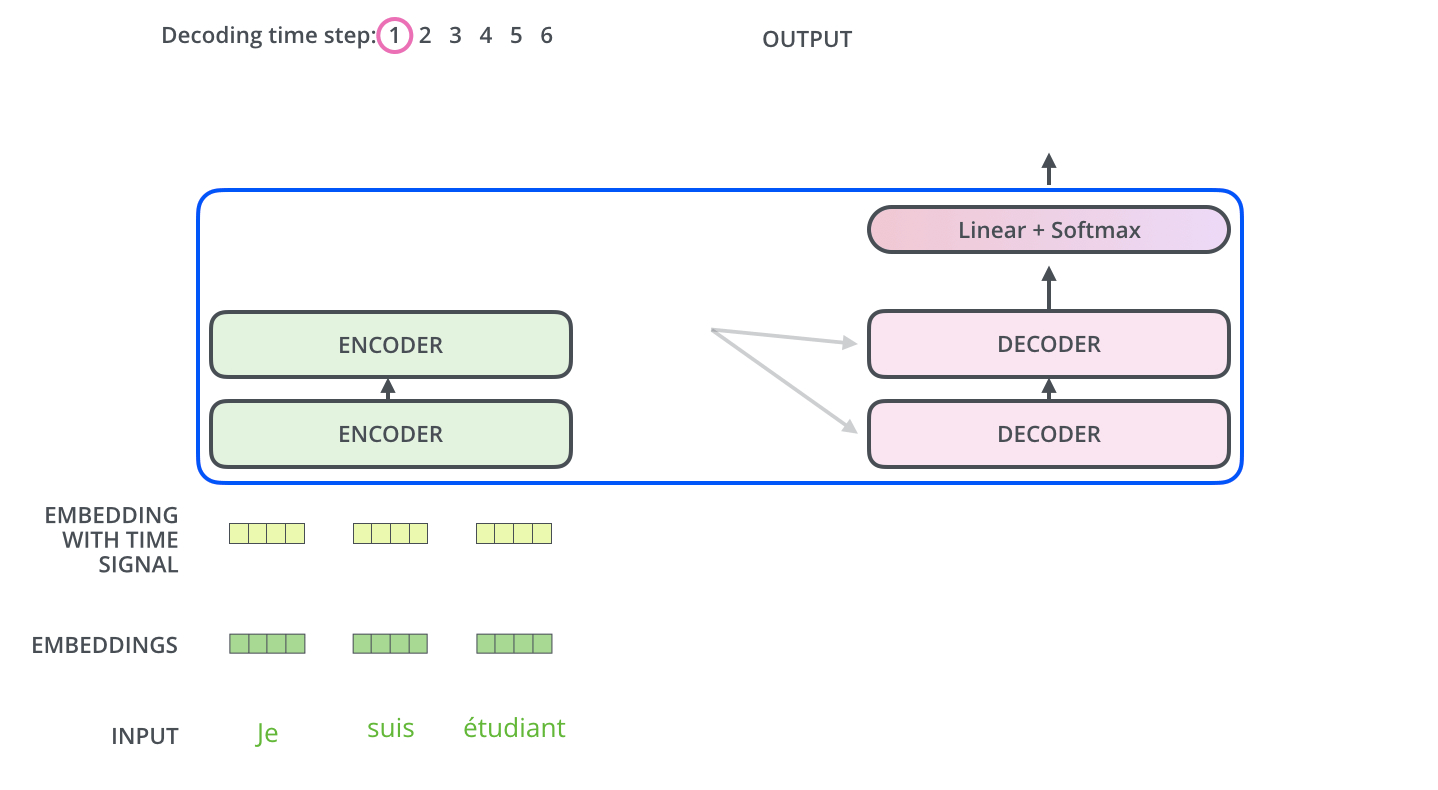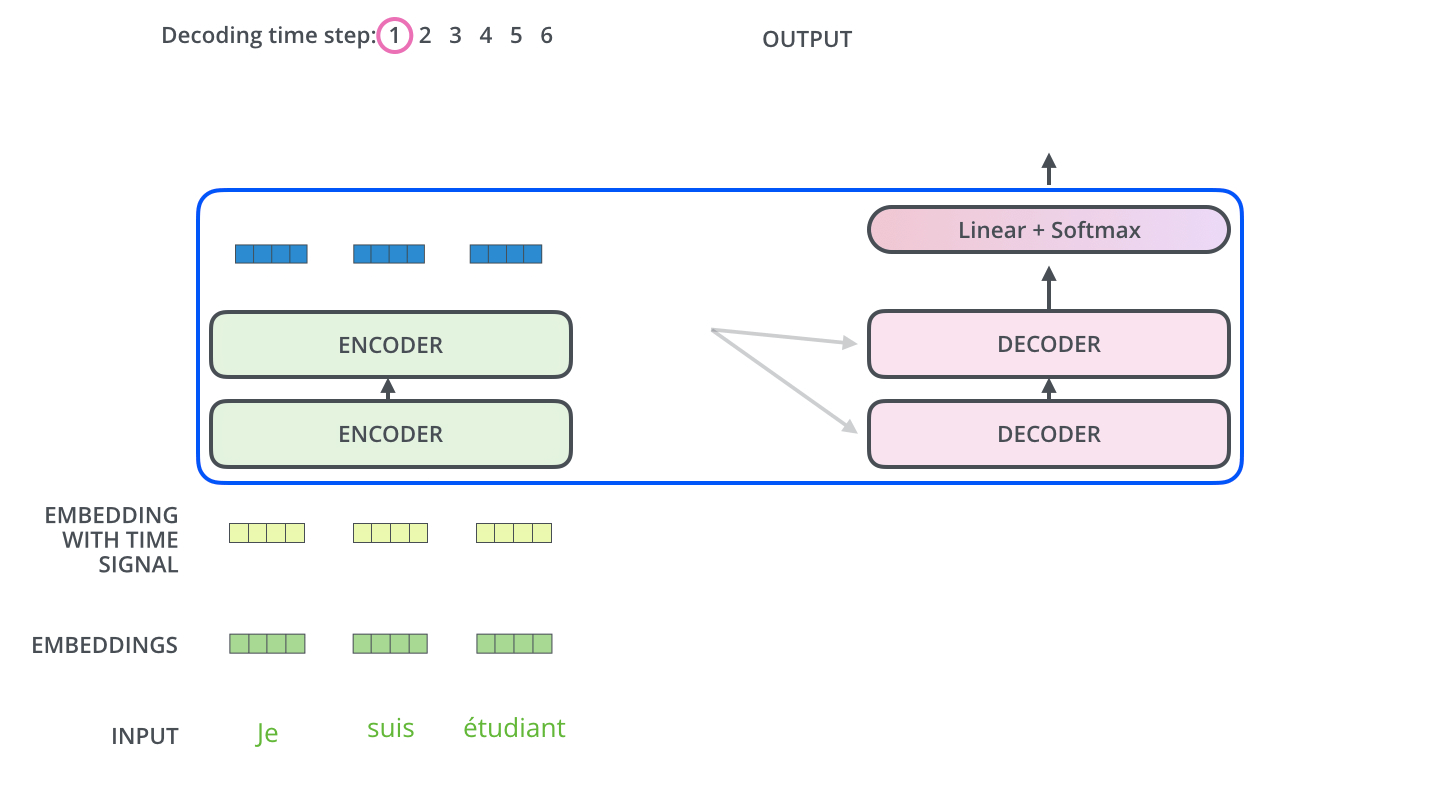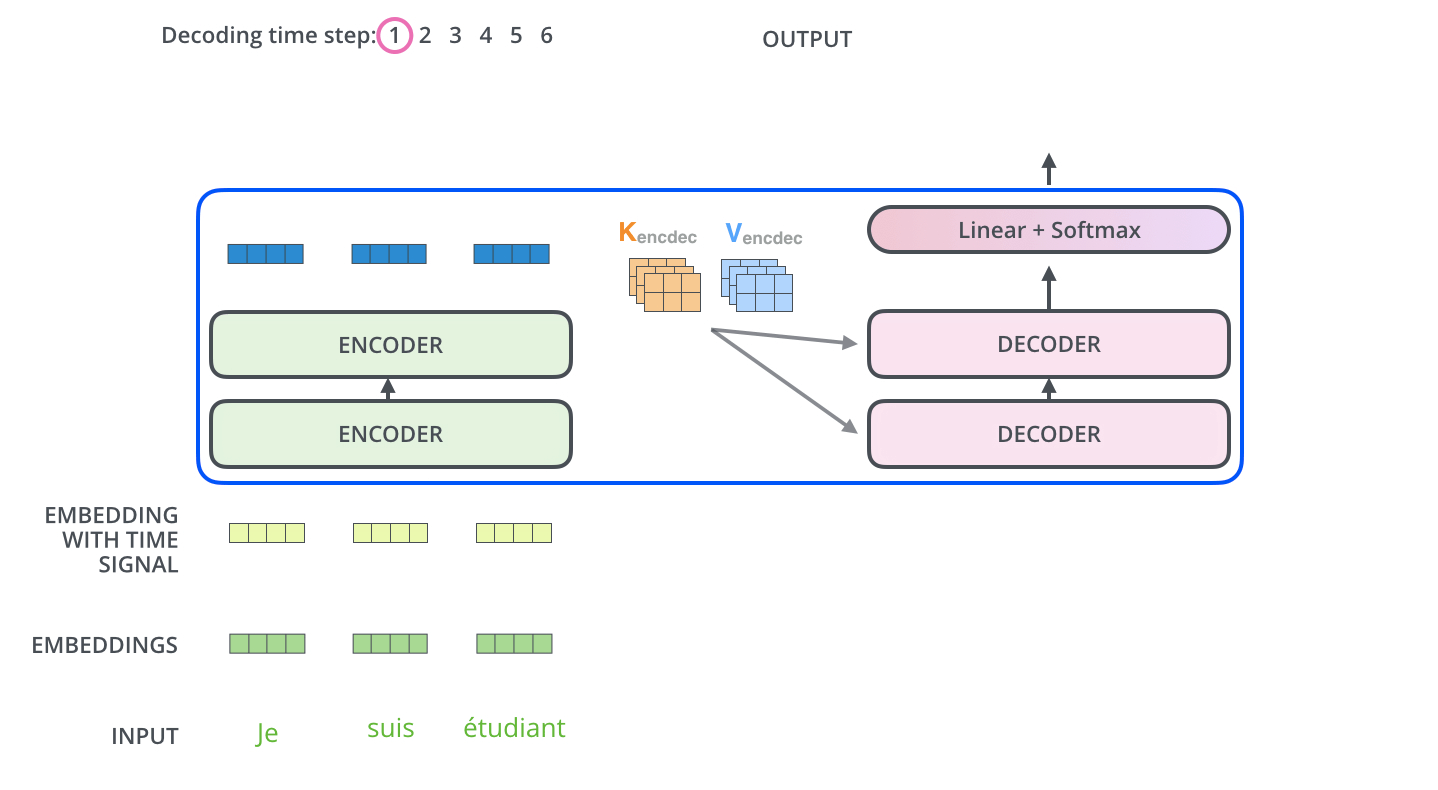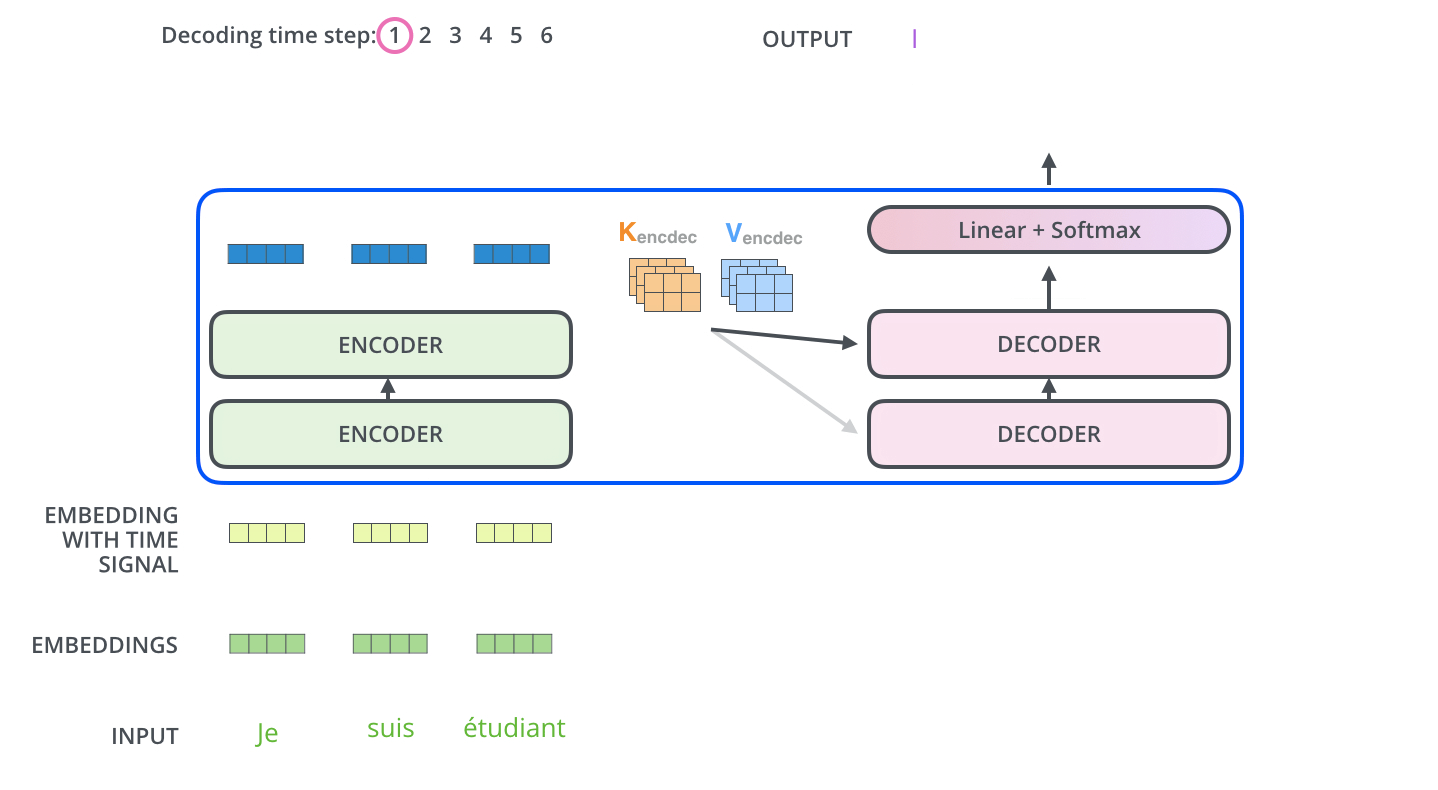
An NMT computer uses deep learning to build an artificial neural network to teach it how to translate between languages. This computational system strives to mimic the billions of neuron cells in the human brain that use observable data to learn and make decisions. These neural networks translate entire sentences without breaking them down into smaller parts. Neural machine translation can also predict the likelihood of a sequence of words.
To do this, NMT uses an encoder-attention-decoder model. An encoding neural network is capable of reading and encoding a source sentence into a ‘meaning vector’ or ‘thought vector.’ This vector is a number sequence that represents the meaning of the sentence. A decoder then produces a translation from the encoded vector.
The encoder-decoder system is trained with large amounts of data to maximize the probability of producing a correct translation from a source sentence. This enables it to capture dependencies in languages, such as syntax structures and gender agreement, resulting in much more fluent translations.
Neural machine translation is a single, well-trained system that can accurately translate source text to a target language. It does away with the need to use specialized systems that are typical of statistical machine learning. Its biggest strength is its ability to perform end-to-end direct learning.
NMT applies to pretty much any language, including ones that are comprehended by relatively few people. Users can fine-tune translations to suit specific types and styles of languages, e.g., UK-English, US-English, and medical, financial, and scientific language. Several industries requiring custom-developed and high-accuracy machine translation use a blend of statistical and neural translation methods.
NMT is a promising technology, but it’s far from perfect. Here are some big advantages and disadvantages of neural machine translation.
- Natural-sounding language NMT can make AI-translated language sound more human and less robotic. Here’s a great example from Google
- Context NMT isn’t perfect, but it does a good job of interpreting translation context. Google made recent strides in training its NMT to pay greater attention to the context of a sentence within a body of work.
- Generalization NMT gets smarter over time. Like the human brain, it can generalize to make new conclusions and connections. It uses these connections to quickly learn different language pairs.
- Good accuracy in some contexts NMT is especially good at translating repetitive content that requires high accuracy like manuals, guides, or reference materials.
- Speed Once an NMT system is trained, the translation speed is impressive. NMT can translate Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities in a little over a minute.
- Flexibility and integrations Another big advantage: NMT can be easily integrated into software with APIs and SDKs.
- Need for clarity in the source text Source text needs to be very clear for NMT to generate a quality translation. Neural machine translation has difficulties with ambiguities, highly technical language, proper nouns, and rare words.
- Poor translation of long sentences NMT generally outperforms other machine translation methods, but there’s an interesting exception. NMT can’t translate long sentences very well.
- Large data sets needed For smaller projects, NMT isn’t always a good fit. NMT systems produce comparably poor results with small data sets. Without a large amount of training data, NMT isn’t going to give you accurate translations.
- Expertise limitations NMT can’t perform well without the expertise and cognitive power of human architects and engineers. Any NMT model must be trained with a large quantity of linguistic data.
- Human post-editing still needed NMT text should always be checked by a human editor. Language interpretation requires a level of critical thinking and nuance that computers haven’t achieved yet.
Thank you for reading. Click link for resources.