This project implements a reinforcement learning agent for playing Atari games using the Arcade Learning Environment (ALE) and PyTorch.
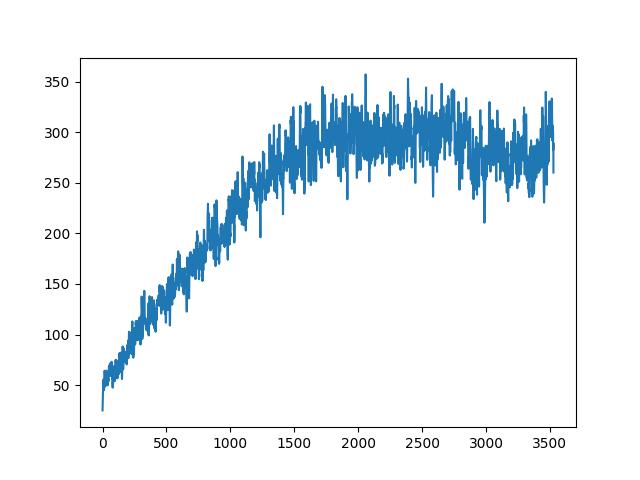
The agent was trained for 10 million steps on the Space Invaders game. The training process took approximately 8 hours on a single NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU. The agent achieved an average reward of around 300 points per episode after training. The agent will be loaded from the checkpoint and evaluated on the Space Invaders environment by default.
agent.py: Contains the implementation of the reinforcement learning agent.neural.py: Defines the neural network architecture used by the agent.main.py: The main script to run the training and evaluation of the agent.wrappers.py: Custom environment wrappers to modify the behavior of the environment.
- Python 3.11
- PyTorch
- Gymnasium
- Arcade Learning Environment (ALE)
- Other dependencies listed in
requirements.txt
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/bgaborg/atari-gym.git cd atari-gym -
Create a virtual environment with uv, and install the required packages:
uv venv source .venv/bin/activate -
Install the required packages:
uv pip install -r pyproject.toml
-
To train the agent, run the main.py script:
python main.py
-
To evaluate the agent, modify the main.py script to load a pre-trained model and run the evaluation loop.
-
Modify the
my_rig_factorparameter in the agent.py script to adjust the memory replay buffer size. -
Install pytorch with cuda support if cuda is available on your machine:
uv pip install torch --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
The Agent class in this project has several parameters that control its behavior and training process. Below is a description of each parameter:
- state_dim: The dimensions of the state space. This is typically a tuple representing the shape of the input state (e.g.,
(4, 84, 84)for a stack of 4 grayscale frames of size 84x84). - action_dim: The number of possible actions the agent can take. This is an integer representing the size of the action space.
- save_dir: The directory where the model checkpoints will be saved.
- iterations: The number of training iterations (episodes) the agent will run.
- checkpoint: (Optional) The path to a checkpoint file to load the agent's state from.
- my_rig_factor: A scaling factor used to adjust the size of the replay buffer and the burn-in period. Default is
0.8. - memory: A deque used as the replay buffer to store past experiences. The maximum length is scaled by
my_rig_factor. - batch_size: The number of experiences sampled from the replay buffer for each training step. Default is
32. - exploration_rate: The initial exploration rate for the epsilon-greedy policy. Default is
1.0. - exploration_rate_decay: The decay rate for the exploration rate. Default is
0.99999975. - exploration_rate_min: The minimum exploration rate. Default is
0.1. - gamma: The discount factor for future rewards. Default is
0.99. - curr_step: The current step count. Used to track the number of steps taken by the agent.
- burnin: The number of experiences to collect before starting the training process. Scaled by
my_rig_factor. Default isint(100_000 * my_rig_factor). - learn_every: The number of steps between each update to the Q-values. Default is
3. - sync_every: The number of steps between updates to the target network. Default is
1_000. - save_every: The number of steps between saving the model checkpoints. Default is
200_000.
- use_cuda: A boolean indicating whether CUDA (GPU) is available.
- use_mps_device: A boolean indicating whether the MPS (Metal Performance Shaders) device is available (for macOS).
- device: The device (CPU, CUDA, or MPS) on which the computations will be performed.
- net: The neural network used by the agent to predict the optimal actions. This is an instance of the
AgentNetclass. - learning_rate: The learning rate for the optimizer. Default is
0.00025. - optimizer: The optimizer used to update the network weights. Default is
torch.optim.Adam. - loss_fn: The loss function used to compute the difference between the predicted Q-values and the target Q-values. Default is
torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss.
- act(state): Given a state, choose an epsilon-greedy action and update the value of the step.
- cache(state, next_state, action, reward, done): Store the experience in the replay buffer.
- recall(): Retrieve a batch of experiences from the replay buffer.
- td_estimate(state, action): Estimate the current Q-values for the given state-action pairs.
- td_target(reward, next_state, done): Compute the target Q-values using the target network.
- update_Q_online(td_estimate, td_target): Update the online network's Q-values using the computed loss.
- update_target_network(): Update the target network to match the online network.
- learn(): Perform a learning step, updating the Q-values and the target network as needed.
These parameters and methods allow the Agent to interact with the environment, store and recall experiences, and update its policy based on the observed rewards.
The AgentNet class defines the neural network architecture used by the agent to predict the optimal actions. This network is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) designed to process visual input from the environment and output Q-values for each possible action.
The network follows a typical CNN structure with convolutional layers followed by fully connected (dense) layers. Here is a high-level overview of the architecture:
-
Input Layer:
- The input to the network is a stack of frames (e.g., 4 grayscale frames of size 84x84).
-
Convolutional Layers:
- Conv2D + ReLU: The first convolutional layer has 32 filters with a kernel size of 8x8 and a stride of 4, followed by a ReLU activation function. This layer reduces the spatial dimensions of the input significantly.
- Conv2D + ReLU: The second convolutional layer has 64 filters with a kernel size of 4x4 and a stride of 2, followed by a ReLU activation function. This layer further reduces the spatial dimensions and increases the depth of the feature maps.
- Conv2D + ReLU: The third convolutional layer has 64 filters with a kernel size of 3x3 and a stride of 1, followed by a ReLU activation function. This layer captures more detailed features from the input.
-
Flatten Layer:
- The output of the convolutional layers is flattened into a 1D tensor to prepare it for the fully connected layers. This transformation converts the 3D feature maps into a 1D vector.
-
Fully Connected Layers:
- Dense + ReLU: The first fully connected layer has 512 units, followed by a ReLU activation function. This layer learns high-level representations from the flattened feature maps.
- Output Layer: The final fully connected layer outputs Q-values for each possible action. The number of units in this layer corresponds to the number of actions in the action space.
The AgentNet class also includes a target network, which is a copy of the online network. The target network is used to provide stable target values for Q-value updates during training. The parameters of the target network are frozen (i.e., they are not updated during training) to ensure stability. This helps to mitigate the problem of instability and divergence that can occur when the Q-values are updated frequently.
The forward method of the AgentNet class takes an input tensor and a model type ('online' or 'target') and passes the input through the corresponding network (online or target) to obtain the Q-values. The online network is used for selecting actions and updating Q-values, while the target network is used to provide stable targets for the Q-value updates.
-
Action Selection:
- The agent uses the online network to predict Q-values for the current state. It then selects an action based on an epsilon-greedy policy, which balances exploration and exploitation.
-
Experience Replay:
- The agent stores experiences (state, action, reward, next state, done) in a replay buffer. This buffer allows the agent to learn from past experiences and break the correlation between consecutive experiences.
-
Training:
- During training, the agent samples a batch of experiences from the replay buffer. It uses the online network to estimate the current Q-values and the target network to compute the target Q-values.
- The loss is calculated as the difference between the estimated Q-values and the target Q-values. The agent then performs backpropagation to update the weights of the online network.
-
Target Network Updates:
- The target network is periodically updated to match the weights of the online network. This periodic update helps to stabilize the training process by providing consistent target values.
By using this neural network architecture, the agent can efficiently process visual input and learn to predict the optimal actions to maximize cumulative rewards in the environment.
The SkipFrame wrapper returns only every skip-th frame and accumulates rewards over skipped frames.
The ActionSpaceWrapper restricts the action space to a subset of allowed actions.
If you encounter any issues, please check the following:
Ensure that all dependencies are installed correctly.
- Verify that your environment is set up correctly (e.g., virtual environment is activated).
- Check the device (CPU/GPU) compatibility and ensure that the data is correctly moved between devices if necessary.
Contributions are welcome! Please open an issue or submit a pull request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
- install deps:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
source $HOME/.local/bin/env
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/bgaborg/atari-gym.git
cd atari-gym
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install -r pyproject.toml
byobu-enable
byobu
cp config.example.json config.json- run the agent:
python main.py