English | 中文
AgiBot X1 is a modular humanoid robot with high dof developed and open-sourced by AgiBot. It is built upon AgiBot's open-source framework AimRT as middleware and using reinforcement learning for locomotion control.
This project is about the reinforcement learning training code used by AgiBot X1. It can be used in conjunction with the inference software provided with AgiBot X1 for real-robot and simulated walking debugging, or be imported to other robot models for training.
- Create a new Python 3.8 virtual environment:
conda create -n myenv python=3.8.
- Install pytorch 1.13 and cuda-11.7:
conda install pytorch==1.13.1 torchvision==0.14.1 torchaudio==0.13.1 pytorch-cuda=11.7 -c pytorch -c nvidia
- Install numpy-1.23:
conda install numpy=1.23.
- Install Isaac Gym:
- Download and install Isaac Gym Preview 4 from https://developer.nvidia.com/isaac-gym.
cd isaacgym/python && pip install -e .- Run an example with
cd examples && python 1080_balls_of_solitude.py. - Consult
isaacgym/docs/index.htmlfor troubleshooting.
- Install the training code dependencies:
- Clone this repository.
pip install -e .
python scripts/train.py --task=x1_dh_stand --run_name=<run_name> --headless
- The trained model will be saved in
/log/<experiment_name>/exported_data/<date_time><run_name>/model_<iteration>.pt, where<experiment_name>is defined in the config file.
python /scripts/play.py --task=x1_dh_stand --load_run=<date_time><run_name>
python scripts/export_policy_dh.py --task=x1_dh_stand --load_run=<date_time><run_name>
- The JIT model will be saved in
log/exported_policies/<date_time>
python scripts/export_onnx_dh.py --task=x1_dh_stand --load_run=<date_time>
- The ONNX model will be saved at
log/exported_policies/<date_time>
- task: Task name
- resume: Resume training from a checkpoint
- experiment_name: Name of the experiment to run or load.
- run_name: Name of the run.
- load_run: Name of the run to load when resume=True. If -1: will load the last run.
- checkpoint: Saved model checkpoint number. If -1: will load the last checkpoint.
- num_envs: Number of environments to create.
- seed: Random seed.
- max_iterations: Maximum number of training iterations.
-
Create a new folder under the
envs/directory, and then create a configuration file<your_env>_config.pyand an environment file<your_env>_env.pyin the folder. The two files should inheritLeggedRobotCfgandLeggedRobotrespectively. -
Place the URDF, mesh, and MJCF files of the new robot in the
resources/folder.
- Configure the URDF path, PD gain, body name, default_joint_angles, experiment_name, etc., for the new robot in
<your_env>_config.py.
- Register the new robot in
humanoid/envs/__init__.py.
Use Mujoco for sim2sim validation:
python scripts/sim2sim.py --task=x1_dh_stand --load_model /path/to/exported_policies/
We use the Logitech F710 Joystick. When starting play.py and sim2sim.py, press and hold button 4 while rotating the joystick to control the robot to move forward/backward, strafe left/right or rotate.
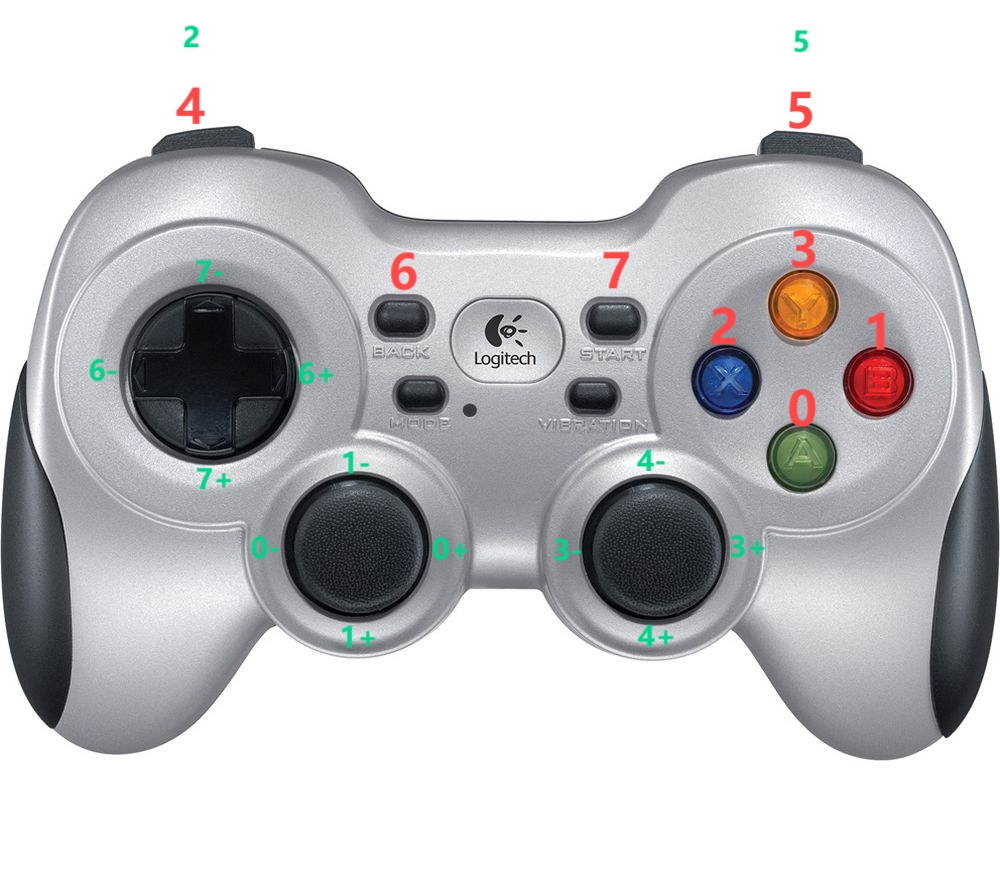
| Button | Command |
|---|---|
| 4 + 1- | Move forward |
| 4 + 1+ | Move backward |
| 4 + 0- | Strafe left |
| 4 + 0+ | Strafe right |
| 4 + 3- | Rotate counterclockwise |
| 4 + 3+ | Rotate clockwise |
.
|— humanoid # Main code directory
| |—algo # Algorithm directory
| |—envs # Environment directory
| |—scripts # Script directory
| |—utilis # Utility and function directory
|— logs # Model directory
|— resources # Resource library
| |— robots # Robot urdf, mjcf, mesh
|— README.md # README document
References
- GitHub - leggedrobotics/legged_gym: Isaac Gym Environments for Legged Robots
- GitHub - leggedrobotics/rsl_rl: Fast and simple implementation of RL algorithms, designed to run fully on GPU.
- GitHub - roboterax/humanoid-gym: Humanoid-Gym: Reinforcement Learning for Humanoid Robot with Zero-Shot Sim2Real Transfer https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.05695