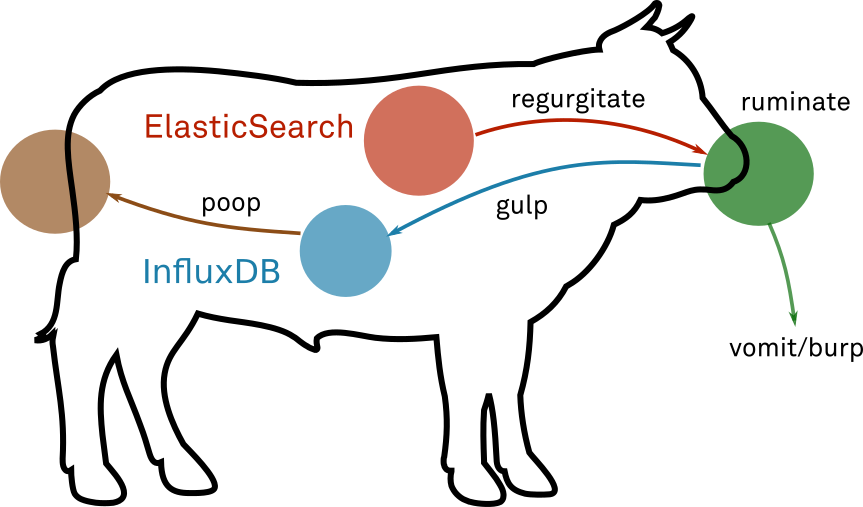
Ruminant queries an ElasticSearch database, processes the results and feeds them
as time series to an Influx database. ETL for a rather specific use case, basically.
Processing data with Ruminant performs a few steps that you should understand:
Find out where to start: First the targeted time series in the Influx
Database is queried in for its last marker timestamp. This timestamp indicates
at what time the last run of Ruminant was performed and is used as starting
point for this run...
Fetch the data from ElasticSearch: A query provided is executed and its result is prepared to be processed. A query can be executed in two manners:
- If no sampler configuration is provided, the query is executed once. This is
kind of execution is a good fit if you can extract timestamps for your time series
from the results of your ElasticSeach query, eg. if the query performs a
date_histogramaggregation for example. - If a query does not contain a
date_histogramaggregation and needs to be executed once per point in your time series, a sampler configuration can be passed. This allows to run the same query multiple times with incrementing timestamps.
This step in known as regurgitate in the ruminant jargon.
Process the results and build time series: ElasticSearch returns the resuls
of the query as JSON data. with simple expressions, Ruminant allows you to
iterate over these results and lets you indicate where in the JSON information
can be found that should be stored with the time series.
This step in known as ruminate in the ruminant jargon.
Persist time series: The set of data points created in the last step is then saved to the Influx database and series specified in your configuration. Also, a new marker timestamp is written that indicates the the new latest point in your series to indicate where to start on the next run.
This step in known as gulp in the ruminant jargon.
Please note: Do not really use this just yet. So far, the project was a quick shot to solve a particular problem. The source itself has neither documentation nor tests to ensure that all the stuff works an expected... Those topics will be addressed soon.
Install via:
go get -u github.com/unprofession-al/ruminant
Run via:
ruminant -h
Feed data from ElasticSearch to InfluxDB
Usage:
ruminant [command]
Available Commands:
burp Test the query and iterator
config Prints the config used to the stdout
gulp Feed data to Infux DB
init Creates the Database if required and sets a start date
poop Dump data from Infux DB to stdout
vomit Throw up to standart output
Flags:
-c, --cfg string config file (default is $HOME/ruminant.yaml) (default "$HOME/ruminant.yaml")
Jump to the examples to find some annotated configuration files.
Main third party components other than the go standard library are: