When you first start off trying to solve a problem, the first solutions you come up with are very complex, and most people stop there. But if you keep going, and live with the problem and peel more layers of the onion off, you can often times arrive at some very elegant and simple solutions. -Steve Jobs
Qascade is a user-friendly way to assign meta-data to your data files. Such meta-data can then be used in your data processing scripts, for example to select data files based on a particular key value (e.g. age > 18). Meta-data can also enable data sharing. In developing Qascade the emphasis has been put on simplicity, user experience and The Rule of Least Power. Using Qascade for meta-data assignment (compared to using XML or JSON) is similar to using Markdown (instead of HTML) for writing notes and Readme files.
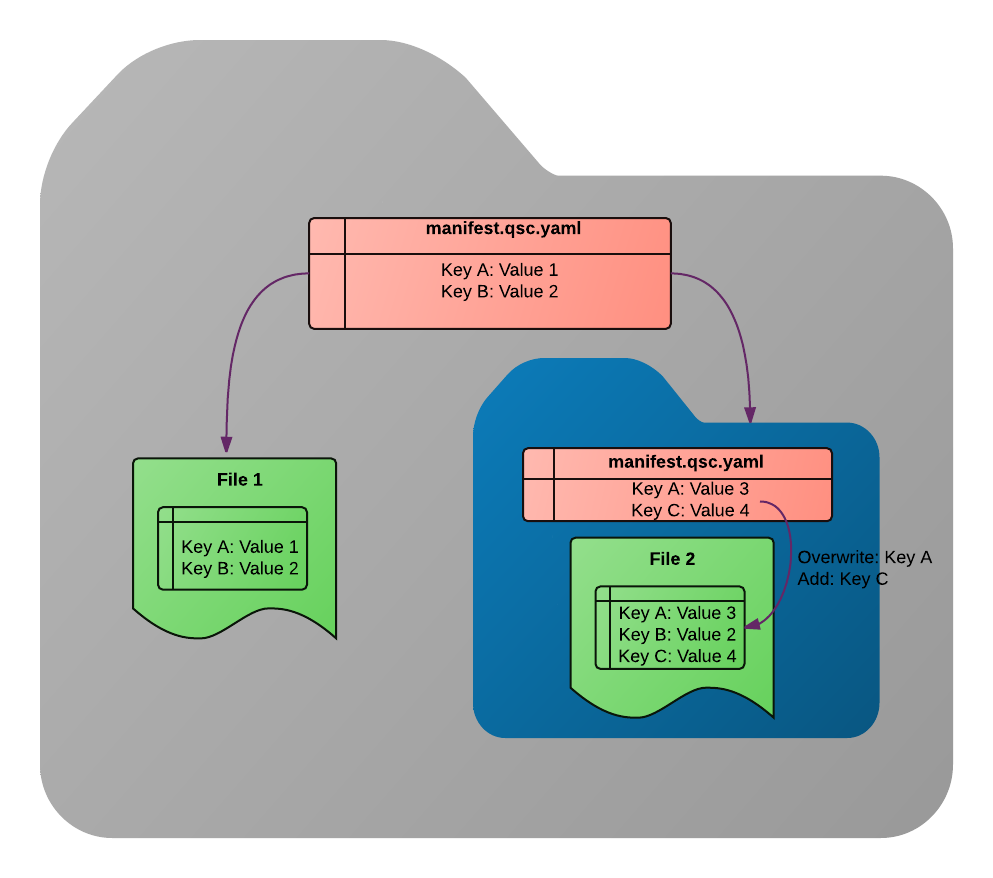
The main idea behind the Qascade is simple: at each level of a file hierarchy, a special manifest.qsc.yaml file (containing YAML-formatted text) is placed which contains (key:value) pairs that are assigned to all files in the folder and its subfolders. Manifest files in subfolders overwrite keys assigned in parent directories:
Special directives are used to assign (key:value) pairs to groups of files, or extract file-specific (key:value) pairs, based on file names or paths. Here is an example Qascade code:
key 1: value 1
(matches *.dat):
key 1: value 2
key 2: value 3
(extract sometitle_S[subjectNumber]_T[taskLabel].h5): direct
It first assigns value 1 to key 1 of all files in the folder and subfolders. It then, for all .dat files, overwrites key 1 values to value 3 and assigns value 3 to key 2. Finally, it extracts values for subjectNumber and taskLabel keys from filenames of files that match sometitle_S[subjectNumber]_T[taskLabel].h5 pattern.
You can learn from the Qascade Reference.
Qascade may be used as the first step of placing files in ESS/BIDS, etc. An ESS driver for Qascade is available in this repository. A guide for placing studies in ESS containers using Qascade is available here.
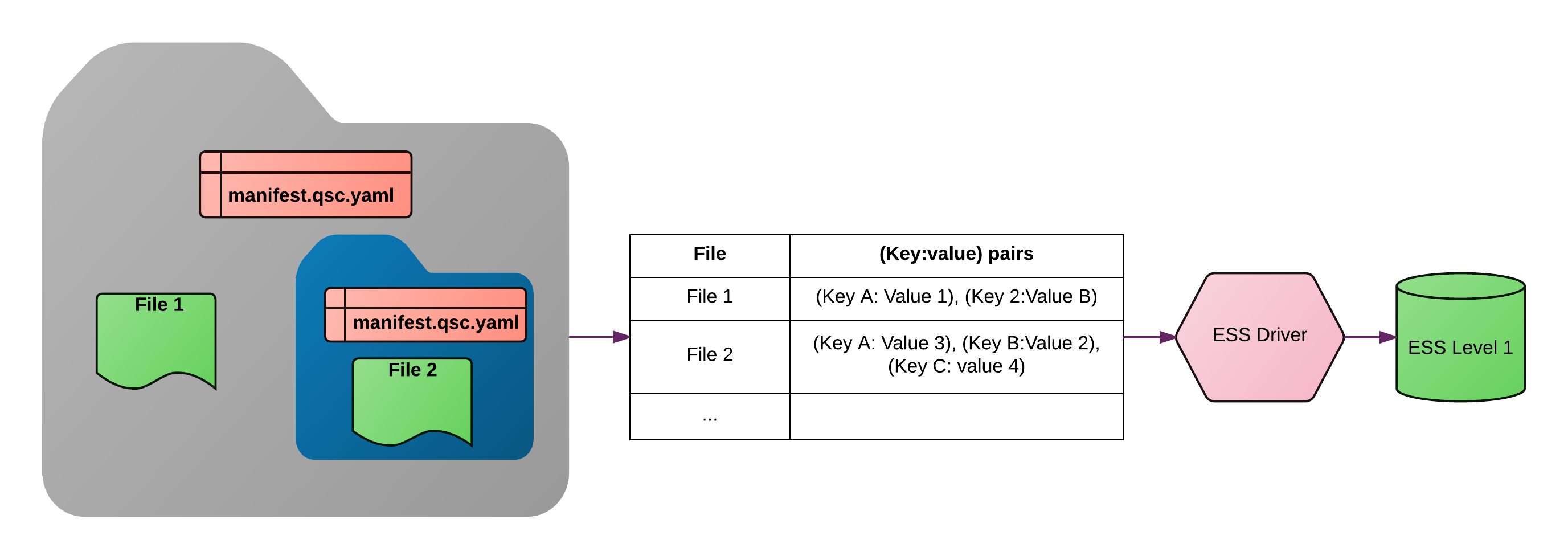
A Qascade parser traverses the folder structure, starting from a root folder, and returns a flat list of files (including their full path), as keys, each associated with an array of (key: value) pairs for the file. The output is then be used by ESS/BIDS/... applications to place the data into domain-specific containers:
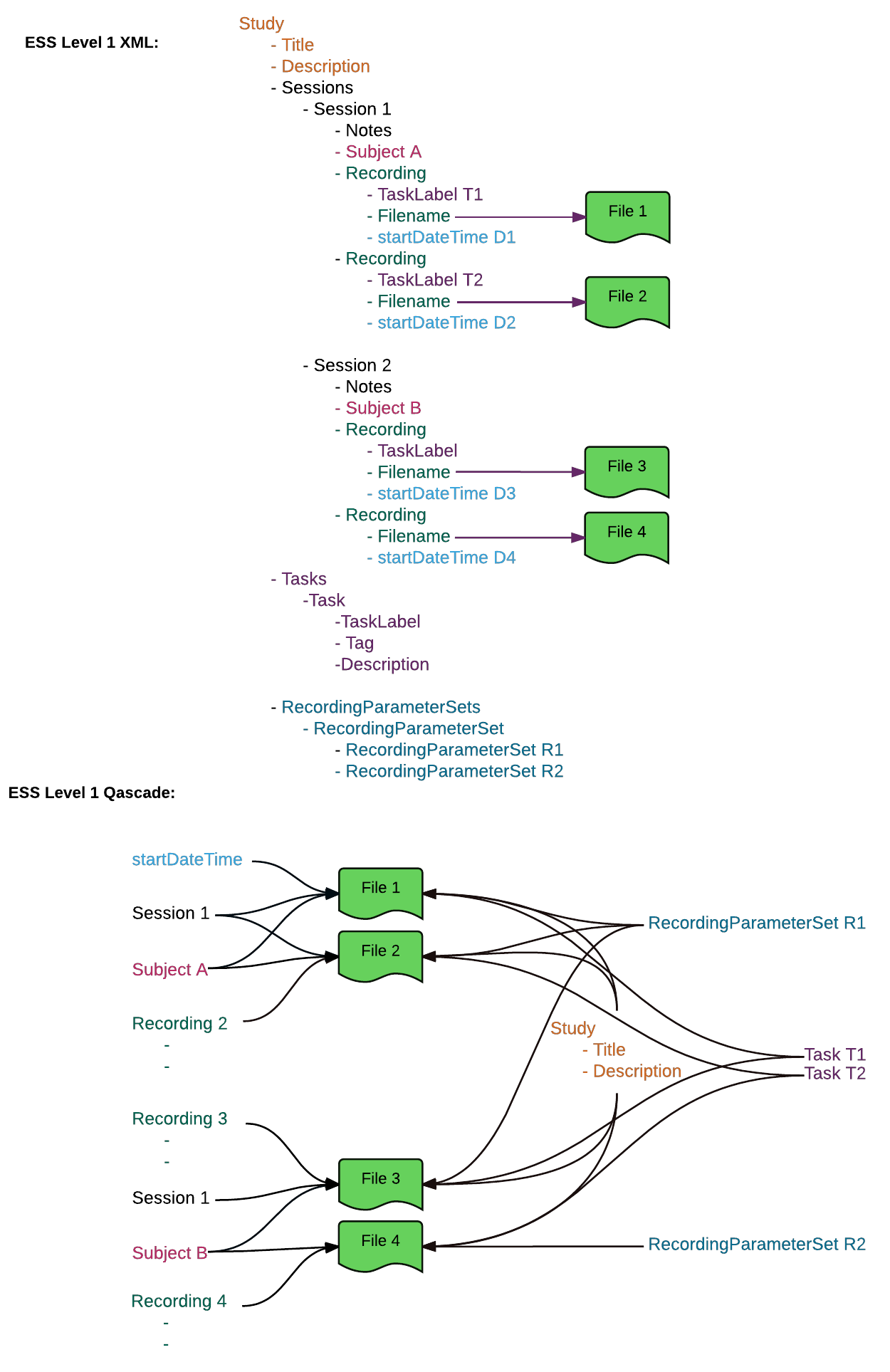
Here is a visual comparison between an ESS Level 1 XML container and ESS Level 1 Qascade:
Qascade development was supported by The Cognition and Neuroergonomics Collaborative Technology Alliance (CaN CTA) program of U.S Army Research Labaratory.