The current use of this repository is to simulate a ROS node for the purposes of developing automated build. See PRSG’s project website for project details
Continuous Integration Etiquette:
-
Request access to to Jenkins notifications if you commit code here.
-
Check out the test suite. (still being developed).
-
Build and run the tests locally before pushing to Github.
-
If you build and run the tests successfully locally, go ahead and push to Github.
-
If you push to Jenkins and get an email failure, please fix it immediately!
-
You should be able to run RViz.
Chrony implements Network Time Protocol, (NTP), in order to keep your system clock accurate. It is designed to work with intermittent network connections.
sudo apt-get install chrony
The script in a later step will expect to use an existing catkin workspace named "catkin_ws". If you haven’t already created this please follow the steps here. These are summarized below for convenience:
$ mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src $ cd ~/catkin_ws/src $ catkin_init_workspace $ cd ~/catkin_ws/ $ catkin_make
Finally add
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
to your ~/.bashrc file.
Add this line to your .bashrc file on the UP and your development machine. Reboot.
export ROS_HOSTNAME=`echo $HOSTNAME`.local
Reboot the machine and test configuration from both ends. If you named your machine 'robot' as advised in Intel documents, you should be able to ping the robot’s processor from your machine. Substitue robot for your machine name if ou elected to use a different name.
$ ping robot.local
To test your laptop/development machine,
$ ssh robot@robot.local $ robot@robot.local's password: robot@robot:~$ ping my_machine.local
This step describes how to set up a pushbutton switch to gracefully shut down the UP. This may help avoid flash corruption.
Install Rpi.GPIO. Try this first:
sudo apt-get install python-rpi.gpio
If that doesn’t work
$ dpkg -L python-rpi.gpio $ wget http://ubilinux.com/ubilinux/pool/main/r/rpi-gpio/python-rpi.gpio_0.6.2%2bubi2-1_amd64.deb $ sudo dpkg -i python-rpi.gpio_0.6.2+ubi2-1_amd64.deb $ sudo groupadd gpio $ sudo adduser robot gpio $ pico /etc/udev/rules.d99-gpio.rules SUBSYSTEM=="bcm2835-gpiomem", KERNEL=="gpiomem", GROUP="gpio", MODE="0660" SUBSYSTEM=="gpio", KERNEL=="gpiochip*", ACTION=="add", PROGRAM="/bin/sh -c 'chown root:gpio /sys/class/gpio/export /sys/class/gpio/une SUBSYSTEM=="gpio", KERNEL=="gpio*", ACTION=="add", PROGRAM="/bin/sh -c 'chown root:gpio /sys%p/active_low /sys%p/direction /sys%p/edge
The file 99-gpio.rules can be found in the doc directory.
Add python /home/robot/catkin_ws/src/robo_magellan/scripts/shutdownSwitch.py & to the UP in /etc/rc.local just before the existing exit 0 line.
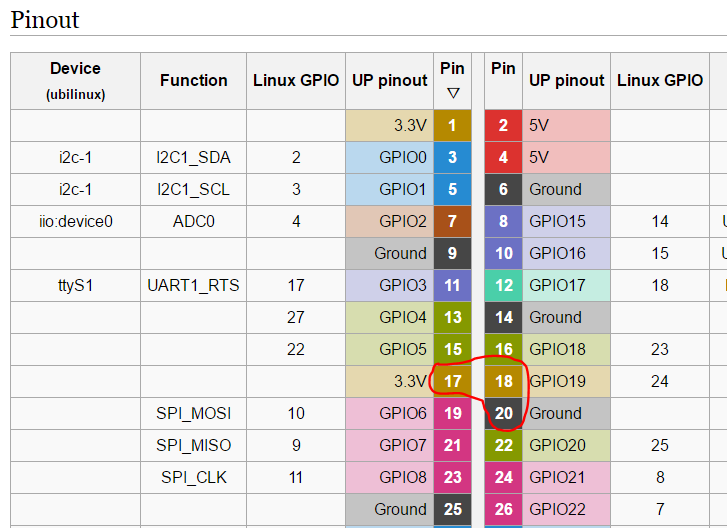
The shutdownSwitch.py script assumes a momentary, normally open switch is connected from UP board pin 18 to ground (pin 20). You may also need an external 10k pullup resistor from pin 18 to 3.3 V (pin 17). A fragment of the UP pinout is included here for clarity.
You will need ROS Kinetic installed on your machine.
Install MAVROS. Just use apt-get.
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-mavros ros-kinetic-mavros-extras
If you haven’t already done so, start by fetching the repository.
cd catkin_ws/src git clone https://github.com/ProgrammingRobotsStudyGroup/robo_magellan.git
If you already have the repository, make sure it’s up to date
cd catkin_ws/src git pull
Then run the installation/update script:
roscd robo_magellan ./victoria.sh