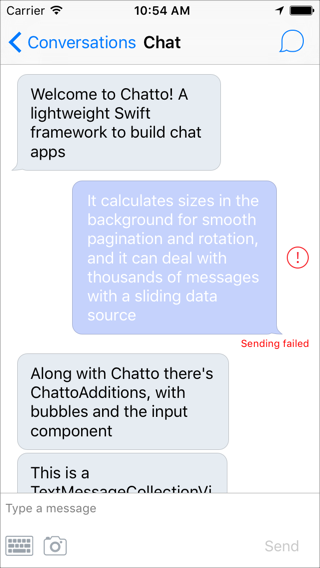
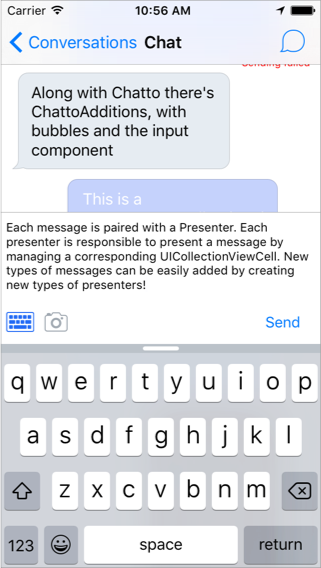
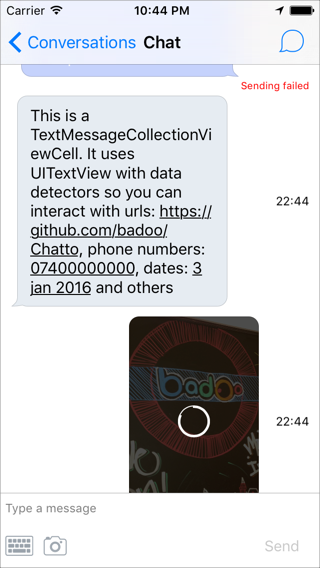
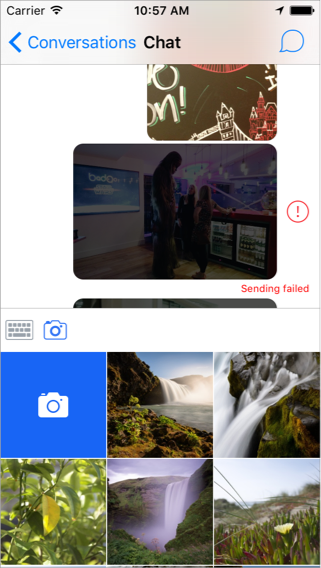
Chatto is a Swift lightweight framework to build chat applications. It's been designed to be extensible and performant. Along with Chatto there is ChattoAdditions, a companion framework which includes cells for messages and an extensible input component. You can find more details about how it was implemented in our blog. See them in action!
- Calculation of collection view changes and layout in background
- Supports pagination in both directions and autoloading
- Message count contention for fast pagination and rotation with thousands of messsages
- Accessory view revealing by swiping from right
- Interactive keyboard dismissal
- Text bubbles
- Photo bubbles
- Extensible input bar
- Subclass ChatViewController
- Override
createChatInputView()to useChattoAdditions.ChatInputBaror provide your own component - Provide a data source with your messages
- Override
createPresenterBuilders(). There will be a presenter for each message that will be responsible for the UI of that message.
override func createPresenterBuilders() -> [ChatItemType: [ChatItemPresenterBuilderProtocol]] {
return [
TextMessageModel.chatItemType: [
TextMessagePresenterBuilder(
viewModelBuilder: TextMessageViewModelDefaultBuilder(),
interactionHandler: TextMessageHandler(baseHandler: self.baseMessageHandler)
)
]
]
}
override func createChatInputView() -> UIView {
let chatInputView = ChatInputBar.loadNib()
self.configureChatInputBar(chatInputView)
self.chatInputPresenter = ChatInputBarPresenter(chatInputView: chatInputView, chatInputItems: self.createChatInputItems())
return chatInputView
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.chatDataSource = self.myDataSource
}The only requirement for your data source items is to conform to the ChatItemProtocol protocol, which basically asks for a unique identifier (uid) and a type. The uid will be used to calculate changes in the collection view and the type to quickly find a presenter builder for it. Your data source must conform to ChatDataSourceProtocol:
public protocol ChatDataSourceProtocol: class {
var hasMoreNext: Bool { get }
var hasMorePrevious: Bool { get }
var chatItems: [ChatItemProtocol] { get }
weak var delegate: ChatDataSourceDelegateProtocol? { get set }
func loadNext(completion: () -> Void)
func loadPrevious(completion: () -> Void)
func adjustNumberOfMessages(preferredMaxCount preferredMaxCount: Int?, focusPosition: Double, completion:(didAdjust: Bool) -> Void) // If you want, implement message count contention for performance, otherwise just call completion(false)
}If you want to handle smooth loading of new pages, or more challenging, smooth rotation with thousands of messages (calculating 10K text message sizes can take ~15s on iPhone 4s) you should opt-in for adjustNumberOfMessages(preferredMaxCount:focusPosition:completion:). See how it's done in ChattoApp!
The presenter is the key entity that enables scalability in Chatto's architecture. Each message will be paired with a presenter who will be responsible for the UI related to that message (cell configuration, calculation of size, user handling,... ). Take a look at TextMessagePresenter, PhotoMessagePresenter in ChattoAdditions and ChatItemPresenterProtocol
public protocol ChatItemPresenterProtocol: class {
static func registerCells(collectionView: UICollectionView)
var canCalculateHeightInBackground: Bool { get } // Default is false
func heightForCell(maximumWidth width: CGFloat, decorationAttributes: ChatItemDecorationAttributesProtocol?) -> CGFloat
func dequeueCell(collectionView collectionView: UICollectionView, indexPath: NSIndexPath) -> UICollectionViewCell
func configureCell(cell: UICollectionViewCell, decorationAttributes: ChatItemDecorationAttributesProtocol?)
func cellWillBeShown(cell: UICollectionViewCell) // optional
func cellWasHidden(cell: UICollectionViewCell) // optional
func shouldShowMenu() -> Bool // optional. Default is false
func canPerformMenuControllerAction(action: Selector) -> Bool // optional. Default is false
func performMenuControllerAction(action: Selector) // optional
}As you may have noticed, there's an interesting decorationAttributes parameter in configureCell(_:decorationAttributes:)
public protocol ChatItemDecorationAttributesProtocol {
var bottomMargin: CGFloat { get }
}Decoration attributes have two different purposes:
- Provide margins for
ChatCollectionViewLayout - Provide context to your presenters so you can further customize your UI (for instance to flag if a bubble should show the tail)
By default, no decorationAttributes will be provided to your presenters, and the margin between messages will be zero. You may opt-in for a message decorator as in ChattoApp
public protocol ChatItemsDecoratorProtocol {
func decorateItems(chatItems: [ChatItemProtocol]) -> [DecoratedChatItem]
}In your decorator you may even create new ChatItems. The decorator in ChattoApp not only provides different margins for the bubbles, but it also inserts new ChatItems that represents sending/failed status. Decoration happens in background so the UI stays responsive while scrolling.
You can return your own input component when overriding createChatInputView() or use ChattoAdditions.ChatInputBar
ChattoAdditions.ChatInputBar is an extensible component on its own. Each input item defines a tabView that serves as the call to action to activate that input item and an inputView with your custom input UI. ChatInputBarPresenter will take a collection of ChatInputItemProtocol and it will configure ChatInputBar to display them.
public protocol ChatInputItemProtocol: AnyObject {
var tabView: UIView { get }
var inputView: UIView? { get }
var presentationMode: ChatInputItemPresentationMode { get }
var showsSendButton: Bool { get }
var selected: Bool { get set }
func handleInput(input: AnyObject)
}-
Make sure
use_frameworks!is added to yourPodfile. -
Include the following in your
Podfile:pod 'Chatto', '= 1.0.0' pod 'ChattoAdditions', '= 1.0.0' # if you want to use the cells or the input component
If you like to live on the bleeding edge, you can use the master branch with:
pod 'Chatto', :git => 'https://github.com/badoo/Chatto' pod 'ChattoAdditions', :git => 'https://github.com/badoo/Chatto'
3. Run pod install
If you’re using Carthage, simply add Chatto to your Cartfile:
github "badoo/Chatto"
- Clone, add as a submodule or download.
- Drag and drop
Chattoand/orChattoAdditionsproject to your workspace - Add
Chattoand/orChattoAdditionsto Embedded binaries
Source code is distributed under MIT license.
##Blog Read more on our tech blog or explore our other open source projects