Seurat is a scene simplification technology designed to process very complex 3D scenes into a representation that renders efficiently on mobile 6DoF VR systems.
This document covers how to import Seurat meshes into Unity. To learn more about the Seurat pipeline, visit the main Seurat GitHub page.
This document is organized into two sections. The first describes the steps to load a mesh produced by Seurat into Unity. The second provides detailed diagnostic steps to examine if the imported Seurat mesh shows artifacts, gaps, or cracks in various places, typically along the edges of the mesh.
The document assumes some familiarity with the Unity Editor, and is written against version 5.6.*.
The instructions in this section assume the following file layout:
c:\Unity_Projects\SeuratImport contains a blank Unity project.
c:\Seurat_Output contains a set of files produced by Seurat: in particular
seurat.obj, seurat.png. Follow these steps to import the Seurat output into
Unity:
- Import Prerequisites
- Open the SeuratImport project in Unity.
- Import the Seurat Unity capture package into the project with Assets | Import Package | Custom Package.
- Import the Seurat mesh and texture as an Asset
- Use Asset | Import New Asset to copy seurat.obj and seurat.png into the Unity project’s Assets folder.
- Browse the Assets folder in Project window.
- Locate the Seurat output model
seurat.objin the Assets folder.
- Add the Seurat mesh to the Scene.
-
Drag and drop the
seurat.objmodel from the Asset folder into the Scene window (or Hierarchy window, as appropriate).Note: Unity may split the mesh into several parts to fit under vertex count limits.
-
Unity should then display a solid-shaded version of the Seurat mesh.
-
- Apply the Seurat shader to the Seurat mesh.
- Locate the new node, seurat instancing the seurat.obj in the Hierarchy
window, and expand the hierarchy it contains until the leaf nodes are
visible. The hierarchy should contain something like the following nodes,
and the leaf nodes will have Mesh Render components attached:
- seurat
- default
- default_MeshPart0
- default_MeshPart1
- default_MeshPart2
- default
- seurat
- Select the first leaf node a Mesh Render component, default_MeshPart0.
- Locate the Mesh Render component in the Inspector panel.
- Apply the Seurat shader to the geometry; click the Shaders popup at the bottom of the panel, and navigate the menu to the shader GoogleVR | Softserve | AlphaBlended, and click that menu option to apply the alpha blended material.
- Locate the new node, seurat instancing the seurat.obj in the Hierarchy
window, and expand the hierarchy it contains until the leaf nodes are
visible. The hierarchy should contain something like the following nodes,
and the leaf nodes will have Mesh Render components attached:
- Apply the Seurat texture atlas to the mesh
- Locate the Seurat output texture atlas seurat.png in the Assets folder.
- Apply the texture atlas to the chunks of the Seurat mesh: drag and drop seurat.png onto each of the leaf nodes, here named default_MeshPart*.
- Configure Texture Atlas Settings
- Select the seurat.png texture in the Assets browser.
- Locate the Inspector panel for the texture.
- Expand the Advanced rollup.
- Disable the option Generate Mip Maps.
- Change Wrap Mode to Clamp.
- Locate the build platform subpanel.
- Enable Override for PC, Mac, & Linux Standalone.
- Change Max Size to a resolution greater-than or equal-to the dimensions of the seurat.png. Typically this will be 4096, but depends on Seurat processing settings. Note: Seurat requires that Unity not resize the texture!
- Click the Apply button at the bottom of the panel.
- Unity will reprocess the texture, and should now display the Seurat mesh correctly.
If the Seurat output has artifacts, or does not look correct, please continue on to the next section. The section provides detailed instructions on configuring both the imported assets, Unity project settings to correctly render Seurat meshes.
This section illustrates what crack artifacts may appear, and lists many Unity
settings that can trigger these artifacts.

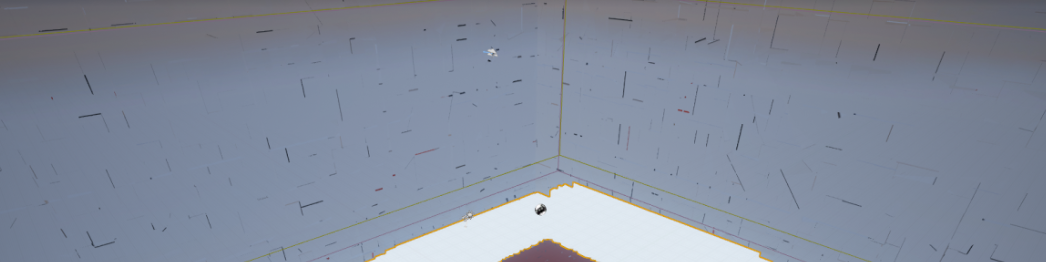
The easiest way to determine the cause of crack or gap artifacts in Seurat output is to set the camera background color to something with great contrast to the scene (e.g. bright red) and see if there are holes in the mesh generated by Seurat.
- If you see holes in the mesh, you should try to rebake with higher quality settings.
- If you do not see holes, adjust texture and shader settings.
- Bilinear Filtering
- For premultiplied alpha, uncheck Alpha is Transparency. Otherwise, Unity will inpaint the transparent areas of the texture (this process can be lengthy) and will show artifacts in areas that are supposed to be completely transparent.
- NO mip maps
- Low or No anisotropic filtering ~ 1-2 in Unity, any higher may cause cracks
- Do not autoresize to power of 2
- Wrap mode: clamp
- A Unity project setting can affect the texture resolution during the Unity application build. Check that the Texture Quality option under Edit | Project Settings | Quality is set to Full Res.
- Make sure mesh compression is turned off for the UV0 channel in Project Settings | Player | Android | Vertex Compression
If you are using MSAA, you may notice edge artifacts. Centroid interpolation
will fix edge sampling errors caused by MSAA. For more information, see Fabien
Giesen’s post. In Unity, this can be done by appending _centroid to the
TEXCOORD# interpolator semantic like so:
struct VertexToFragment {
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0_centroid;
}Fragment shader texture coordinate precision is important. Use highp or
float precision for texture coordinate variables rather than lowp modifier
or the HLSL min16 prefix.
IMPORTANT: Centroid requires Open GL ES 3.0, and is performance intensive. Only use centroid interpolation if you are using MSAA, and absolutely need it. Currently the _centroid modifier is implicated in GPU driver issues on Pixel devices. Workarounds / bug fixes are in progress.
Unless you absolutely need depth write (e.g. you are doing something fancy, like casting dynamic shadows off Seurat geometry) - you should prefer Alpha Blending.
- UV0 set to _centroid interpolation OR disable MSAA
- Cull Off
- ZWrite Off
- ZTest LEqual
- Queue: Transparent
- Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
- UV0 set to _centroid interpolation OR disable MSAA
- Cull Off
- ZWrite On
- ZTest LEqual
- Queue: Transparent
- Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
- Alpha-to-coverage
- Unity: AlphaToMask On
Some Seurat scenes can have gaps (cracks, you could say) of varying size against the background. You should let the team know if you encounter these. Still, colors from background color can bleed through and appear as cracks.
Several things in Unity can generate a background color:
- Geometry in the scene drawn before Seurat’s mesh. Try toggling it on and off to see if a skybox mesh is generating cracks, for example.
- The Skybox Material option of the Scene tab of Lighting inspector panel (Window | Lighting | Settings), can control the background color. To evaluate if this feature is contributing to the problem, try selecting a black material or a bright red material to see if this changes any of the cracks.
- In the Camera inspector panel of the node containing the LDI Headbox for the capture, Clear Flags and Background Color control buffer color initialization for the capture.
If none of the above fixes the issue, or you see holes in the mesh - try rebaking with higher quality capture settings.
DISCLAIMER: This is not an officially supported Google product.