Blog developed in django with the same appearance of a research paper written in Latex.
- CSS and Latex fonts integrated
- Posts are presented in two columns like a paper
- Formulas can be added with Latex notation
- Share in social networks
- RSS feed
- Post search
- Blog optimized for SEO
- Comments with disqus
- Easy writing with Ckeditor
- (Optional) Web optimization with CloudFlare
- (Optional) Instalation of free SSL certificate
Example of sciblog: http://miguelgfierro.com
We need to install several libraries:
$ apt-get install -y python-dev libpq-dev python-pip git apache2 libapache2-mod-wsgi
$ pip install django
NOTE: django version must be 1.7 or 1.8.
The first step is to generate the database. In the projects folder:
$ python manage.py syncdb
Django will ask you to create a superuser. You have to put the username and password. The email is optional.
This will generate a file called db.sqlite3 which is the database where all the blog content is stored.
After that you have to make what is called a migration, to create the tables in your database. To do that:
$ python manage.py makemigrations
$ python manage.py migrate
In another terminal you have to run django development server:
$ python manage.py runserver
In a browser put the link: http://localhost:8000/admin/
The panel will ask you to put username and password. Once you are in django dashboard you can start to add content to your blog.
When you are in localhost you have to set DEBUG = True in sciblog/settings.py. You can set it to False but you won't see the images the user uploaded through the admin dashboard. In production this is handled by apache.
To work with disqus comments you have to get your DISQUS_API_KEY and DISQUS_WEBSITE_SHORTNAME. They can be obtained https://disqus.com/api/applications/
First make sure that you have installed git, apache2 and libapache2-mod-wsgi as explained before.
$ cd /var/www
$ git clone https://github.com/hoaphumanoid/sciblog.git
$ cd sciblog
$ python manage.py syncdb
$ python manage.py makemigrations
$ python manage.py migrate
Set the correct permissions:
$ chown www-data:www-data /var/www/sciblog
$ chown www-data:www-data /var/www/sciblog/db.sqlite3
$ chown www-data:www-data /var/www/sciblog/img
Configure apache (in sciblog.conf change miguelgfierro.com for your url):
$ cp sciblog.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/
$ a2ensite sciblog.conf
$ a2enmod rewrite
$ a2enmod expires
$ service apache2 restart
Press add in Post to add your first post. You can add different sections, images and formulas. If you use a formula please select the flag Post with Latex formula. This will load the js necessary to render the Latex code. If the flag is not activated then the js is not added to the template (we don't want extra page load if we are not using formulas, right?).
You will see that your blog is working properly going to the url: http://localhost:8000 (in production you'll have to add something like http://miguelgfierro.com)
Go to the admin console and add your first flat page. A flat page is a static html code.
In Flat pages press add. In url put /about/ (don't forget / in both sides). In title put your name, in sites put your site and in content put whatever you want.
When you are in production you have to set DEBUG = False in sciblog/settings.py.
Also the first time you enter in your admin console (http://miguelgfierro.com/admin/) you have to go to sites and EDIT the default site, which is example.com. Change it for the name of your site without http:// (my case would be miguelgfierro.com).
This will set the first entry in the database to your site, which is related to the variable SITE_ID = 1 in sciblog/settings.py. You can see the number of the site in http://miguelgfierro.com/admin/sites/site/1/. If you add another site, then it will have a different number in the database, so for everything to work you have to change the variable SITE_ID. In my experience it is better if you don't touch anything :-)
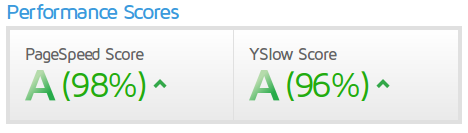
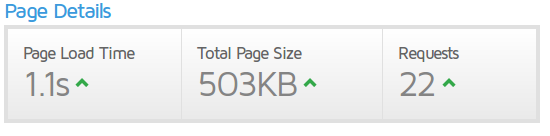
You can use Cloudflare to speed up your page and protect it. You just need to change the DNS. This is how my web looks like in terms of speed using gtmetrix:
You can install a free SSL certificate with Let's Encript. Google prioritizes pages with SSL security, so https has became a key element for SEO. The first step is to set to True the flag HTTPS in settings.py.
The basic installation in an apache server is very straightforward, as it is explained here. In the file sciblog.conf you have the configuration to activate the SSL. Furthermore, it allows to redirect http://example.com, https://example.com, http://www.example.com to https://example.com.
$ git clone https://github.com/letsencrypt/letsencrypt
$ cd letsencrypt
$ ./letsencrypt-auto --help
$ ./letsencrypt-auto --apache
$ a2enmod ssl
$ service apache2 restart
NOTE: if you decide to set the SSL certificate along with Cloudflare, it is better to pause Cloudflare while installing the SSL certificate to check that it is working correctly in your server. Later, you can resume CloudFlare and go to Crypto and set SSL to full strict.
If you want to thank me, please do it. You can write a poem emphasizing my wonderful qualities or get a tattoo with my amazing face (here you will find my face). I also accept cash. You can send an email to my personal assistant hoaphumanoid@gmail.com.