TBD
I used dataset which i made by myself, using site av.by for extract and load image. You can also download entire dataset. Dataset contain about 400.000 unprocessed image. Also, if you want to download processed dataset, with most popular brand that contain about 250.000, you can download it too.
Original dataset contain folder with brand and modelname, like:
│
└───Audi
| └───A4
│ │ | 47623453.jpg
│ │ | 43244243.jpg
│ | |...
| |
| └───A6
| | | 34525252.jpg
| | | 42455252.jpg
| | |...
| |
| |...
|
└───BMW
| └───X5
| | | 23425253.jpg
| │ | 76543523.jpg
| │ |...
| |
| |...
|
|...
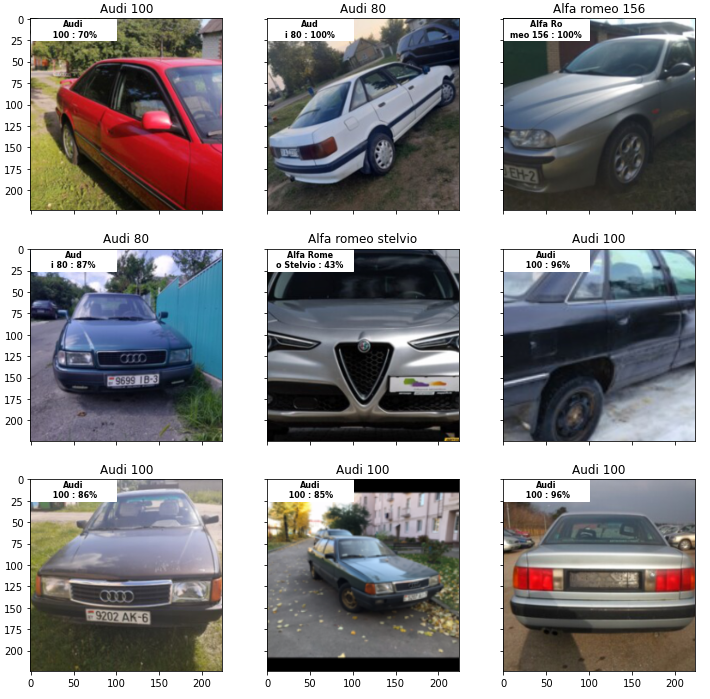
Three sample images are shown below.
While checking through the data, i observed that the dataset contained many unwanted images, e.g., pictures of wing mirrors, door handles, GPS panels, or lights.
Examples of unwanted images can be seen below.
There are multiple possible approaches to filter non-car images out of the dataset:
- Process images manually
- Train another model to classify car/no-car
- Use a pretrained model
I decided to use a pretrained model since it is the most direct one, easy and outstanding pre trained models are easily available. I choose MOBILENET V2 in pytorch framework with the pretrained "imagenet" weights.
In a first step, i figure out the indices and classnames of the imagenet labels corresponding to car images.
CAR_IDX = [656, 627, 817, 511, 468, 751, 705, 757, 717, 734, 654, 675, 864, 609, 436]Next i load pretrained model. Then i load images and preprocess them.
def process_img(filename: str):
input_image = Image.open(filename)
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
input_tensor = preprocess(input_image)
input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
return input_batchAfter prediction i filter unwanted image by using probability of prediction and threshold value.
def is_car_acc_prob(predictions: torch.Tensor, thresh: float):
prob = np.array(torch.nn.functional.softmax(predictions), dtype=float)
car_probs = prob[:, CAR_IDX]
car_probs_acc = car_probs.sum(axis=1)
return car_probs_acc > threshWhile tuning the prefiltering procedure, i tried different threshold value and finally came to the conclusion that optimal value of threshold is beetwen 0.35-0.5. In this range, most unnecessary photos such as the car interior are removed and we do not lose too many car images which are necessary for us. I decide to set a threshold value=0,4. Also in the this process and observed the following :
- Many of the car images model classified as “beach wagons”. i thus decided to also consider the “beach wagon” index class in imagenet as one of the CAR_IDX.
- Images showing the front of a car are often assigned a high probability of “grille”, which is the grating at the front of a car used for cooling, This assignment is correct but a lot of images with grating at the front of a car represent an open hood of the car and are not very useful for further training of the model.
Also after filtering the images i left pictures only of those car models in which there were enough pictures for training. Basically, these were quite popular and well-known car models.
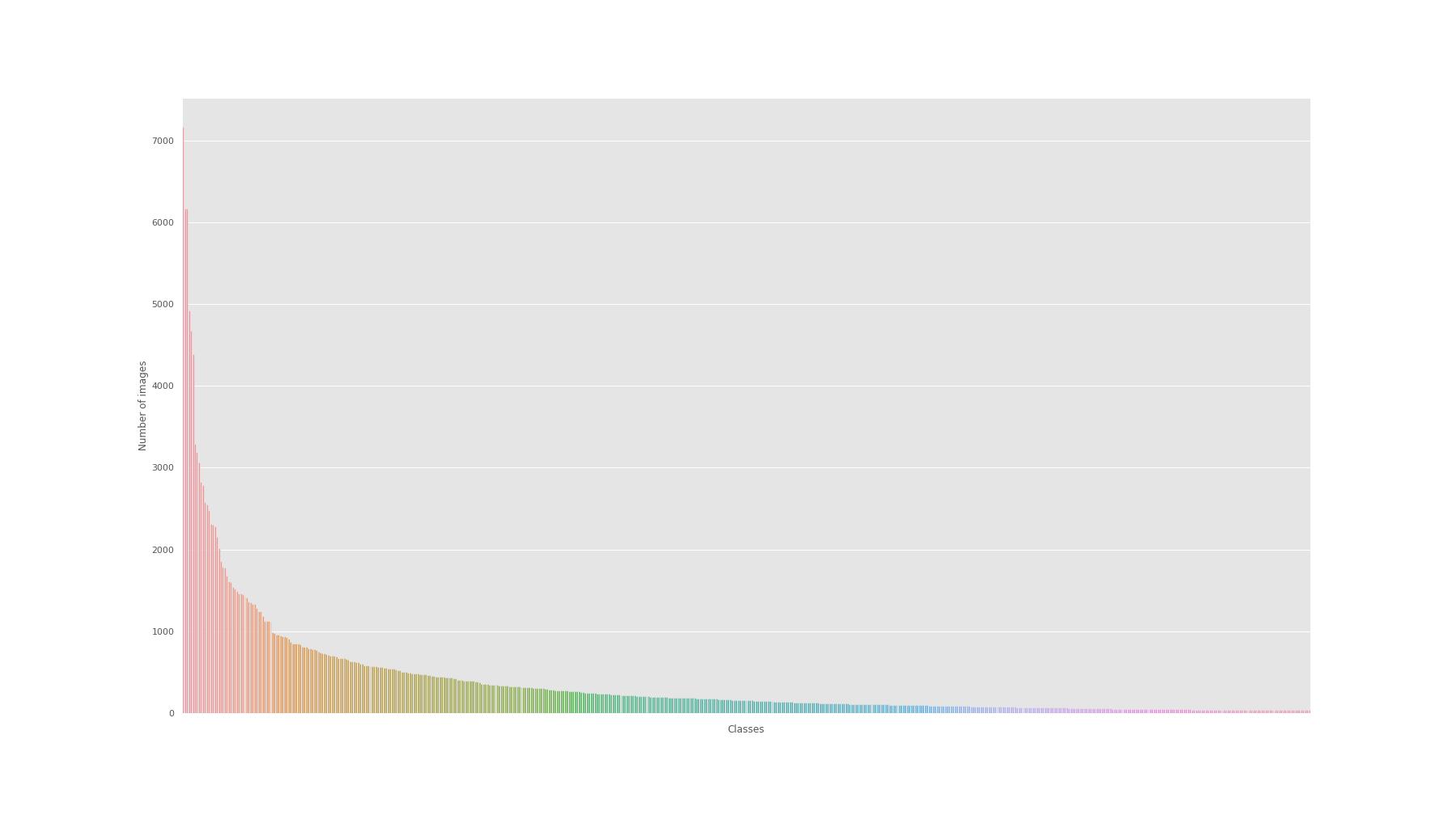
The prefiltered dataset contains images from 603 car models. Dataset containing about 220.000 labeled images. The class occurrences are distributed as follows:
The number of images per class (car model) ranges from 35 to slightly below 7000. We can see that the dataset is very imbalanced. In the picture you can see that several popular models have a very large number of images(~2000-7000), but on average, one car model has about 200 images. It is essential to keep this in mind when training and evaluating the model.
For my baseline i choose pre-training EfficientNet. The architecture of the model you can see this. For training model i use Google Colab with free GPU and conducted training in several stages because of free limits in Colab. After import model i change input classes and create train function. For th loss i used CrossEntropyLoss, for optimizer i use SGD with lr=0,001 and momentum=0,9.
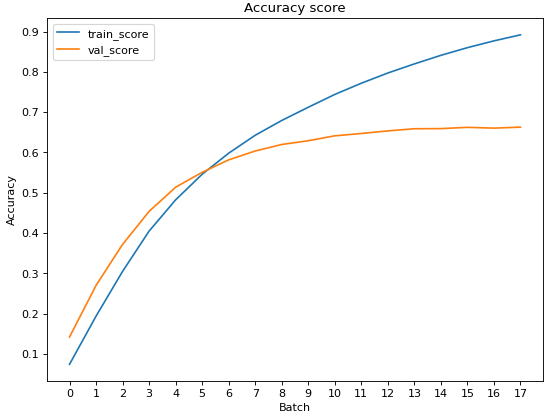
For metric classification i used f1-score. The mean of 100 sampling result is 0,8. I make a plot of train and validation accuracy after completing the training.
Also i make a beautiful visualization of confidence of our neural network.
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=3,figsize=(12, 12), \
sharey=True, sharex=True)
for fig_x in ax.flatten():
random_characters = int(np.random.uniform(0,1000))
im_val, label = val_dataset[random_characters]
img_label = " ".join(map(lambda x: x.capitalize(),\
val_dataset.label_encoder.inverse_transform([label])[0].split('_')))
imshow(im_val.data.cpu(), \
title=img_label,plt_ax=fig_x)
actual_text = "Actual : {}".format(img_label)
fig_x.add_patch(patches.Rectangle((0, 0),100,25,color='white'))
font0 = FontProperties(size='x-large')
font = font0.copy()
prob_pred = predict_one_sample(model_ft, im_val.unsqueeze(0))
predicted_proba = np.max(prob_pred)*100
y_pred = np.argmax(prob_pred)
predicted_label = label_encoder.classes_[y_pred]
predicted_label = predicted_label[:len(predicted_label)//2] + '\n' + predicted_label[len(predicted_label)//2:]
predicted_text = "{} : {:.0f}%".format(predicted_label,predicted_proba)
fig_x.text(50, 1, predicted_text , horizontalalignment='center', fontproperties=font,
verticalalignment='top',fontsize=8, color='black',fontweight='bold')Because of the dataset is not balanced i will try to research different trick such as:
- Use Focal Loss instead of CrossEntropyLoss
- Make undersampling or oversampling
- Use data augmentation
- Use learning rate scheduler
- Use re-weighting method
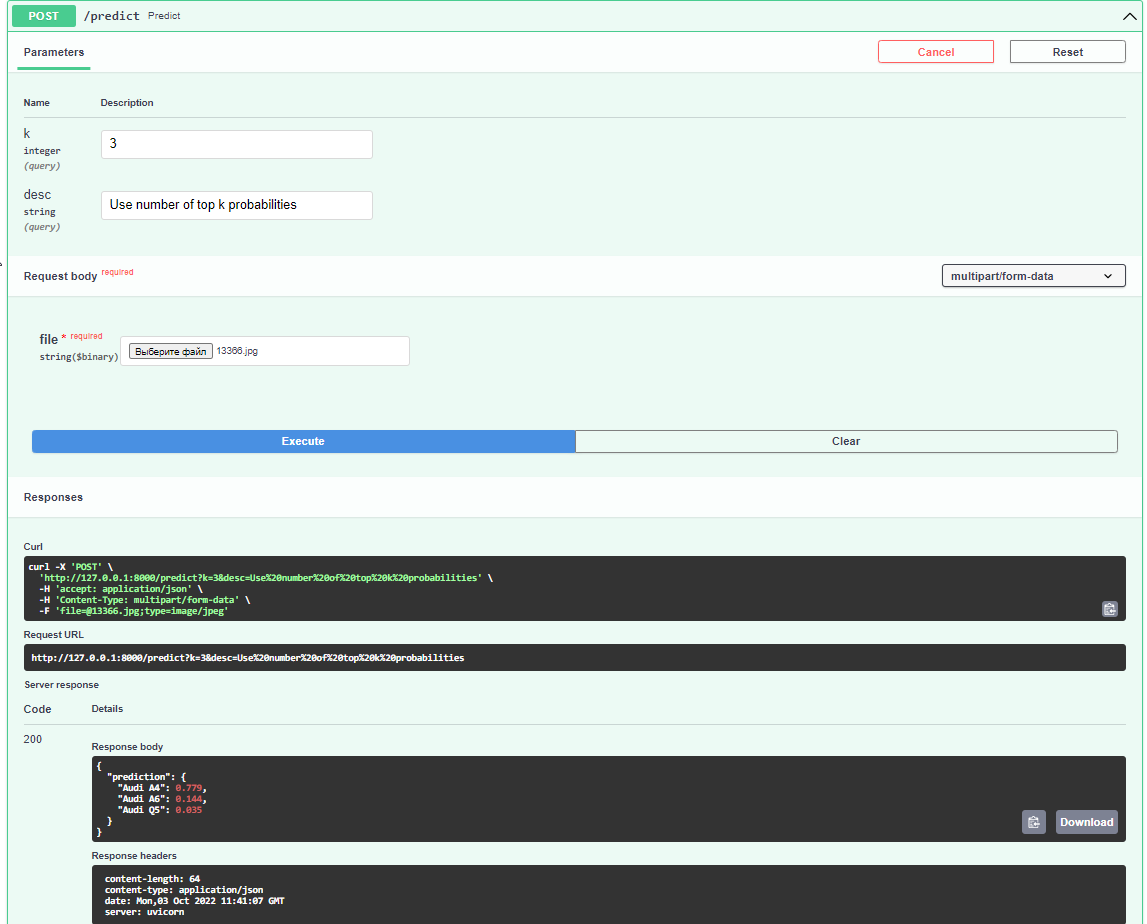
FastAPI is a Python web framework that makes it easy for developers to build fast (high-performance), production-ready REST APIs. If you’re a data scientist who works mostly with Python, FastAPI is an excellent tool for deploying your models as REST APIs. FastAPI have some advantages instead of Flask, such as FastAPI is based on an faster and more modern interface ASGI, FastAPI uses Pydantic, FastAPI supports OpenAPI and allows you to output API specs automatically
For a baseline of create post method which process and predict uploaded image.