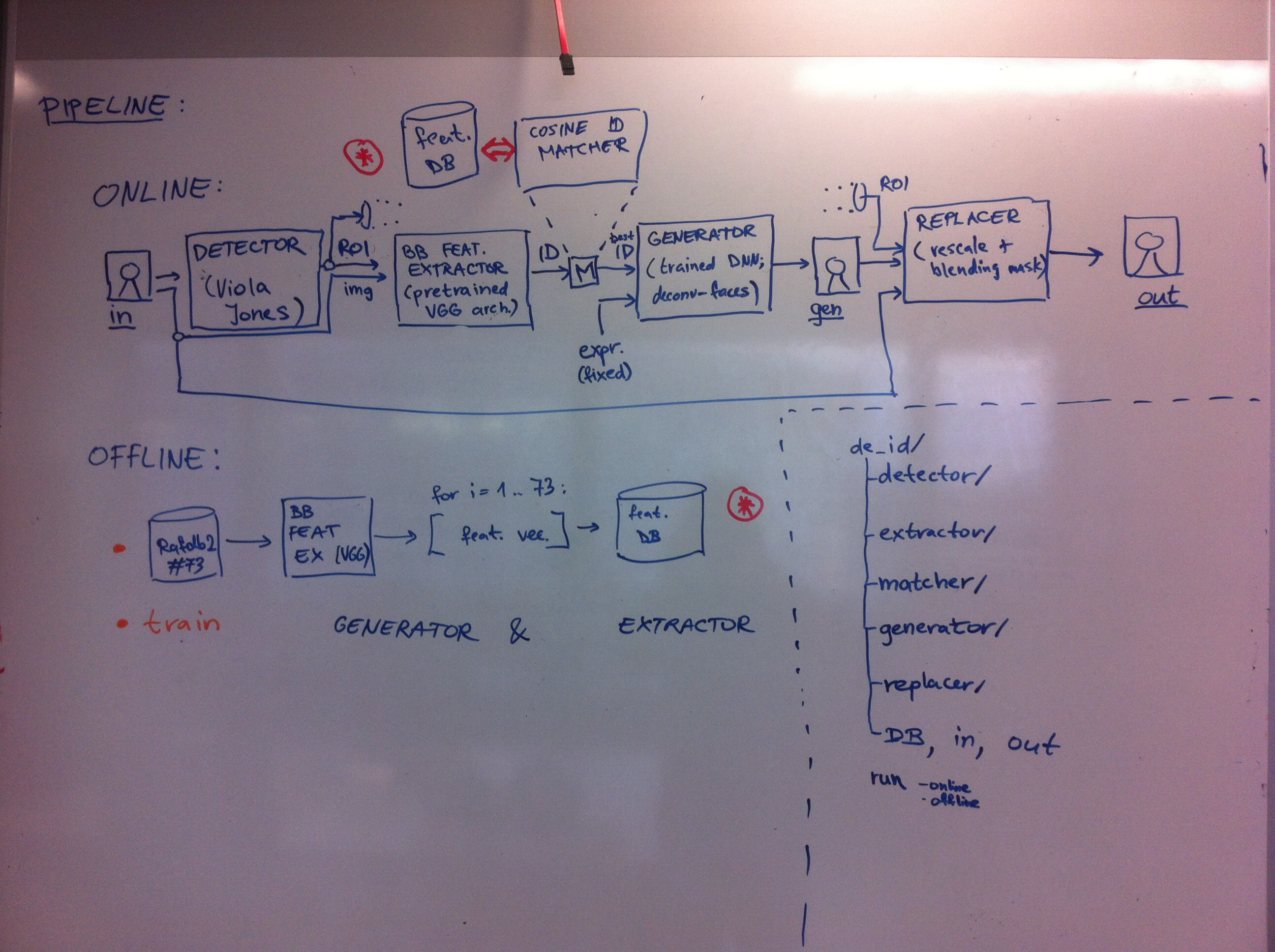
This is the original implementation of deidentification pipeline, described in the paper:
Face deidentification with generative deep neural networks by B. Meden, R. C. Malli, S. Fabijan, H. K. Ekenel, V. Struc, P. Peer, published in IET Signal Processing (2017)
This README describes the contents of the repository, how to set-up this project, lists all the requirements and relevant resources.
This repository contains the original implementation of face de-identification pipeline (as cited above). There are two modes of operation: OFFLINE (used to train, ran only once, to obtain models for ONLINE processing pipeline).
OFFLINE processing includes training of Generator and (possibly new) Extractor + converting the image DB to feature vector DB using the Extractor module. ONLINE processing includes whole pipeline as shown on pipeline schematic down below.
The pipeline consists of 5 independent modules, which are integrated together into unified pipeline:
- Detector
- DONE:included demo was obtained here (Viola Jones detector demo, http://docs.opencv.org/3.1.0/d7/d8b/tutorial_py_face_detection.html)
- DONE: pipeline integration
- DONE: added SSD detector (however currently Viola Jones gives more aesthetically pleasing results)
- Extractor
- DONE: converted version from caffe to keras was provided by @rcmalli (https://github.com/rcmalli/keras-vggface)
- DONE: use a pretrained VGG Face model for feature extraction (http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/software/vgg_face/)
- Matcher
- DONE (returned ID was not properly calculated yet - it was using only image index):
- DONE: implement cosine metric & matching (comparing vectors from feature DB and input feature vector, return ID of best match in feature DB)
- TODO: perform additional tests for matching procedure
- Generator
- (included code was obtained here: original github repository)
- DONE: demo works
- DONE: improve the quality of generated images
- DONE: pipeline integration
- TODO: try to improve GNN model with new model using newer models (many options here: end-to-end autoencoders, GANs, etc.)
- Replacer
- DONE: version 1 used gauss mask weighting to merge generated image and input image (with visible artefacts)
- DONE: version 2 implements inplace image blending to replace detected ROI from input image with rescaled generated image.
- TODO: improve replacement of SSD detections
- TODO: address context of input images
Other repository directories include:
- in - directory for input data (images, videos)
- out - directory for output data (processed images, videos)
- DB - directory with databases (required to run the pipeline)
Install Generator & Extractor dependencies first, since this was the first tested and configured module which works (the rest of the modules would have to adapt to these dependencies). Development OS is Ubuntu 16.04. / Linux Mint 18.1. Pipeline also works on Windows 10 with properly installed requirements and compatible GPU.
Install Anaconda with Python>=3.5: https://www.continuum.io/downloads.
Create a conda environment:
#!bash
# create environment
conda create -n python35 python=3.5 anaconda
# activate environment
source activate python35
# Install numpy, scipy, tensorflow, keras, tqdm ...
pip install numpy, scipy, tensorflow-gpu, keras, tqdm, h5py
#!python
# When in python try to import all dependencies to see if everything works
import numpy, scipy, tqdm
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
#!bash
# Install opencv3 to Anaconda
conda install -c menpo opencv3 -n python35
# Install dlib v 18.18 (for detecting facial landmarks)
conda install -c menpo dlib=18.18 -n python35
Dependencies are also listed in requirements.txt (but this was generated from independently from this codebase, so all packages might not be required).
Authors: Blaz Meden, Refik Can Mallı, Sebastjan Fabijan, Hazım Kemal Ekenel, Vitomir Štruc and Peter Peer Code maintained by: Blaz Meden Contributor: Refik Can Mallı
@ARTICLE{Meden2017_FDGNN,
author = {Blaz Meden and Refik Can Mallı and Sebastjan Fabijan and Hazım Kemal Ekenel and Vitomir Štruc and Peter Peer},
keywords = {formal anonymity models;GNN;image blurring;artificial surrogate faces;automated recognition tools;generative deep neural networks;novel face deidentification pipeline;},
ISSN = {1751-9675},
language = {English},
abstract = {Face deidentification is an active topic amongst privacy and security researchers. Early deidentification methods relying on image blurring or pixelisation have been replaced in recent years with techniques based on formal anonymity models that provide privacy guaranties and retain certain characteristics of the data even after deidentification. The latter aspect is important, as it allows the deidentified data to be used in applications for which identity information is irrelevant. In this work, the authors present a novel face deidentification pipeline, which ensures anonymity by synthesising artificial surrogate faces using generative neural networks (GNNs). The generated faces are used to deidentify subjects in images or videos, while preserving non-identity-related aspects of the data and consequently enabling data utilisation. Since generative networks are highly adaptive and can utilise diverse parameters (pertaining to the appearance of the generated output in terms of facial expressions, gender, race etc.), they represent a natural choice for the problem of face deidentification. To demonstrate the feasibility of the authors’ approach, they perform experiments using automated recognition tools and human annotators. Their results show that the recognition performance on deidentified images is close to chance, suggesting that the deidentification process based on GNNs is effective.},
title = {Face deidentification with generative deep neural networks},
journal = {IET Signal Processing},
year = {2017},
month = {May},
publisher ={Institution of Engineering and Technology},
copyright = {© The Institution of Engineering and Technology},
url = {http://digital-library.theiet.org/content/journals/10.1049/iet-spr.2017.0049}
}
I would like to thank @rcmalli for his generous help during the development of this work and for providing pretrained VGGFace implementation for Keras framework (https://github.com/rcmalli/keras-vggface).