The Deepfence Runtime Threat Mapper is a subset of the Deepfence cloud native workload protection platform, released as a community edition. This community edition empowers the users with following features:
-
Visualization: Visualize kubernetes clusters, virtual machines, containers and images, running processes, and network connections in near real time.
-
Runtime Vulnerability Management: Perform vulnerability scans on running containers & hosts as well as container images.
-
Container Registry Scanning: Check for vulnerabilities in images stored on AWS ECR, Azure Container Registry, Google Container Registry, Docker Hub, Docker Self-Hosted Private Registry, Quay, Harbor, Gitlab and JFrog registries.
-
CI/CD Scanning: Scan images as part of existing CI/CD Pipelines like CircleCI, Jenkins & GitLab.
-
Integrations with SIEM, Notification Channels & Ticketing: Ready to use integrations with Slack, PagerDuty, HTTP endpoint, Jira, Splunk, ELK, Sumo Logic and Amazon S3.
https://deepfence.io/community-demo-form/
- Architecture
- Features
- Getting Started
- How do I use Deepfence?
- Security
- Support
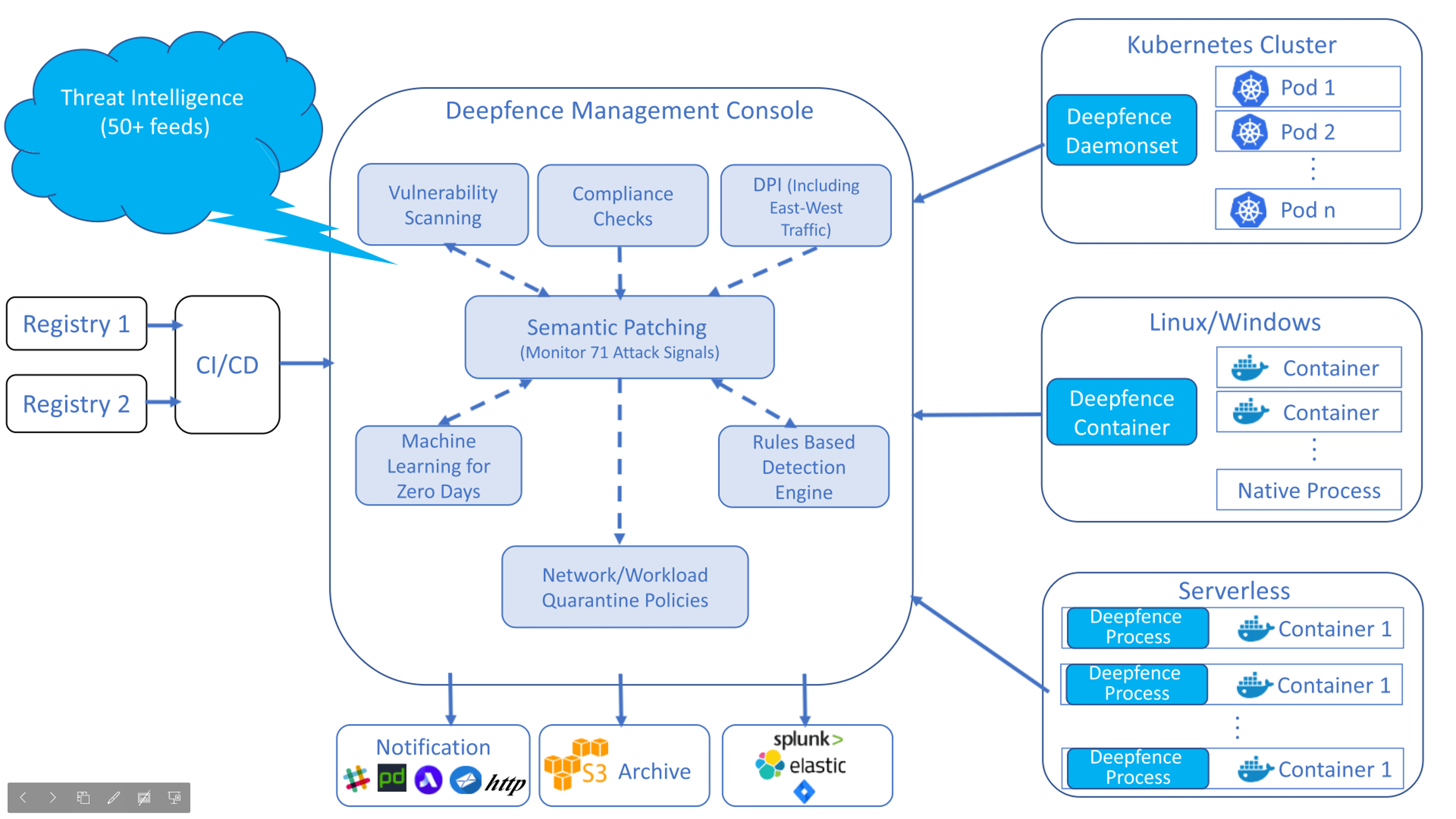
A pictorial depiction of the Deepfence Architecture is below
| Features | Runtime Threat mapper (Community Edition) | Workload Protection Platform (Enterprise Edition) |
|---|---|---|
| Discover & Visualize Running Pods, Containers and Hosts | ✔️ (unlimited) | ✔️ (unlimited) |
| Runtime Vulnerability Management for hosts/VMs | ✔️ (unlimited) | ✔️ (unlimited) |
| Runtime Vulnerability Management for containers | ✔️ (unlimited) | ✔️ (unlimited) |
| Container Registry Scanning | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| CI/CD Integration | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Multiple Clusters | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Integrations with SIEMs, Slack and more | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Compliance Automation | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Deep Packet Inspection of Encrypted & Plain Traffic | ❌ | ✔️ |
| API Inspection | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Runtime Integrity Monitoring | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Network Connection & Resource Access Anomaly Detection | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Workload Firewall for Containers, Pods and Hosts | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Quarantine & Network Protection Policies | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Alert Correlation | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Serverless Protection | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Windows Protection | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Highly Available & Multi-node Deployment | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Multi-tenancy & User Management | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Enterprise Support | ❌ | ✔️ |
The Deepfence Management Console is first installed on a separate system. The Deepfence agents are then installed onto bare-metal servers, Virtual Machines, or Kubernetes clusters where the application workloads are deployed, so that the host systems, or the application workloads, can be scanned for vulnerabilities.
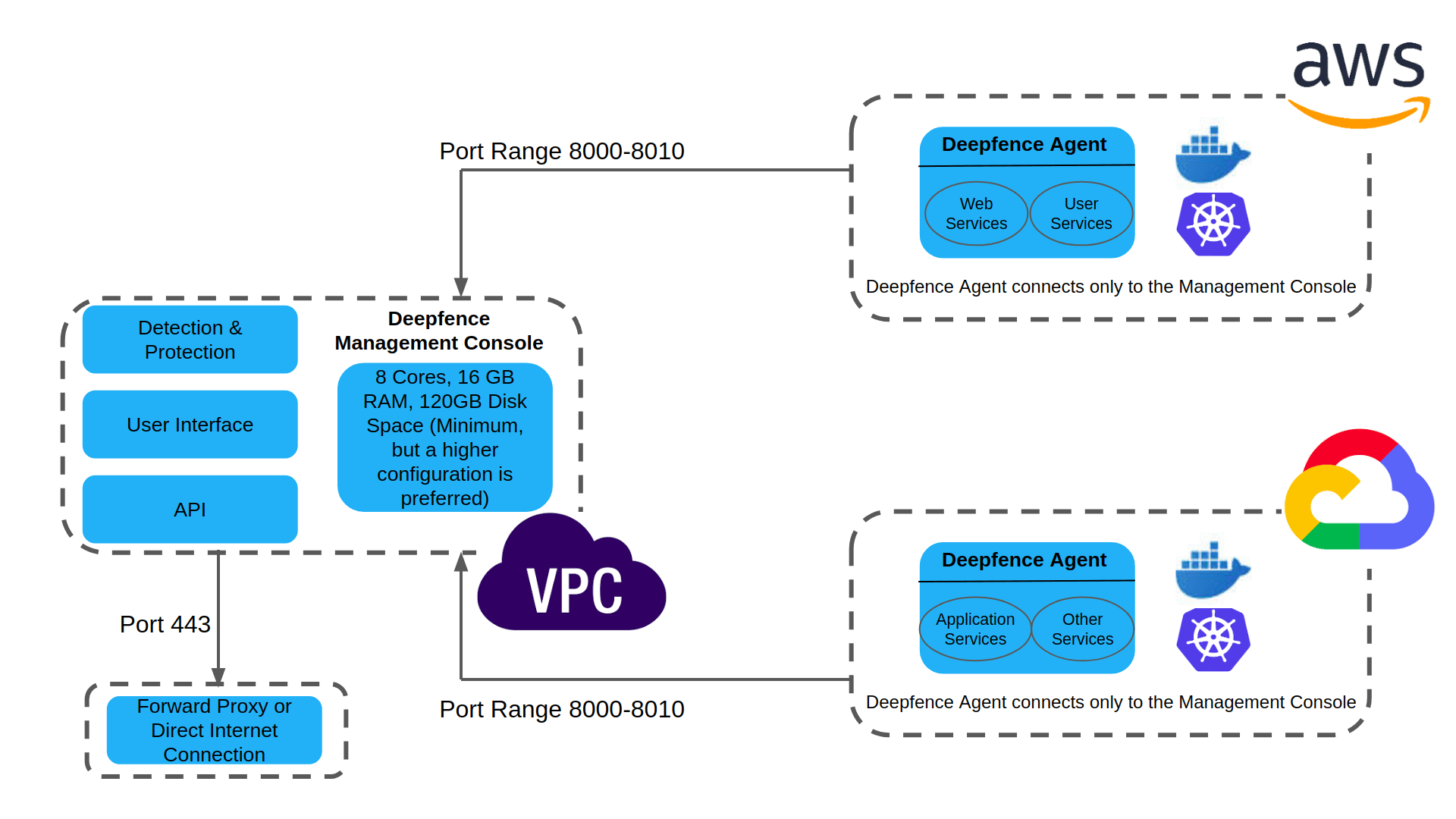
A pictorial depiction of the Deepfence security platform is as follows:
| Feature | Requirements |
|---|---|
| CPU: No of cores | 4 |
| RAM | 16 GB |
| Disk space | At-least 120 GB |
| Port range to be opened for receiving data from Deepfence agents | 8000 - 8010 |
| Port to be opened for web browsers to be able to communicate with the Management console to view the UI | 443 |
| Docker binaries | At-least version 18.03 |
| Docker-compose binary | Version 1.20.1 |
Following table gives the number of nodes that can be supported with different console machine configurations assuming a single node deployment of console. Memory optimised instances are shown to perform better.
| CPU | RAM | Nodes supported |
|---|---|---|
| 4 cores | 16 GB RAM | 250 nodes |
| 8 cores | 16 GB RAM | 500 nodes |
| 8 cores | 32 GB RAM | 1000 nodes |
| 16 cores | 32 GB RAM | 1400-1500 nodes |
In order to support higher numbers of nodes (i.e. hosts as number of containers can be unlimited theoritically based on their life times) ThreatMapper needs to be deployed as a 3 node k8s cluster to scale up to 10000 nodes, instructions to follow.
Installing the Management Console is as easy as:
- Download the file docker-compose.yml to the desired system.
- Execute the following command
docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml up -dThis is the minimal installation required to quickly get started on scanning various container images. The necessary images may now be downloaded onto this Management Console and scanned for vulnerabilities.
- Terraform module to provision Deepfence ThreatMapper on GCP Compute Engine
Custom TLS certificates are supported for the web application hosted on the console machine. On the console machine users have to place the certificate and private key on /etc/deepfence/certs folder. Deepfence looks for the file with .key and .crt extentions on the specified location on the host.
In order to check a host for vulnerabilities, or if docker images or containers that have to be checked for vulnerabilities are saved on different hosts, then the Deepfence agent needs to be installed on those hosts.
| Feature | Requirements |
|---|---|
| CPU: No of cores | 2 |
| RAM | 1 GB |
| Disk space | At-least 30 GB |
| Connectivity | The host on which the Deepfence Agent is to be installed, is able to communicate with the Management Console on port range 8000-8010. |
| Linux kernel version | >= 4.4 |
| Docker binaries | At-least version 18.03 |
| Deepfence Management Console | Installed on a host with IP Address x.x.x.x |
Installation procedure for the Deepfence agent depends on the environment that is being used. Instructions for installing Deepfence agent on some of the common platforms are given in detail below:
Installing the Deepfence Agent is now as easy as:
- In the following docker run command, replace x.x.x.x with the IP address of the Management Console
docker run -dit --cpus=".2" --name=deepfence-agent --restart on-failure --pid=host --net=host --privileged=true -v /var/log/fenced -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v /:/fenced/mnt/host/:ro -v /sys/kernel/debug:/sys/kernel/debug:rw -e DF_BACKEND_IP="x.x.x.x" deepfenceio/deepfence_agent_ce:latest
For detailed instructions to deploy agents on Amazon ECS, please refer to our Amazon ECS wiki page.
- Start deepfence agent (replace x.x.x.x with the IP address of the Management Console)
# helm 2
helm install --repo https://deepfence.github.io/ThreatMapper/files/helm-chart deepfence-agent --name deepfence-agent --set managementConsoleIp=x.x.x.x
# helm 3
helm install deepfence-agent --repo https://deepfence.github.io/ThreatMapper/files/helm-chart deepfence-agent --set managementConsoleIp=x.x.x.x- Delete deepfence agent
# helm 2
helm delete --purge deepfence-agent
# helm 3
helm delete deepfence-agentFor detailed instructions to deploy agents on Google GKE, please refer to our Google GKE wiki page.
For detailed instructions to deploy agents on Azure Kubernetes Service, please refer to our Azure AKS wiki page.
For detailed instructions to deploy agents on Google GKE, please refer to our Self-managed/On-premise Kubernetes wiki page.
Now the Deepfence Security Platform has been successfully installed, here are the steps to begin --
The first step is to register a user with the Management Console.
- If the Management Console has been installed on a system with IP address x.x.x.x, fire up a browser (Chromium (Chrome, Safari) is the supported browser for now), and navigate to https://x.x.x.x/
After registration, it can take anywhere between 30-60 minutes for initial vulnerability data to be populated. The download status of the vulnerability data is reflected on the notification panel.
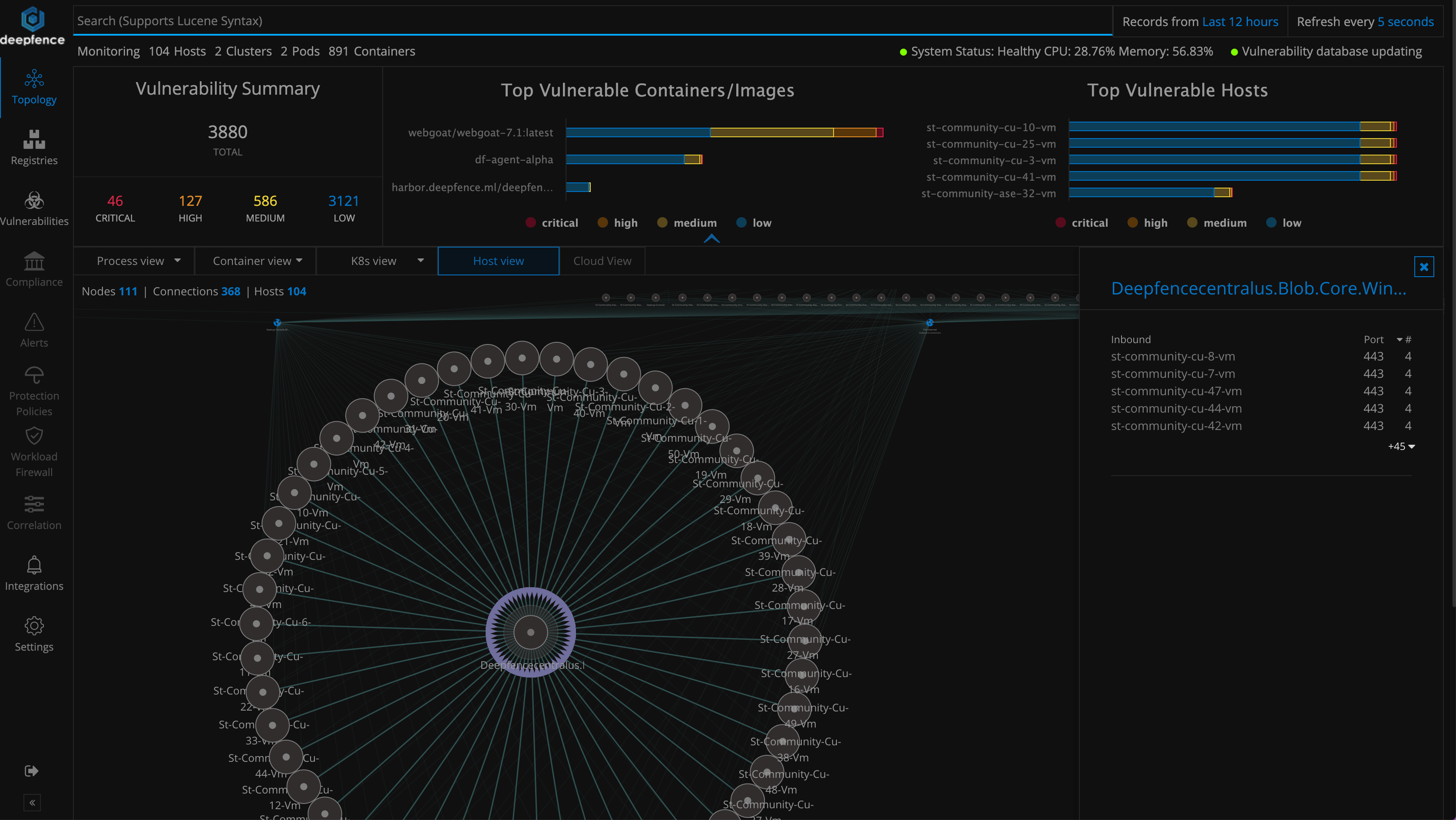
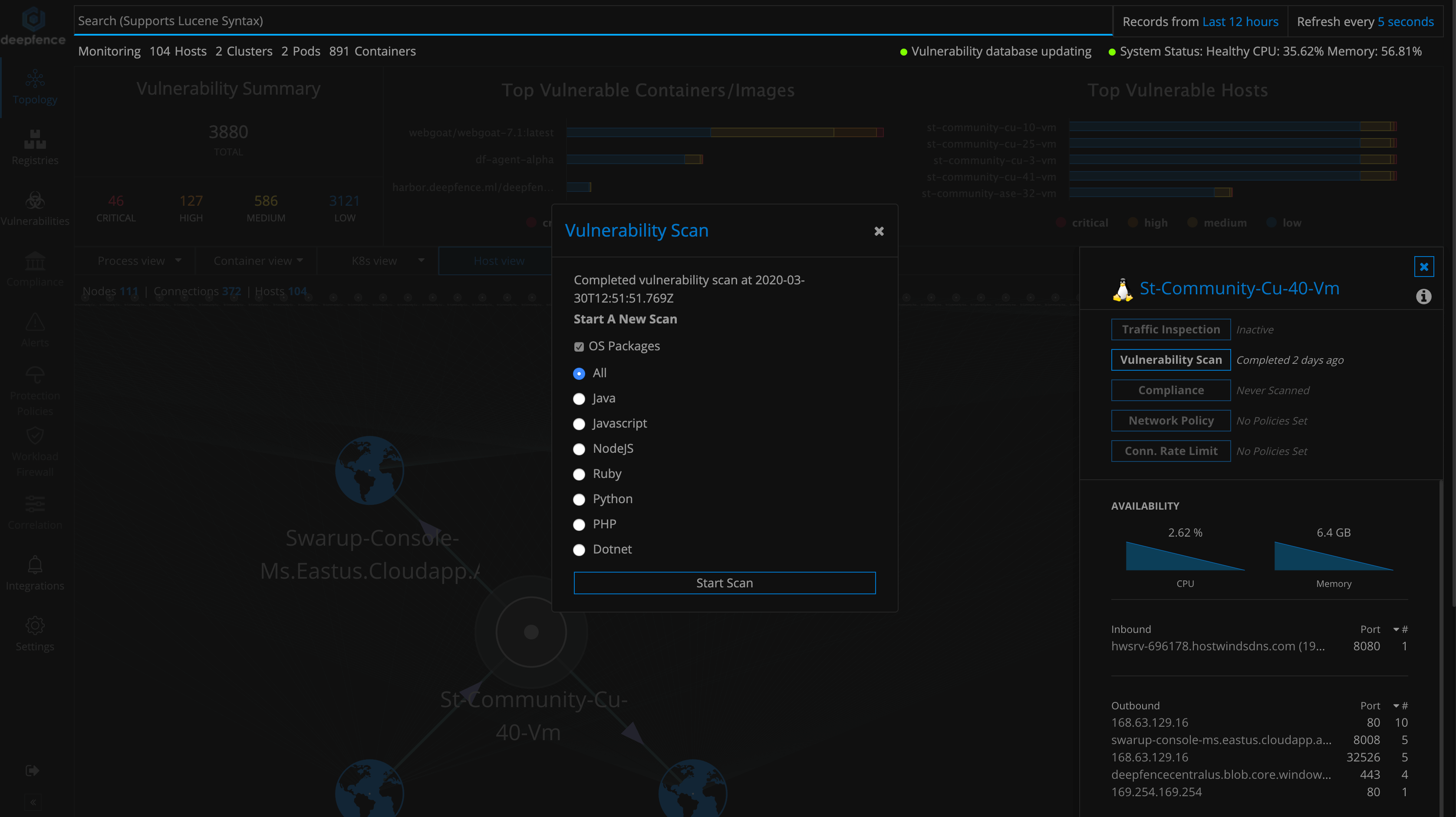
You can visualize the entire topology of your running VMs, hosts, containers etc. from the topology tab. You can click on individual nodes to initiate various tasks like vulnerability scanning.
From the topology view, runtime vulnerability scanning for running containers & hosts can be initiated using the console dashboard, or by using the APIs. Here is snapshot of runtime vulnerability scan on a host node.
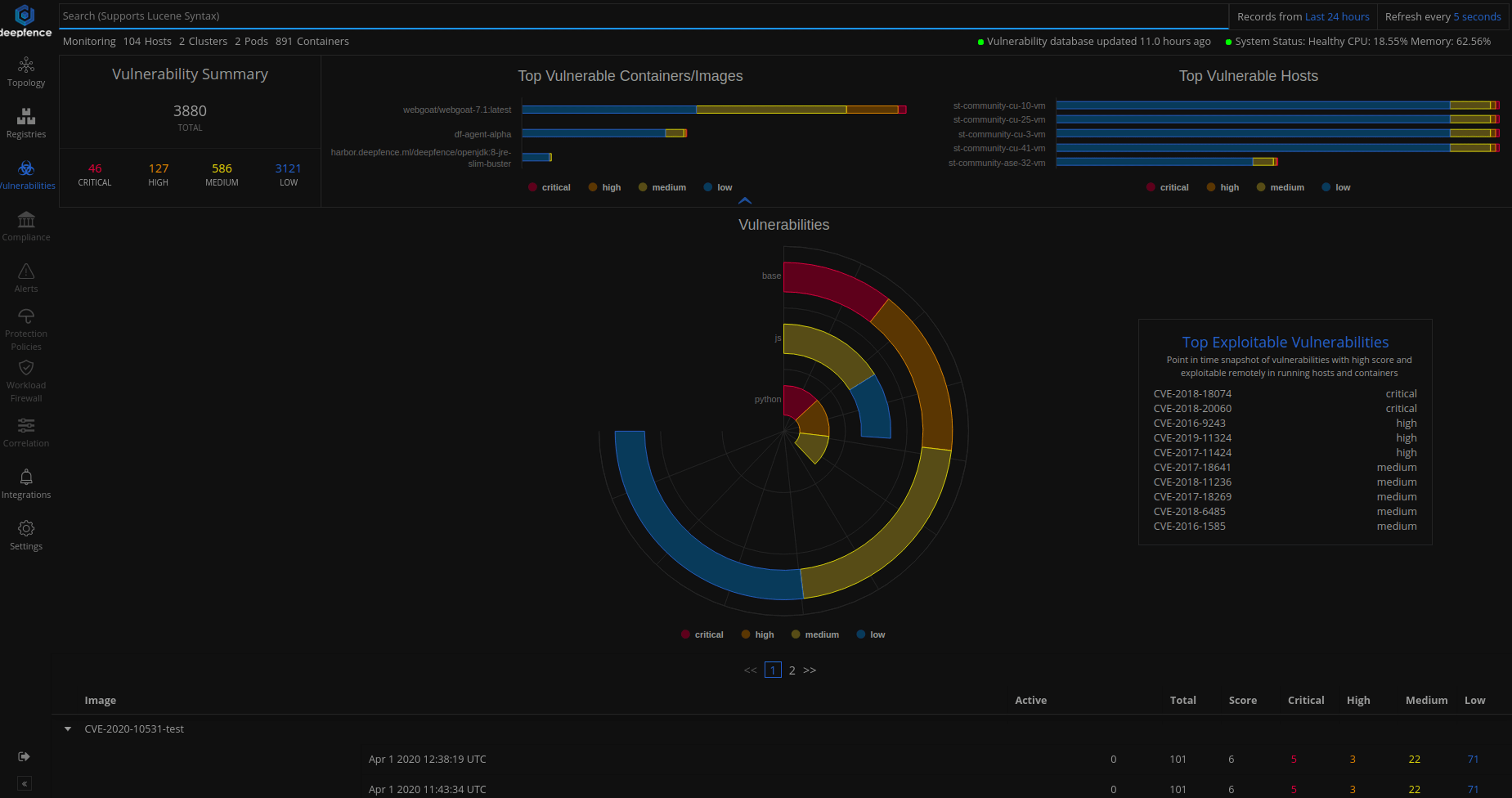
The vulnerabilities and security advisories for each node, can be viewed by navigating to Vulnerabilities menu as follows:
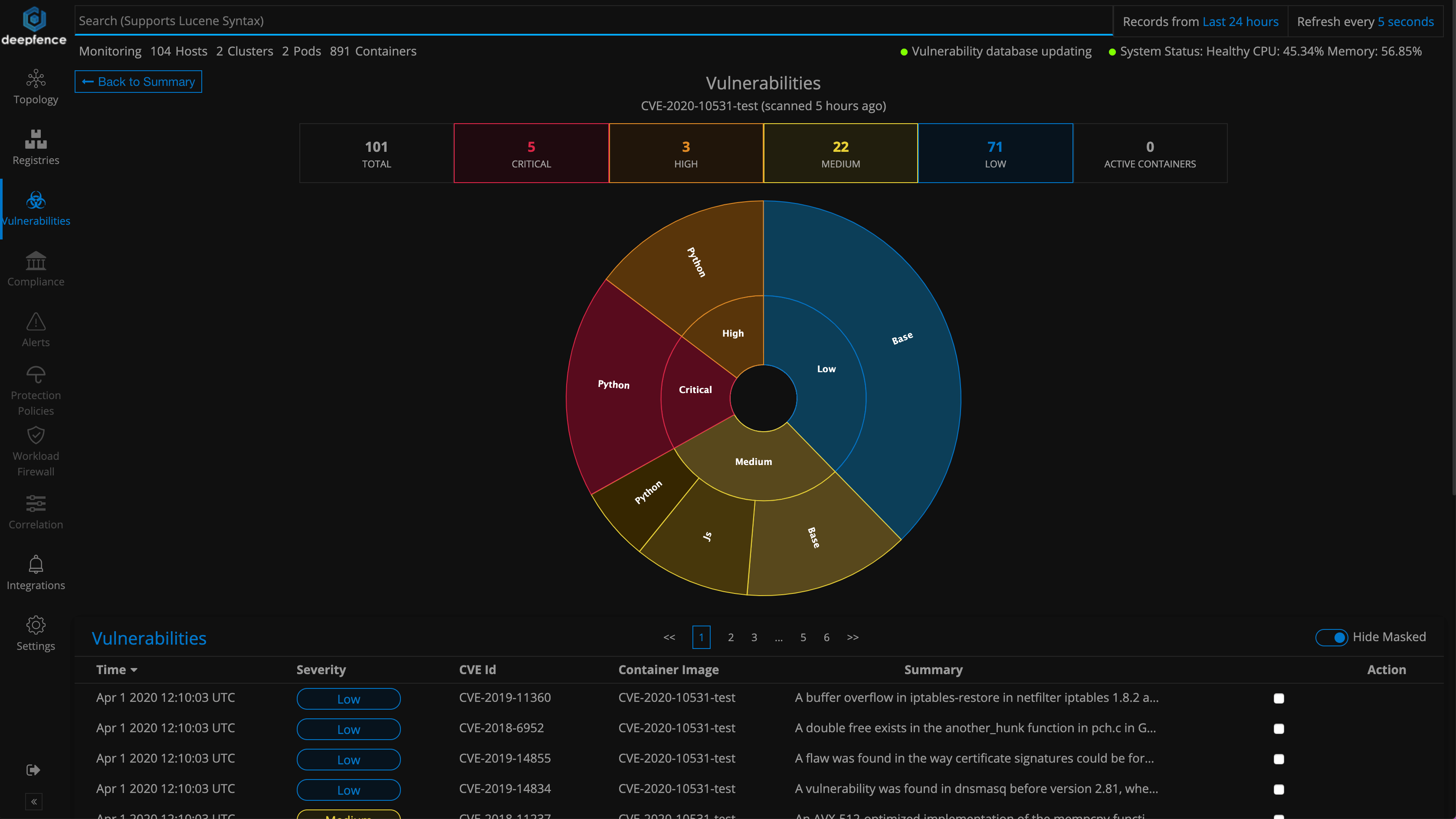
Clicking on an item in the above image gives a detailed view as in the image below:
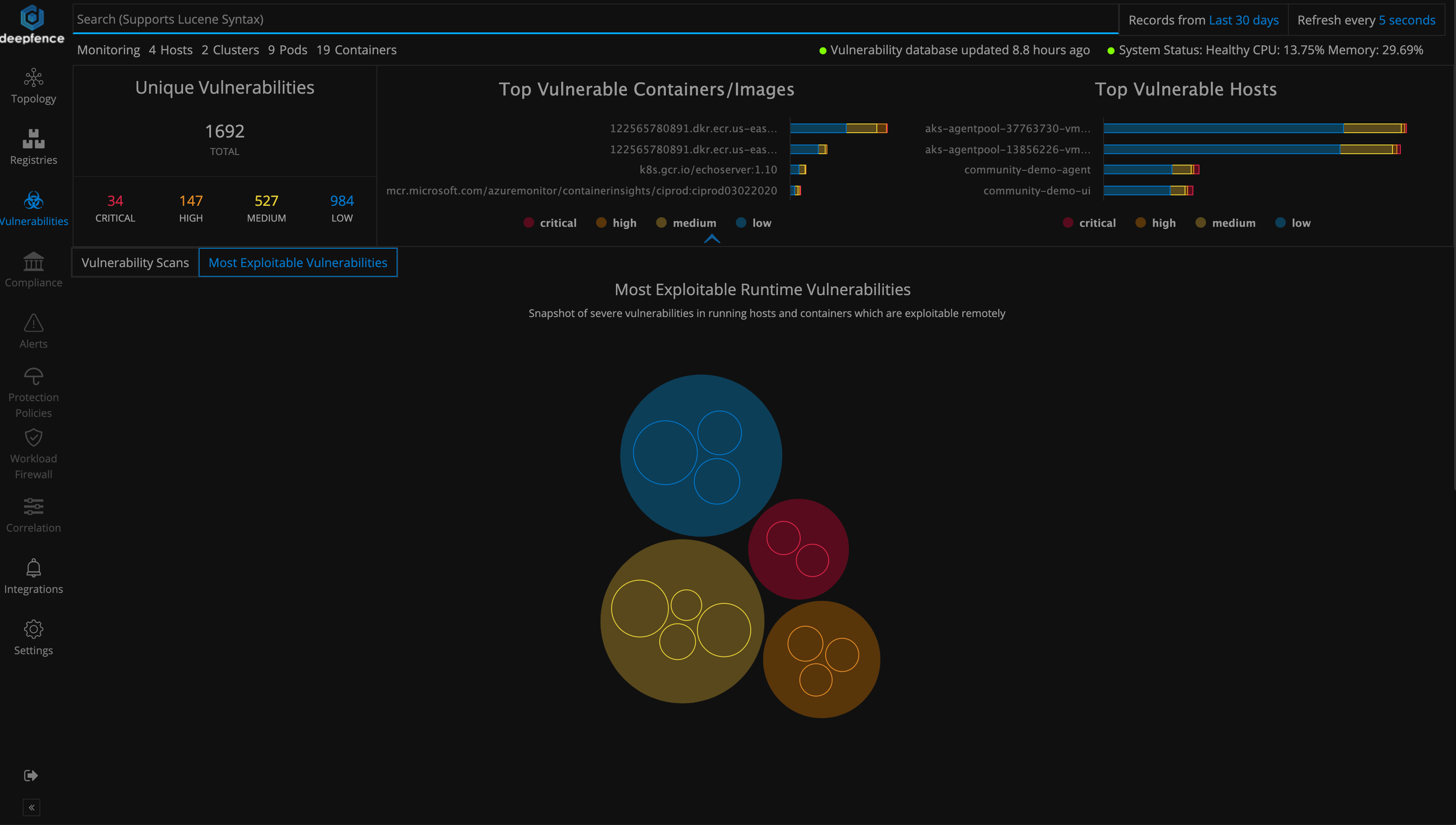
Most Exploitable Vulnerabilities tab gives a ranked list of vulnerabilities across images to be fixed at priority. Rank is calculated using various parameters like whether the image is running or not, cve score and severity of the vulnerability.
Optionally, users can tag a subset of nodes using user defined tags and scan a subset of nodes as explained in our user tags wiki page.
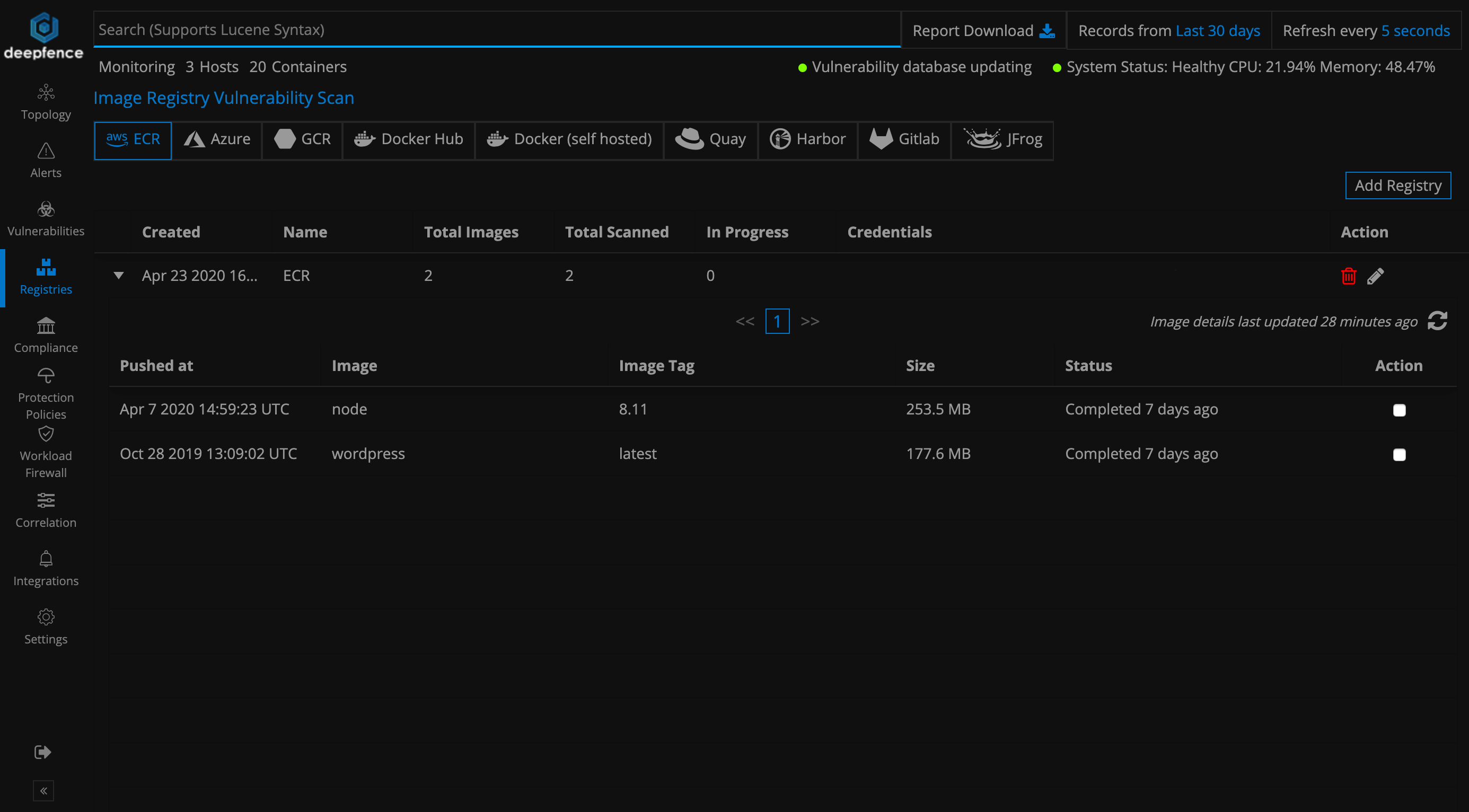
You can scan for vulnerabilities in images stored in AWS ECR, Azure Container Registry, Google Container Registry, Docker Hub, Docker Self-Hosted Private Registry, Quay, Harbor, Gitlab and JFrog from the registry scanning dashboard. First, you will need to click the "Add registry" button and add the credentials to populate available images. After that you can select the images to scan and click the scan button as shown the image below:
For CircleCI integration, refer to our CircleCI wiki and for Jenkins integration, refer to our Jenkins wiki page for detailed instructions.
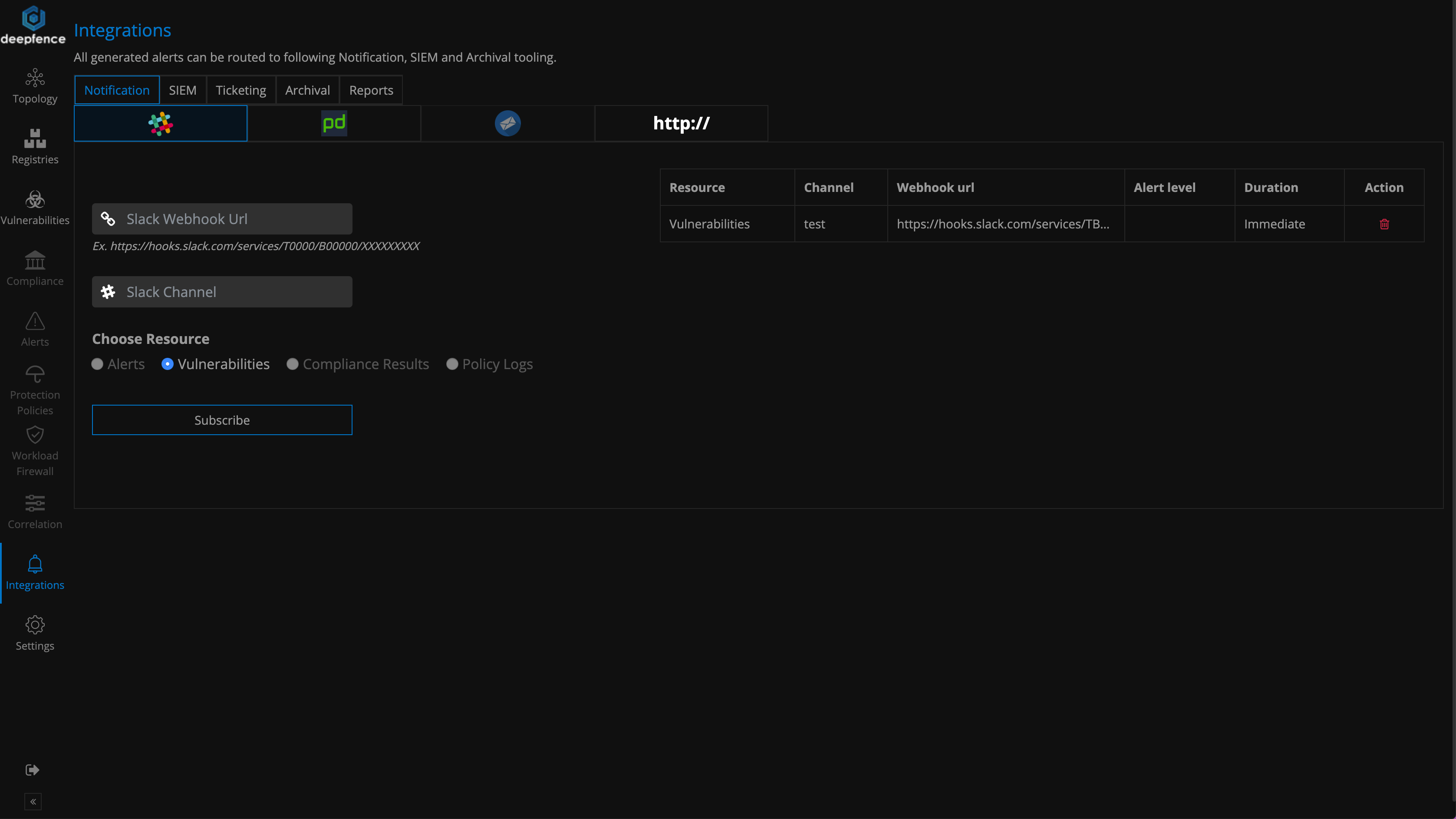
Deepfence logs and scanning reports can be routed to various SIEMs and notifications channels by navigating to Notifications screen.
For detailed instructions on integrations with slack refer to our slack wiki page
For detailed instructions on integrations with sumo logic refer to our sumo logic wiki page
For detailed instructions on integrations with PagerDuty refer to our PagerDuty wiki page
Deepfence provides a suite of powerful API’s to control the features, and to extract various reports from the platform. The documentation of the API’s are available here, along with sample programs for Python and GO languages.
Users are strongly advised to control access to the Deepfence Management Console, so that it is only accessible on port range 8000-8010 from those systems that have installed the Deepfence agent. Further, we recommend to open port 443 on the Deepfence Management Console only for those systems that need to use a Web Browser to access the Management Console.
We periodically scan our own images for vulnerabilities and pulling latest images should always give you most secure Deepfence images. In case you want to report a vulnerability in the Deepfence images, please reach out to us by email -- (community at deepfence dot io).
Please file Github issues as needed and/or join Deepfence Community Slack channel.