This is the official implementation of the CVPR 2022 paper "Learning Rotation-Equivariant Features for Visual Correspondence" by Jongmin Lee, Byungjin Kim, Seungwook Kim, and Minsu Cho.
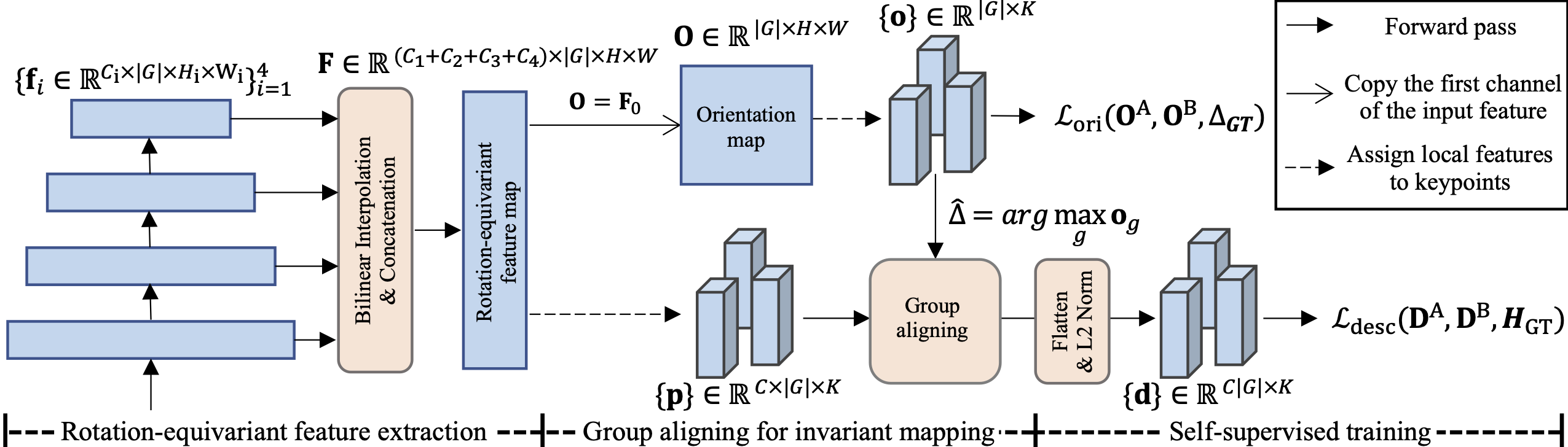
Extracting discriminative local features that are invariant to imaging variations is an integral part of establishing correspondences between images. In this work, we introduce a self-supervised learning framework to extract discriminative rotation-invariant descriptors using group-equivariant CNNs. Thanks to employing group-equivariant CNNs, our method effectively learns to obtain rotation-equivariant features and their orientations explicitly, without having to perform sophisticated data augmentations. The resultant features and their orientations are further processed by group aligning, a novel invariant mapping technique that shifts the group-equivariant features by their orientations along the group dimension. Our group aligning technique achieves rotation-invariance without any collapse of the group dimension and thus eschews loss of discriminability. The proposed method is trained end-to-end in a self-supervised manner, where we use an orientation alignment loss for the orientation estimation and a contrastive descriptor loss for robust local descriptors to geometric/photometric variations. Our method demonstrates state-of-the-art matching accuracy among existing rotation-invariant descriptors under varying rotation and also shows competitive results when transferred to the task of keypoint matching and camera pose estimation.
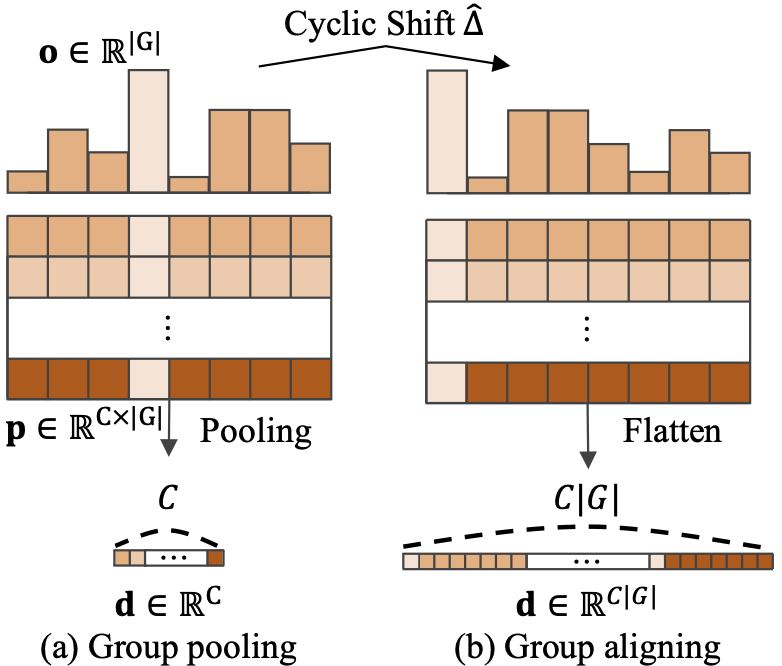
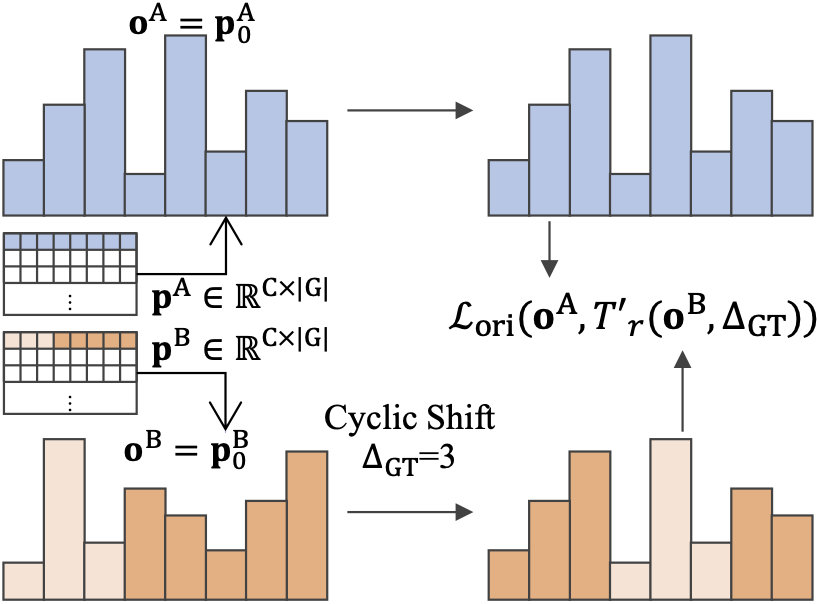
(Left) Group Pooling vs. Group Aligning, (Right) Orientation Alignment Loss
PyTorch source code for CVPR2023 paper.
"Learning Rotation-Equivariant Features for Visual Correspondence".
Jongmin Lee, Byungjin Kim, Seungwook Kim, Minsu Cho. CVPR 2023.
[Paper (ArXiv)] [Paper (OpenAccess)] [Project page]
git clone https://github.com/bluedream1121/RELF.gitRun the script to install all the dependencies. You need to provide the conda install path (e.g. ~/anaconda3) and the name for the created conda environment.
bash installation.sh [conda_install_path] RELF
- Ubuntu 22.04
- python 3.10
- pytorch 2.0.0
- torchvision 0.15.0
- kornia 0.4.1
- opencv-python 4.7.0.72
- e2cnn 0.2.3
-
Download the train-2014 and val-2014 set of COCO dataset.
-
Download the evaluation dataset, Roto-360 (1.93G) [Download Roto-360] (Password: relf)
-
Download the evaluation dataset, HPatches (2.02G) [Download HPatches] (Password: relf)
-
Organize files like the following
data
├── roto360/
├── hpatches-sequences-release/
└── coco/
├── train2014/
└── val2014/
Orientation=16 python train.py --model 're_resnet'
python train.py --model e2wrn16_8R_stl
-
Hyperparameters:
- model: The name of backbone network.
're_resnet': Rotation-Equivariant ResNet-18'e2wrn16_8R_stl': Rotation-Equivariant Wide-ResNet-16-8
- num_group: The order of rotation group. default=16
- channels: The number of channels of the ReResNet. default=64
- training_breaker: The number of training iteration per epoch. default=1000
- model: The name of backbone network.
You can download the pretrained weights in here: [best models] (password : relf).
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset roto360 --model 're_resnet' --load_dir [Trained_models]
- load_dir: Path of pre-trained weights.
- eval_dataset: The name of evaluation dataset:
roto360,hpatches. - candidate: Multiple descriptor extraction strategy. Default: top1 (No multiple extraction) or 0.6.
- detector: The name of keypoint detector.
Roto-360 Results
Results on the Roto-360 dataset. `*' denotes the results with the multiple descriptor extraction by orientation candidnates.
The models are evaluated using all 360 image pairs.
| Model | MMA@3 | MMA@5 | MMA@10 | pred. match. | total points | Links | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REKD_release | 90.18 | 91.34 | 93.08 | 688.2 | 1160.7 | model | Official pretrained model |
| REKD_release* | 91.69 | 92.82 | 94.34 | 1332.8 | 2339.5 | model | Official pretrained model |
<REKD_release>
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset roto360 --model 're_resnet' --load_dir [Trained_models]
<REKD_release*>
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset roto360 --model 're_resnet' --load_dir [Trained_models] --candidate 0.6 You can download the pretrained weights in here: [Re-ResNet-18] [Re-WideResNet-16-8] (password : relf).
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model 're_resnet' --load_dir best_model.pt
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model 're_resnet' --load_dir best_model.pt --candidate 0.6
python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model e2wrn16_8R_stl --load_dir best_model_wrn.pt --multi_gpu 0
- model: The name of backbone network.
're_resnet': Rotation-Equivariant ResNet-18'e2wrn16_8R_stl': Rotation-Equivariant Wide-ResNet-16-8
- load_dir: Path of pre-trained weights.
- eval_dataset: The name of evaluation dataset:
roto360,hpatches. - candidate: Multiple descriptor extraction strategy. Default: top1 (No multiple extraction) or 0.6.
- detector: The name of keypoint detector.
HPatches viewpoint variations
Results on HPatches viewpoint variations. `*' denotes the results with the multiple descriptor extraction by orientation candidnates. † denotes a trained model with larger backbone size (Re-WideResNet16-8).
| Model | MMA@3 | MMA@5 | MMA@10 | pred. match. | total points | Links | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REKD_release | 63.96 | 70.97 | 77.76 | 512.1 | 1126.1 | model | Official pretrained model |
| REKD_release* | 67.45 | 74.62 | 81.12 | 1010.7 | 2175.9 | model | Official pretrained model |
| REKD_release† | 70.05 | 78.06 | 84.92 | 630.9 | 1126.1 | model | Official pretrained model |
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model 're_resnet' --load_dir best_model.pt
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model 're_resnet' --load_dir best_model.pt --candidate 0.6
python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model e2wrn16_8R_stl --load_dir best_model_wrn.pt --multi_gpu 0
HPatches illumination variations
Results on HPatches illumination variations. `*' denotes the results with the multiple descriptor extraction by orientation candidnates. † denotes a trained model with larger backbone size (Re-WideResNet16-8).
| Model | MMA@3 | MMA@5 | MMA@10 | pred. match. | total points | Links | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REKD_release | 63.06 | 70.50 | 77.65 | 512.1 | 1126.1 | model | Official pretrained model |
| REKD_release* | 65.35 | 73.01 | 80.21 | 1010.7 | 2175.9 | model | Official pretrained model |
| REKD_release† | 69.50 | 78.02 | 85.37 | 630.9 | 1126.1 | model | Official pretrained model |
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model 're_resnet' --load_dir best_model.pt
Orientation=16 python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model 're_resnet' --load_dir best_model.pt --candidate 0.6
python evaluate.py --eval_dataset hpatches --model e2wrn16_8R_stl --load_dir best_model_wrn.pt --multi_gpu 0
If you find our code or paper useful to your research work, please consider citing our work using the following bibtex:
@InProceedings{Lee_2023_CVPR,
author = {Lee, Jongmin and Kim, Byungjin and Kim, Seungwook and Cho, Minsu},
title = {Learning Rotation-Equivariant Features for Visual Correspondence},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2023},
pages = {21887-21897}
}
We would like to thank the following papers for their github source code contributions.
We rely heavily on the following three repositories.
- GIFT: Learning Transformation-Invariant Dense Visual Descriptors via Group CNNs (NeurIPS 2019)
- ReDet: A Rotation-equivariant Detector for Aerial Object Detection
- Self-Supervised Equivariant Learning for Oriented Keypoint Detection (CVPR 2022)
We use some functions from the following three repositories.
- Self-Supervised Learning of Image Scale and Orientation Estimation (BMVC 2021)
- R2D2: Repeatable and Reliable Detector and Descriptor (NeurIPS 2019)
- Key.Net: Keypoint Detection by Handcrafted and Learned CNN Filters (ICCV 2019)
Questions can be left as issues in the repository.