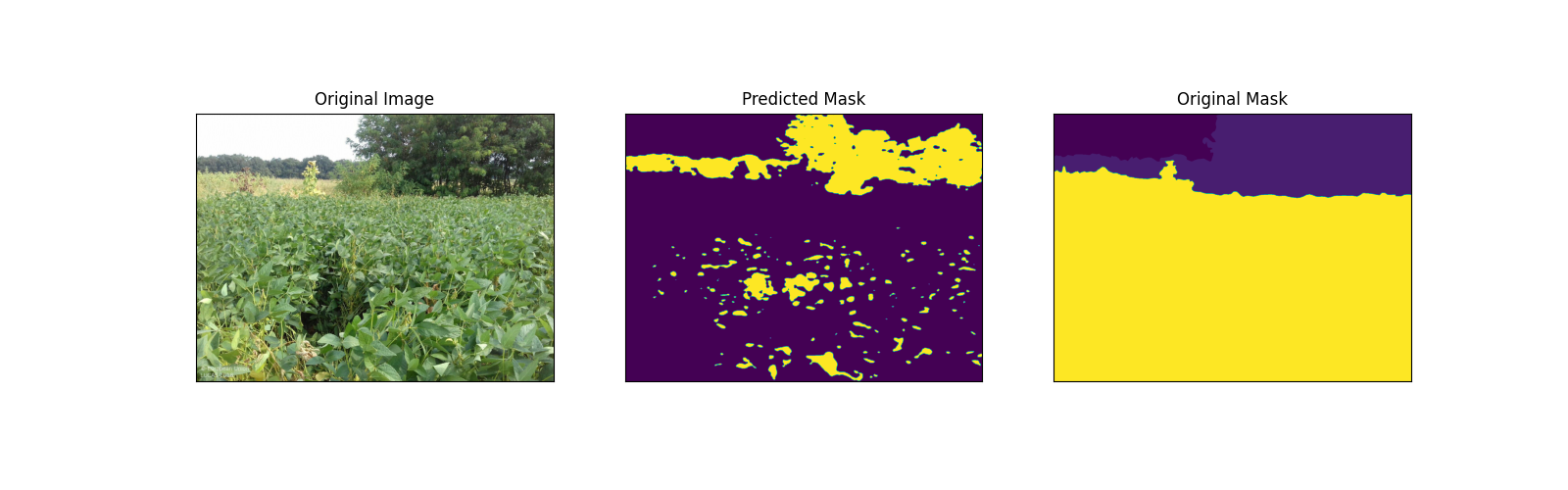
This is worked example using data sourced from the Land Use and Coverage Area frame Survey (LUCAS) data set, following a strict sampling and acquisition protocol. Landscape objects and elements were fully delineated on the street (eye) level landscape images and can provide critical context for land-use and land-cover assessments and comparison to satellite remote sensing data.
This worked example provides a single class segmentation example framework which should be easily expanded to multiclass problems. The code relies on pytorch and the Lightning modelling framework. Environment and Docker files are provided to ease code deployment.
Run the following code from the terminal to set up your repository and conda environment. Make sure that miniconda and python are installed prior.
conda env create -f environment.yml --name mlenv
conda activate mlenvAn isolated, self-contained environment can be created using the provided Dockerfile.
# In the main project directory run
docker build -f Dockerfile -t mlenv .
Data will be mounted in the docker virtual machine at /workspace and is fully accessible (writing and reading of files on your local file system), using the following command.
docker run -it --rm -v "${PWD}":/workspace/ mlenv
Download the data in the main project directory in the data/ directory.
The data used in this project can be downladed in:
- Raw data : (https://data.jrc.ec.europa.eu/dataset/adace32a-465f-412b-bc11-be1bc06322d3)
- Raw data, ML data :(https://beta.source.coop/repositories/jrc-lucas/jrc-lucas-ml/description/)
We recommend to use the second link and copy the contents of ml_data to the data folder.
The structure of the data should be:
├── data
│ ├── ml_data <- name of the folder with the images and masks
│ │ ├── images <- images folder
│ │ └── masks <- mask folder
Using the data/prepare_data.py script divide the data in a train, validation and test datasets. This split will be written as a data.json file in the directory containing the list of this split, the original data will not be moved. the script requires to set the path to the images and masks and the csv containing the labels of the masks.
./prepare_data.py -i ./ml_data/ -l ./classes_dataset.csvUse the src/train.py script to train the model. The script requires a number of parameters, the path to the data.json file, the location where to store the model and a trigger to set it to train, i.e. "train".
./train.py -d ../data/ml_data/ -m ./models/deeplab_config.json -o ../models/ --trainThe data can be tested using the "test" trigger.
./train.py -d ../data/ml_data/ -m ./models/deeplab_config.json -o ../models/ --testUse the src/inference.py script to inference.
./inference.py -i ../data/ml_data/path_image.jpg -m ./models/deeplab_config.json -c ../models.lst.ckpt -o ../plots/