An Autodesk Fusion360 addin that can export a cut list of parts in a variety of formats. Useful for woodworking or other crafts that mostly cut shapes out of rectangular stock.
It's compatible with many modeling styles and does not require a specific document structure or workflow.
- Operates on bodies, selected either directly or by selecting components
- Groups parts by matching bounding box dimensions and materials
- The largest dimension is called
length, the next largestwidth, and the smallestheight - Accounts for part rotation when matching bounding boxes
- Customize grouping conditions
- The largest dimension is called
- Exports to text, HTML, JSON, CSV, and more
- Additional filtering options for bodies (e.g. visibility)
- Download the latest release
- Unzip the file on your computer
- Start Fusion360 and open the "Scripts & Addins" dialog (Shift+S)
- Go to the "Add-Ins" tab
- Click the green "+" (plus) sign next to "My Add-Ins"
- Selected the extracted folder from Step 2
- Click the "Run" button (or restart Fusion 360) to start the add-in
The wiki also has a detailed version of these steps with annotated screenshots.
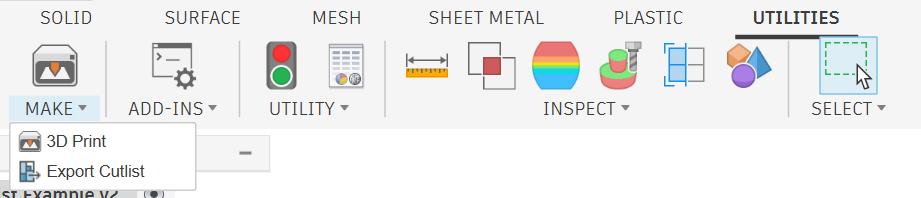
The "Export Cutlist" command is added to the "Make" panel:
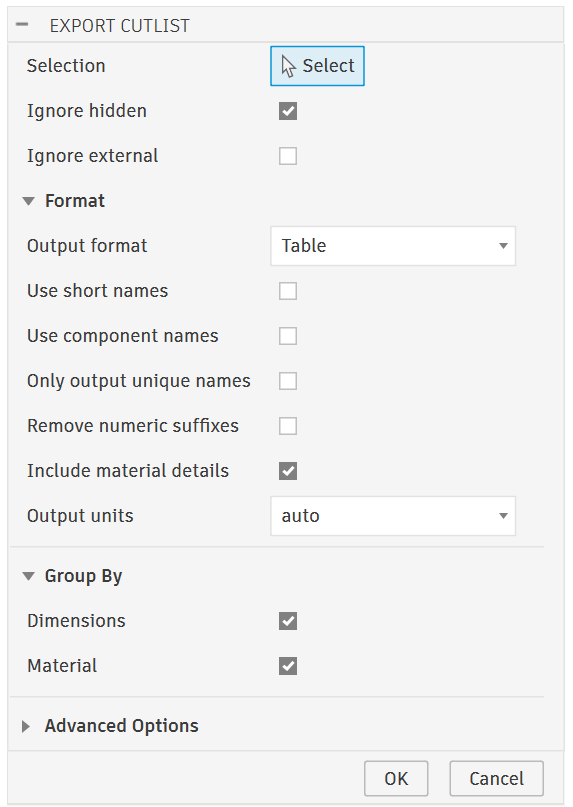
After selecting the command, a dialog appears where you can select components and bodies and set other options:
When you are ready to export, click "OK". A file selection dialog will open asking where to save the file. Choose a file and click "Save". A message box will open confirming the file was saved.
The addon can export cutlists in the following formats:
- Plain text
- JSON
- HTML
- CSV
- CSV as used by https://cutlistoptimizer.com
- TSV as used by https://cutlistevo.com
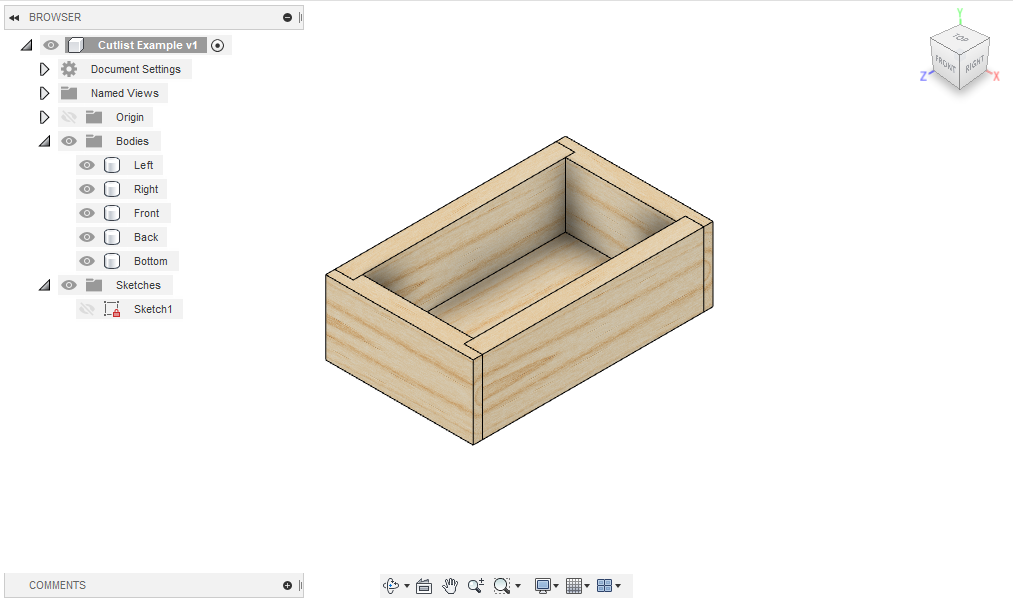
The cutlist for a simple box with a bottom was exported as a table, JSON, and CSV to demonstrate the different formats.
count material length (in) width (in) height (in) names
=========================================================================
2 Pine 6.00 2.00 0.50 Left
Right
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 Pine 4.00 2.00 0.50 Back
Front
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 Plywood, Finish 6.00 3.50 0.25 Bottom
[
{
"count": 2,
"dimensions": {
"units": "in",
"length": "6.00",
"width": "2.00",
"height": "0.50"
},
"material": "Pine",
"names": [
"Left",
"Right"
]
},
{
"count": 2,
"dimensions": {
"units": "in",
"length": "4.00",
"width": "2.00",
"height": "0.50"
},
"material": "Pine",
"names": [
"Back",
"Front"
]
},
{
"count": 1,
"dimensions": {
"units": "in",
"length": "6.00",
"width": "3.50",
"height": "0.25"
},
"material": "Plywood, Finish",
"names": [
"Bottom"
]
}
]count,material,length (in),width (in),height (in),names
2,Pine,6.00,2.00,0.50,"Left,Right"
2,Pine,4.00,2.00,0.50,"Back,Front"
1,"Plywood, Finish",6.00,3.50,0.25,Bottom
The addon uses the folowing algorithm to detect rotated parts:
- Find the planar face with the largest perimeter
- Find the orientation vector of the longest edge of the face
- Rotate the body so that the normal vector of the face is aligned with the Z axis and the orientation vector of the longest edge is aligned with the X axis
- Return the axis-aligned bounding box of the rotated body
This should produce correct results for most common situations in woodworking, where almost all parts will have at least one flat face that is aligned with one of the stock faces.
Bodies that don't work with this algorithm (e.g. because they have no planar faces) use the axis-aligned bounding box computed by Fusion 360. You can also disable the rotation heuristic and always use axis-aligned boxes in the advanced options.
MIT
Pull requests or issues suggesting additional features or output formats are welcome. If reporting a bug, please attach or a link to a design that reproduces the issue.