Sample Amazon Lex Web Interface
This is a sample Amazon Lex web interface. It provides a chatbot UI component that can be integrated in your website. The interface allows a user to interact with a Lex bot directly from a browser using text or voice.
- Mobile ready responsive UI with full page or embeddable widget modes
- Support for voice and text with the ability to seamless switch from one mode to the other
- Voice support provides automatic silence detection, transcriptions and ability to interrupt responses and replay recordings
- Display of Lex response cards
- Ability to programmatically configure and interact with the chatbot UI using JavaScript
- Use of NodeJS 10.x for Lambda functions. Note that this feature requires use of NodeJS 10.16.3 or higher and npm version 6.13.0 or higher to build the LexWebUi.
- Moved use of Polly for initial speech instruction to be used by Cognito Auth Role only
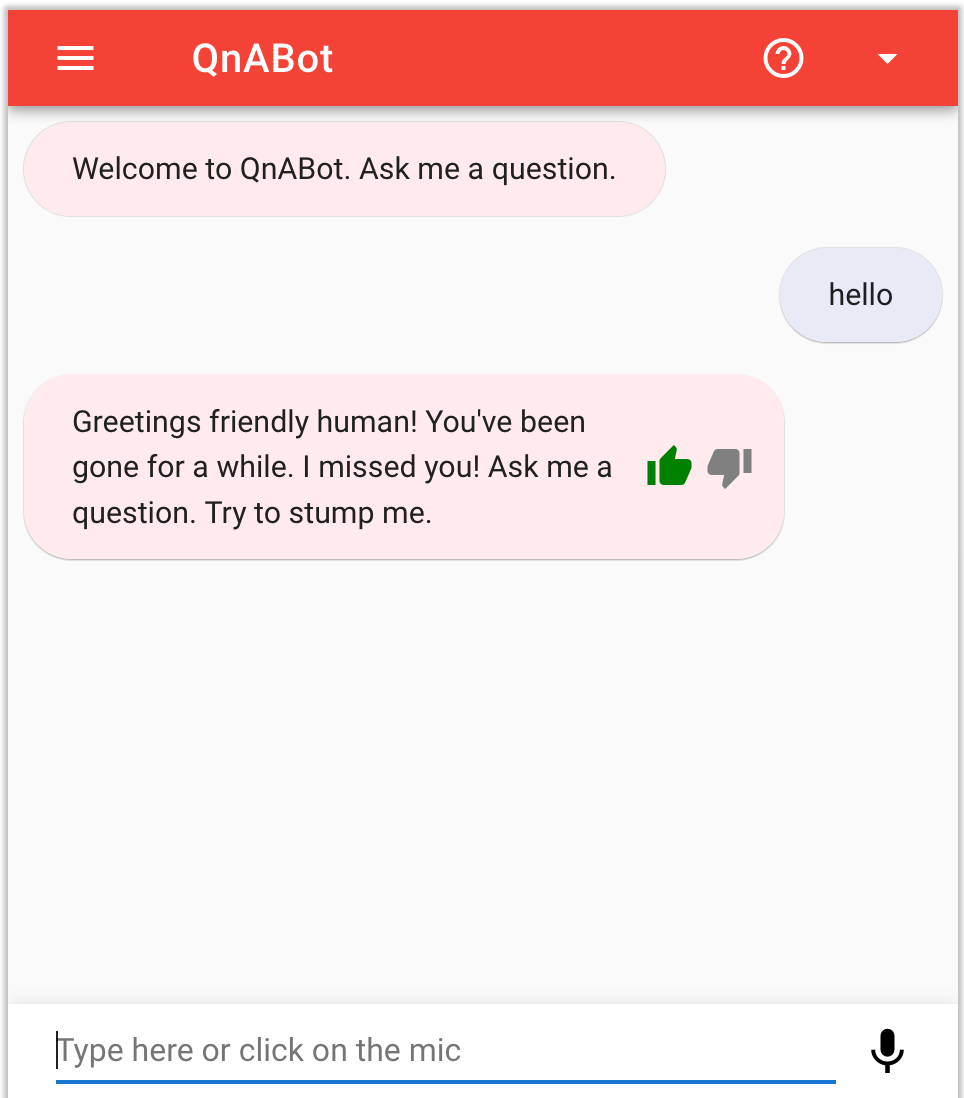
- Inline message feedback buttons
- Help Button
Sends a help message to the bot - Back Button
Resends the previous message
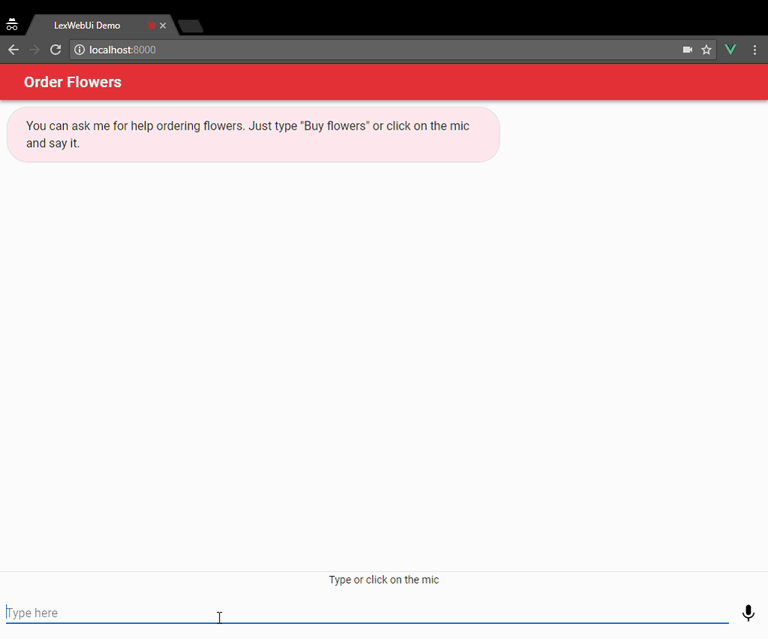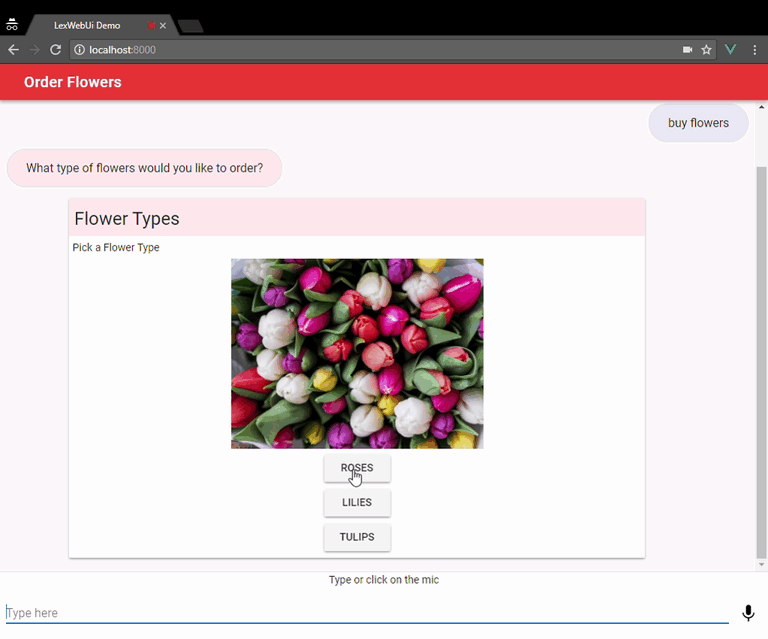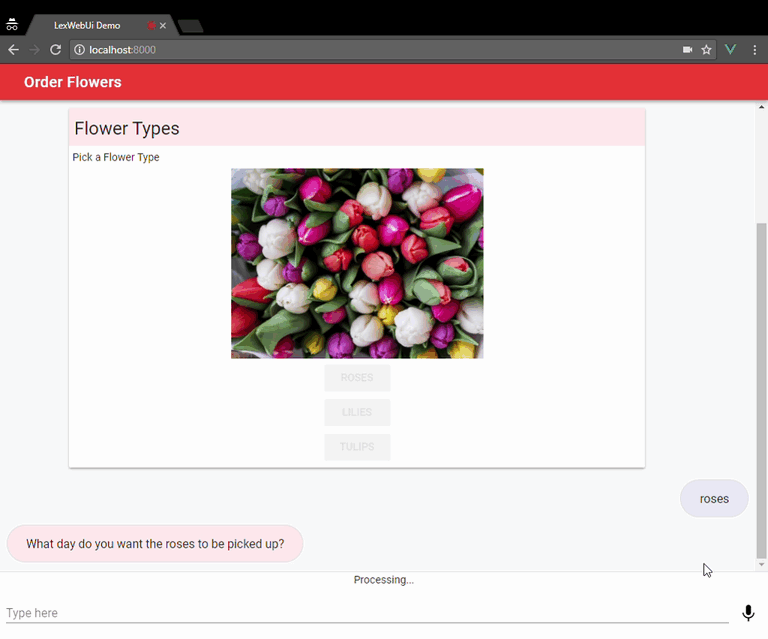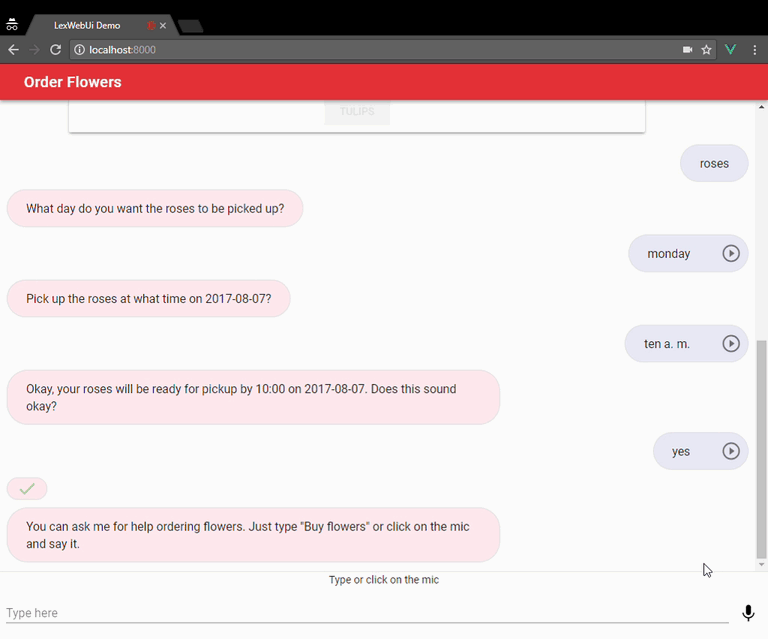
It can be used as a full page chatbot UI:
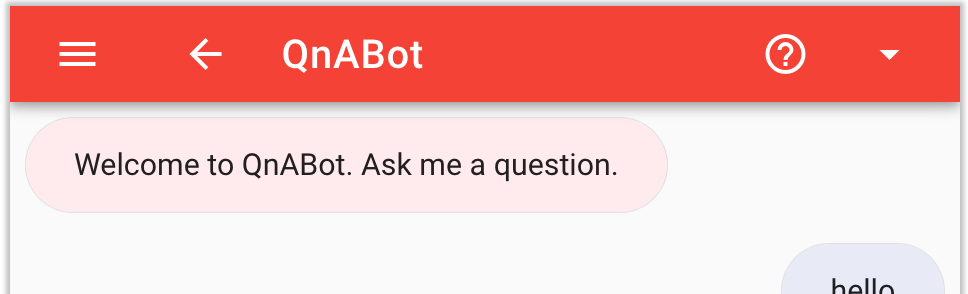
Or embedded into an existing site as a chatbot widget:
The easiest way to test drive the chatbot UI is to deploy it using the AWS CloudFormation templates provided by this project. Once you have launched the CloudFormation stack, you will get a fully working demo site hosted in your account.
Click this button to launch it:
By default, the CloudFormation template creates a sample Lex bot and a Amazon Cognito Identity Pool to get you started. It copies the chatbot UI web application to an Amazon S3 bucket including a dynamically created configuration file. The CloudFormation stack outputs links to the demo and related configuration once deployed. See the CloudFormation Deployment section for details.
You can modify the configuration of the deployed demo site to customize the chatbot UI. It can also be further configured to be embedded it on your web site. See the sections below for code samples and a description of the configuration and deployment options.
In addition to the CloudFormation deployment mentioned above, there are other methods to integrate and deploy this project. Here is a summary of the various methods:
| # | Method | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CloudFormation Deployment using the CloudFormation templates provided by this project | Fully automated deployment of a hosted web application to an S3 bucket with an optional CI/CD pipeline. By default, it also creates a Cognito Identity Pool and a sample Lex bot | Use when you want to have a infrastructure as code approach that automatically builds and configures the chatbot UI resources |
| 2 | Mobile Hub Deployment using the import file: lex-web-ui-mobile-hub.zip | Deploys a pre-built version of the chatbot UI to S3 and CloudFront. It creates the Cognito Identity Pool and a sample Lex bot. You can use the Mobile Hub Console to manage it or make changes (e.g. linking to another bot) | Use when you want an easy deployment using the AWS Console or for quick manual testing |
| 3 | Use the pre-built libraries from the dist directory of this repo | We provide a pre-built version of the chatbot UI component and a loader library that you can use on your web site as a stand alone page or as an embeddable iframe | Use when you have an existing site and want to add the chatbot UI to it by simply copying or referencing the library files |
| 4 | Use npm to install and use the chatbot UI as a Vue component | Enables developers to consume this project as an npm package that provides a Vue component. See the Npm Install and Vue Component Use section for details | Use when developing front-end based web applications built using JavaScript and bundled with tools such as webpack |
See the Usage and Deployment sections below for details.
This project provides a set of JavaScript libraries used to dynamically insert the chatbot UI in a web page. The chatbot UI is loaded and customized by including these libraries in your code and calling their functions with configuration parameters.
The chatbot UI can be displayed either as a full page or embedded in an iframe. In this section, you will find a brief overview of the libraries and configuration parameters. It is useful to get familiar with the concepts described in the Libraries and Configuration sections before jumping to the code examples.
The list below describes the libraries produced by this project. Pre-built versions of the libraries are found under the dist directory of this repository.
- Chatbot UI component. A UI widget packaged as a JavaScript reusable
component that can be plugged in a web application. The library is
provided by the
lex-web-ui.jsfile under the dist directory. It is bundled from the source under the lex-web-ui directory. This library is geared to be used as an import in a webpack based web application but can also be instantiated directly in a web page provided that you manually load the dependencies and explicitly pass the configuration. See the component's README for details - Loader. A script that adds the chatbot UI component library
described in the item above to a web page. It facilitates the
configuration and dependency loading process. The library
is provided by the
lex-web-ui-loader.jsfile under the dist directory. It is bundled from the sources under the src/lex-web-ui-loader directory. This library is used by adding a few script tags to an HTML page. See the loader README for details
The chatbot UI component requires a configuration object pointing to an existing Lex bot and to an Amazon Cognito Identity Pool to create credentials used to authenticate the Lex API calls from the browser. The configuration object is also used to customize its behavior and UI elements of the chatbot UI component.
The CloudFormation and Mobile Hub deployment methods, from this project, help with building a base configuration file. When deploying with those methods, the base configuration is automatically pointed to the the resources created in the deployment (i.e. Lex and Cognito).
You can override the configuration at run time by passing parameters to the library functions or using various dynamic configuration methods provided by the loader library (e.g. JSON file, events). For details, see the ChatBot UI Configuration Loading section of the loader library documentation and the Configuration and Customization section of the chatbot UI component documentation.
The examples below are organized around the following use cases:
To render the chatbot UI as a stand-alone full page, you can use two alternatives: 1) directly use the chatbot UI component library or 2) use the loader library. These libraries (see Libraries) provide pre-built JavaScript and CSS files that are ready to be included directly into an HTML file to display a full page chatbot UI.
When you use the chatbot UI component directly, you have to manually load the component's dependencies and provide its configuration as a parameter. The loader library alternative provides more configuration options and automates the process of loading dependencies. It encapsulates the chatbot UI component in an automated load process.
The loader library provides the easiest way to display the chatbot UI. The
entry point to this library is the lex-web-ui-loader.js script. This
script facilitates the process of loading run-time dependencies and
configuration.
If you deploy using the CloudFormation or Mobile Hub methods, you will
get an S3 bucket with the loader library script and related files in a
way that is ready to be used. Alternatively, you can copy the files from
the dist directory of this repository to your web server and include the
loader.
In its most simple setup, you can use the loader library like this:
<!-- include the loader library script -->
<script src="./lex-web-ui-loader.js"></script>
<script>
/*
The loader library creates a global object named ChatBotUiLoader
It includes the FullPageLoader constructor
An instance of FullPageLoader has the load function which kicks off
the load process
*/
// The following statement instantiate FullPageLoader and
// calls the load function.
// It is assumed that the configuration is present in the
// default JSON file: ./lex-web-ui-loader-config.json
new ChatBotUiLoader.FullPageLoader().load();
</script>Similar to the iFrame loading technique described later, the FullPageComponentLoader now provides an API allowing a subset of events to be sent to the Lex Web UI Component. These events are ping and postText. See the full page for description of this API.
For more details and other code examples about using the loader script in a full page setup, see the full page section of the loader documentation. You can also see the source of the index.html page used in the demo site.
Directly loading the chatbot UI component works at a lower level than using the loader library as described above. This approach can be used if you want to manually control the rendering, configuration and dependency loading process.
The entry point to the chatbot UI component is the lex-web-ui.js
JavaScript file. The UI CSS styles are contained in the lex-web-ui.css
file. The component depends on the Vue,
Vuex, Vuetify
and AWS SDK libraries. You
should either host these dependencies on your site or load them from a
third-party CDN.
The HTML code below is an illustration of directly loading the chatbot UI library and its dependencies.
NOTE: The versions of the links below may need to be pointed to the latest supported versions.
<html>
<head>
<!-- Font Dependencies -->
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Roboto:300,400,500,700|Material+Icons" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<!-- Vuetify CSS Dependencies -->
<link href="https://unpkg.com/vuetify@0.16.9/dist/vuetify.min.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<!-- LexWebUi CSS from dist directory -->
<link href="./lex-web-ui.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<!-- page specific LexWebUi styling -->
<style type="text/css">
#lex-web-ui-app { display: flex; height: 100%; width: 100%; }
body, html { overflow-y: auto; overflow-x: hidden; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- application will be dynamically mounted here -->
<div id="lex-web-ui"></div>
<!--
Vue, Vuex, Vuetifiy and AWS SDK dependencies must be loaded before lex-web-ui.js.
Loading from third party CDN for quick testing
-->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@2.5.3"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.0.1"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuetify@0.16.9"></script>
<script src="https://sdk.amazonaws.com/js/aws-sdk-2.149.0.min.js"></script>
<!-- LexWebUi Library from dist directory -->
<script src="./lex-web-ui.js"></script>
<!-- instantiate the web ui with a basic config -->
<script>
// LexWebUi supports numerous configuration options. Here
// is an example using just a couple of the required options.
var config = {
cognito: {
// Your Cognito Pool Id - this is required to provide AWS credentials
poolId: '<your cognito pool id>'
},
lex: {
// Lex Bot Name in your account
botName: '<your lex bot name>'
}
};
// load the LexWebUi component
var lexWebUi = new LexWebUi.Loader(config);
// instantiate Vue
new Vue({
el: '#lex-web-ui',
store: lexWebUi.store,
template: '<div id="lex-web-ui-app"><lex-web-ui/></div>',
});
</script>
</body>
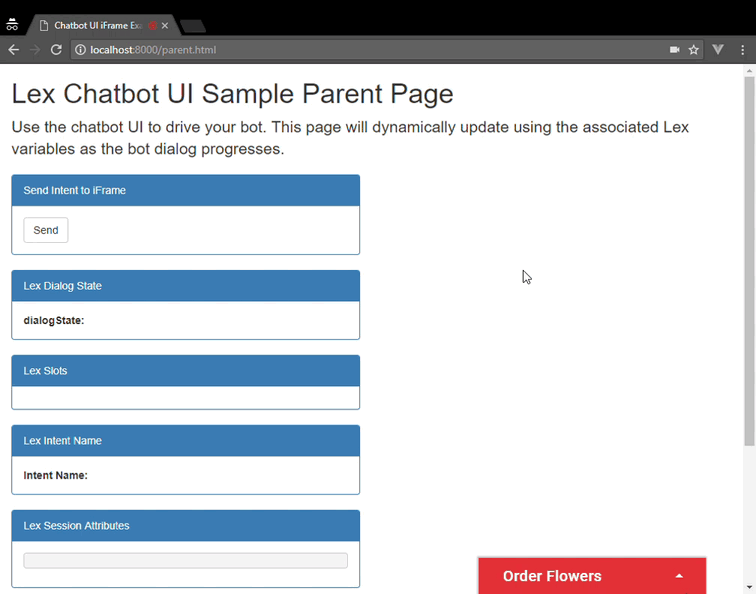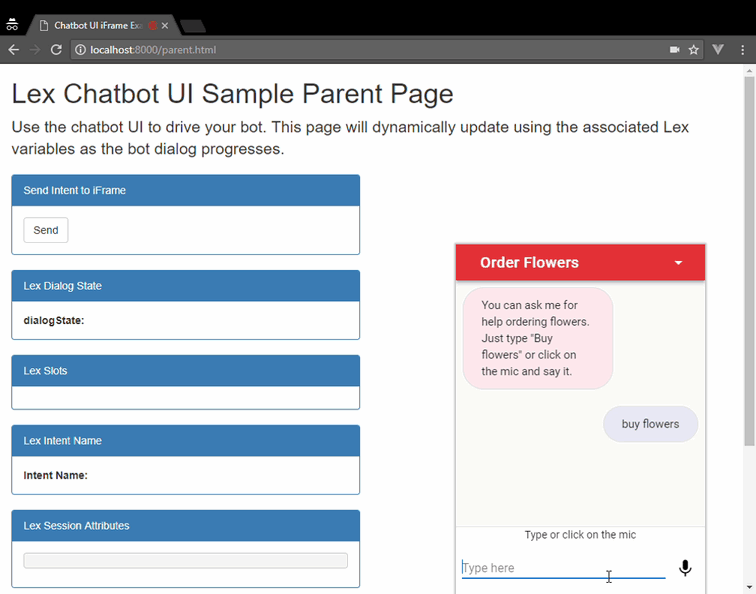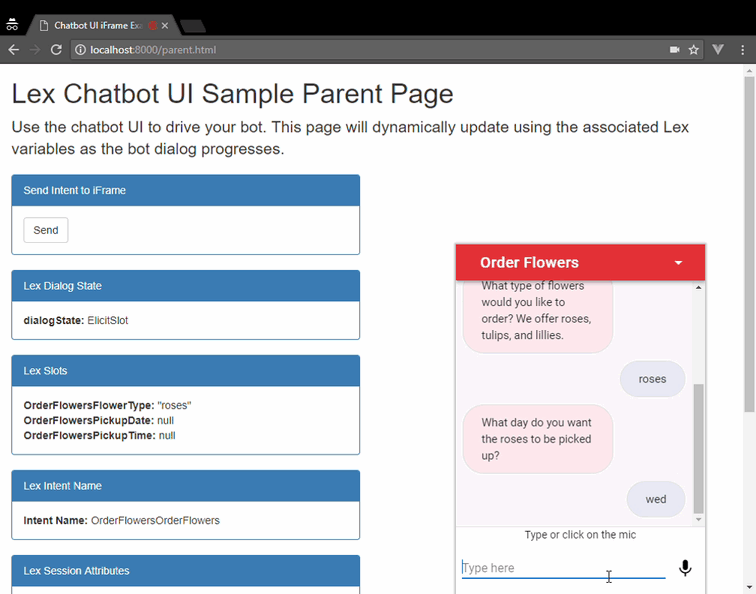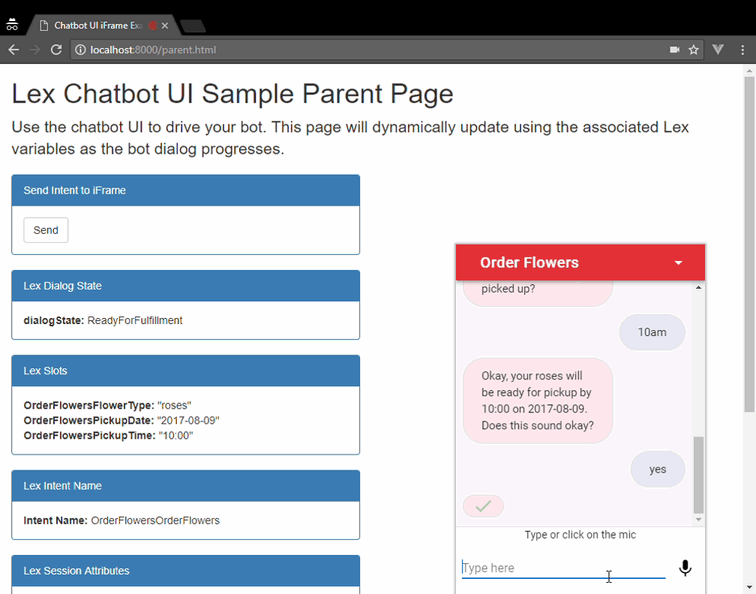
</html>You can embed the chatbot UI into an existing page using an iframe.
This approach provides a self-contained widget that can interact with
the parent page hosting the iframe. The lex-web-ui-loader.js loader
library provides the functionality to add it as an iframe in a page.
This loader script dynamically creates the iframe tag and supports passing asynchronous configuration using events and JSON files. It also provides an API between the iframe and the parent page which can be used to pass Lex state and other events. These features are detailed in the Iframe Embedding section of the library.
The HTML code below is a basic example of a parent page that adds the
chatbot UI as an iframe. In this scenario, the libraries and related
files from the dist directory of this repo are hosted in the same
directory as the parent page.
Please note that the loaderOptions variable has an iframeSrcPath
field which defines the path to the full page chatbot UI. This variable
can be pointed to a page like the one described in the stand-alone
page section.
<html>
<head>
<title>My Parent Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to my parent page</h1>
<!-- loader script -->
<script src="./lex-web-ui-loader.js"></script>
<script>
/*
The loader library creates a global object named ChatBotUiLoader
It includes the IframeLoader constructor
An instance of IframeLoader has the load function which kicks off
the load process
*/
// options for the loader constructor
var loaderOptions = {
// you can put the chatbot UI config in a JSON file
configUrl: './chatbot-ui-loader-config.json',
// the full page chatbot UI that will be iframed
iframeSrcPath: './chatbot-index.html#/?lexWebUiEmbed=true'
};
// The following statement instantiates the IframeLoader
var iframeLoader = new ChatBotUiLoader.IframeLoader(loaderOptions);
// chatbot UI config
// The loader can also obtain these values from other sources such
// as a JSON file or events. The configUrl variable in the
// loaderOptions above can be used to put these config values in a file
// instead of explicitly passing it as an argument.
var chatbotUiConfig = {
ui: {
// origin of the parent site where you are including the chatbot UI
// set to window.location.origin since hosting on same site
parentOrigin: window.location.origin,
},
iframe: {
// origin hosting the HTML file that will be embedded in the iframe
// set to window.location.origin since hosting on same site
iframeOrigin: window.location.origin,
},
cognito: {
// Your Cognito Pool Id - this is required to provide AWS credentials
poolId: '<your cognito pool id>'
},
lex: {
// Lex Bot Name in your account
botName: '<your lex bot name>'
}
};
// Call the load function which returns a promise that is resolved
// once the component is loaded or is rejected if there is an error
iframeLoader.load(chatbotUiConfig)
.then(function () {
console.log('iframe loaded');
})
.catch(function (err) {
console.error(err);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>For more examples showing how to include the chatbot UI as an iframe, see the source of the parent.html page and the Iframe Embedding documentation of the loader library.
You can use the npm package manager to install this project. The npm installation provides a library that you can import as a module into your JavaScript code. The component is built as a reusable Vue plugin. This approach is geared to be used in a webpack based project.
Package installation using npm:
# install npm package from github repo
npm install --save awslabs/aws-lex-web-ui
# you may need to install co-dependencies:
npm install --save vue vuex vuetify material-design-icons roboto-fontfaceThis is a quick example showing how to import the library in your project:
// assumes that a bundler like webpack will handle import/require
// using es6 module
import LexWebUi from 'aws-lex-web-ui';
// or using require
var LexWebUi = require('aws-lex-web-ui');
// import the debug non-minimized version
import LexWebUi from 'aws-lex-web-ui/dist/lex-web-ui';The source of the chatbot UI component resides under the lex-web-ui directory. For further details about the chatbot UI component see its README file.
This repository provides a sample site that you can use as a base for development. The site is a couple of HTML pages can be found in the src/website directory. The pages includes the index.html file which loads the chatbot UI in a stand-alone page and the parent.html which page loads the chatbot UI in an iframe.
These pages are the same ones that are deployed by the CloudFormation
and Mobile Hub deployment methods in this project. They use the
lex-web-ui-loader.js loader library to display and configure the chatbot
UI. You can run a development version of this sample site on your machine.
This project provides a simple HTTP server to serve the sample site. You can run the server using Node.js on your local machine or a test server.
The chatbot UI requires proper configuration values in the files located
under the src/config directory. Modify the values in the
lex-web-ui-loader-config.json and/or aws-config.js files under the
src/config directory. If you deployed the demo site using Mobile
Hub or CloudFormation methods provided by this project, you can copy
the automatically generated config files from the S3 buckets to your
development host.
As a minimum,you would need to pass an existing Cognito Pool Id
and Lex Bot name. For example, set the appropriate values in the
src/config/lex-web-ui-loader-config.json file:
...
cognito: {
"poolId": "us-east-1:deadbeef-fade-babe-cafe-0123456789ab"
},
lex: {
"botName": "myHelpBot"
}
...Before you run the local development server, you need to install the development dependencies with the command:
npm installTo start the HTTP server web on port 8000, issue the command:
# serves http://localhost:8000/index.html
# and http://localhost:8000/parent.html
npm startIf you want to hack the libraries under the src/lex-web-ui-loader
directory, the project provides a hot reloadable webpack dev
server setup with the
following command:
# runs on port 8000
npm run devFor a more advanced local host development and test environment, see the Dependencies and Build Setup documentation of the chatbot UI component.
This project provides deployment options using AWS CloudFormation or AWS Mobile Hub. Both deployment options can be used to launch a fully configured working demo site and related resources (e.g. Lex bot and Cognito Identity Pool).
The CloudFormation deployment is the preferred method as it allows to automatically build, configure and deploy the application (including an optional CI/CD pipeline) and it provides a higher degree of flexibility when integrating with an existing environment. The Mobile Hub deployment allows to quickly create a demo site with minimal pre-deployment configuration requirements but may need manual post-deployment steps.
The CloudFormation stack creates a web app in an S3 bucket which you can link from your site. The S3 bucket also hosts the configuration, JavaScript and CSS files which can be loaded by your existing web pages. The CloudFormation deployment is documented in the README file under the templates directory.
The Mobile Hub deployment is done by importing the lex-web-ui-mobile-hub.zip file using the Mobile Hub console. When this file is imported by Mobile Hub, it creates a project that hosts the chatbot UI web app in S3 and CloudFront. It also automatically deploys and configures a sample Lex bot based on the Order Flowers bot (you can later change it to import a different bot into the project) and an Amazon Cognito Identity Pool.
To launch with Mobile Hub:
- Sign in to the AWS Mobile Hub console
- Click this button:
- Once the project is imported, you should be able to browse to the sample web app by choosing Hosting and Streaming in the Mobile Hub project and clicking the links under Launch my web app
NOTE: If the Mobile Hub deployed site causes the browser to download the files instead of rendering it, you will have to re-sync the files to the S3 bucket using the S3 console or aws cli. See the Add Mobile Hub Hosting and Streaming to Your Mobile App section of the Mobile Hub documentation for details.