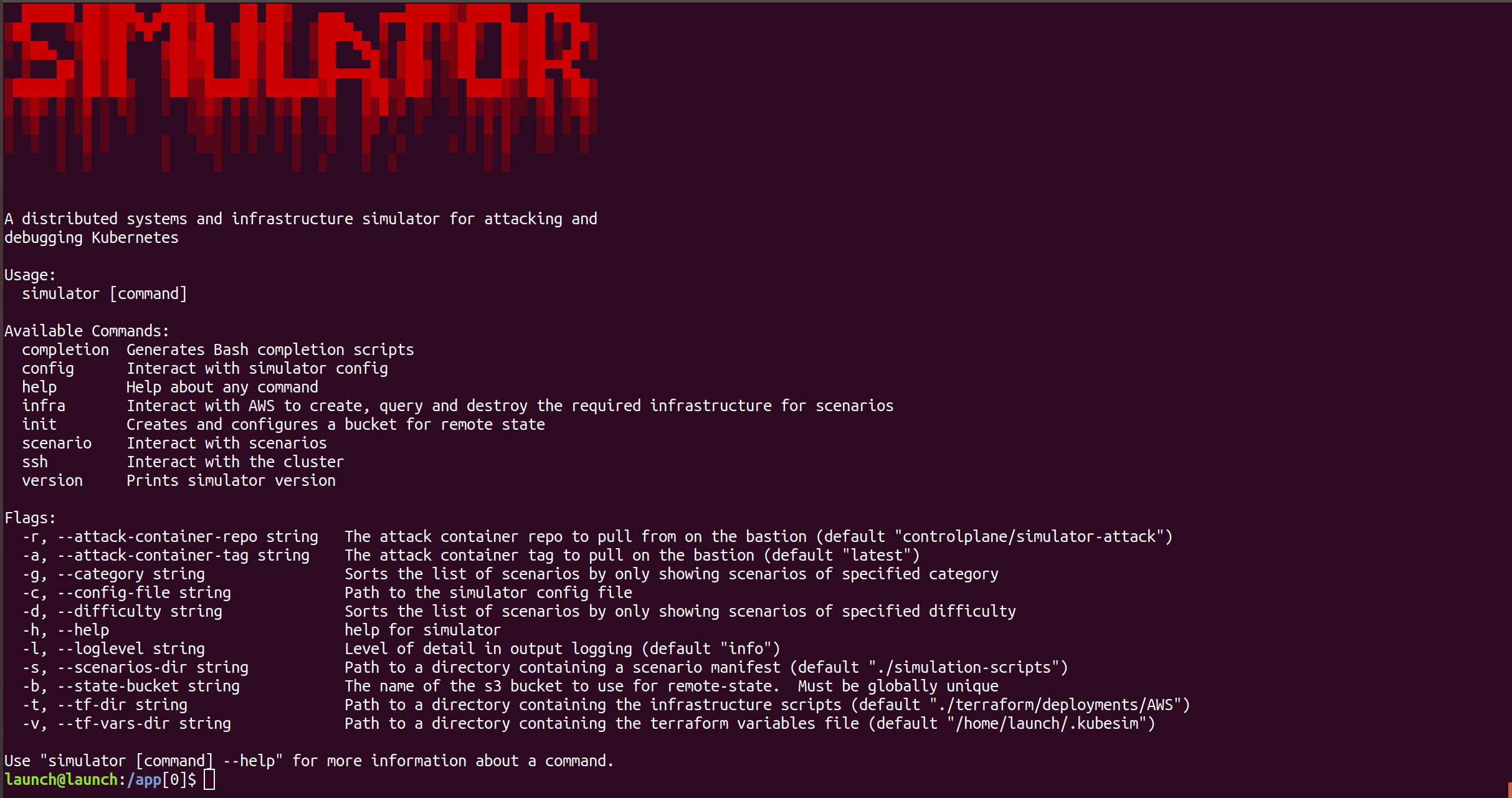
A distributed systems and infrastructure simulator for attacking and debugging
Kubernetes: simulator creates a Kubernetes cluster for you in your AWS
account; runs scenarios which misconfigure it and/or leave it vulnerable to
compromise and trains you in mitigating against these vulnerabilities.
For details on why we created this project and our ultimate goals take a look at the vision statement.
Ensure the AWS requirements are met and configured.
Clone this repository and run:
make run
This will drop you into a bash shell in a launch container. You will have a
program on the PATH named simulator to interact with.
Before you launch your environment, please see the How It All Works section to ensure you have the necessary credentials and permissions in place and know what you are standing up.
Create a remote state bucket for terraform
simulator init
You will be asked for the name for a S3 bucket for the Terraform remote state, which must be globally unique as per AWS standards. If this does not exist it will be created, otherwise the existing bucket will be used.
Create the infra if it isn't there
simulator infra create
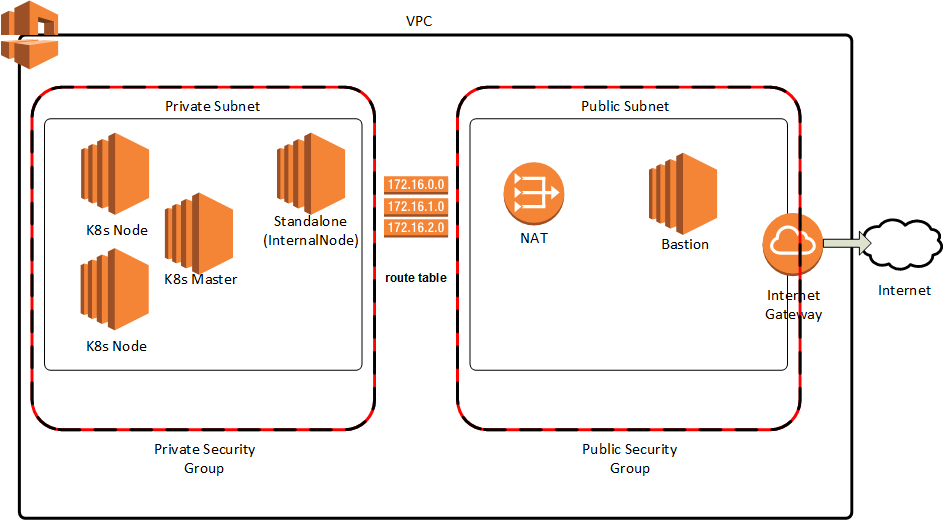
This will standup the infrastructure, including an initial Kubernetes Cluster
List available scenarios
simulator scenario list
This will list all currently available scenarios. You can filter the list by difficulty or category using the appropriate arguments
To get a better idea of what is involved in each scenario, e.g. node-shock-tactics
simulator scenario describe node-shock-tactics
Launch a scenario (sets up your cluster)
simulator scenario launch node-shock-tactics
This will launch your selected scenario.
Login to the environment
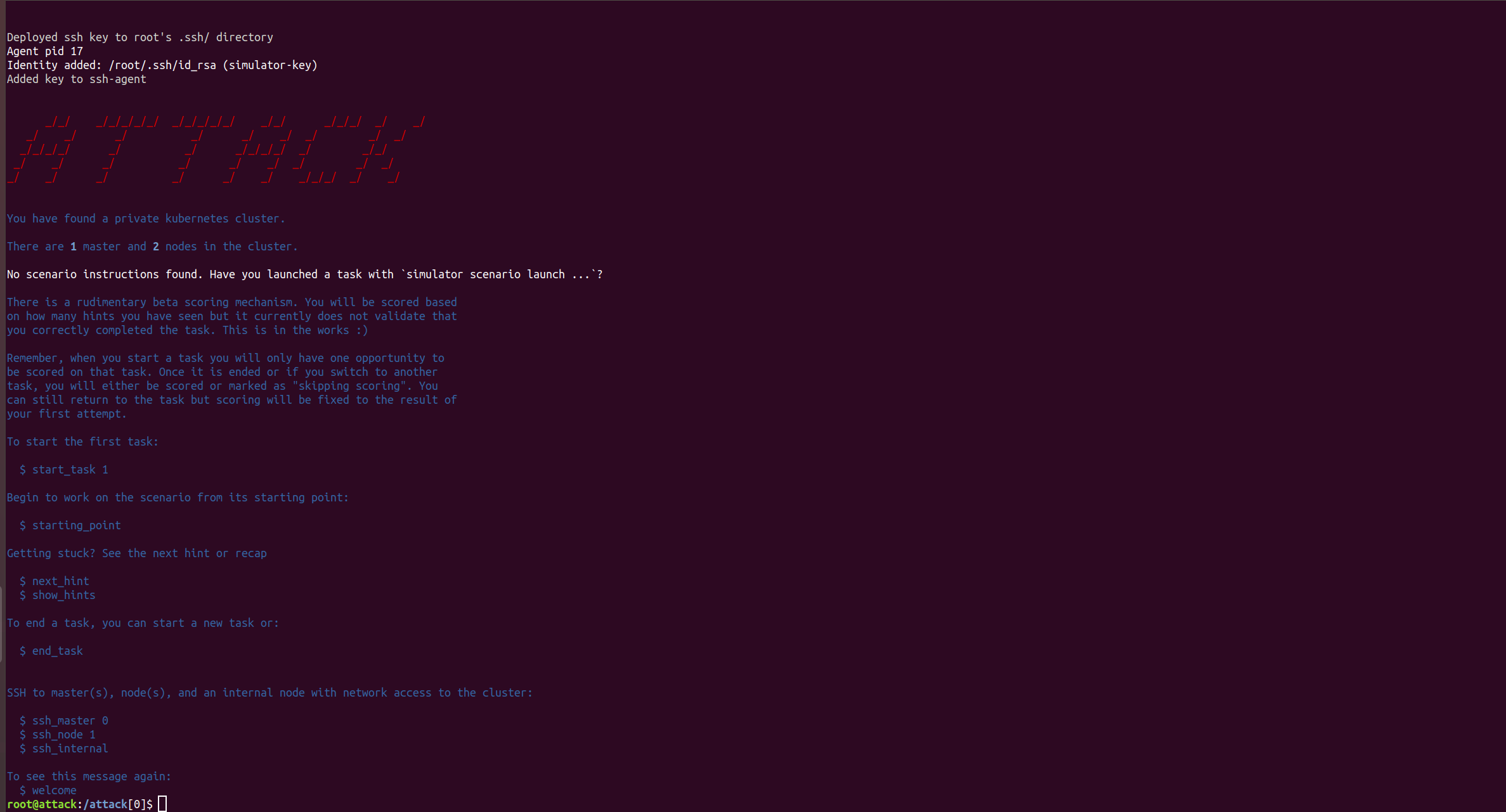
simulator ssh attack
Running simulator ssh attack logs you into a container running on the Bastion host. Upon login, an outline of the challenge will be displayed. In addition, shortcuts for logging into the master, or nodes, of the Kubernetes cluster and how to show hints and start tasks are displayed. starting_point logs you into the correct starting point for the task you have started in the scenario.
From within the ssh attack container you have access to a range of helper commands such as start_task, next_hint and show_hints.
Start task
start_task 1
The start_task command is used to inform the simulator which task you are undertaking with the number associated, and therefore what hints are available to aid you with that task.
Accessing hints
next_hint
The next_hint command will provide a hint to help you complete the task you have started with the start_task command.
Viewing all hints that have been requested
show_hints
The show_hints command will display all the hints you have requested to that point, in the task you have started.
Ending a task
end_task
or
start_task 2
The end_task command will end the task you are currently on and score you. This will also happen if you move onto the a new task with the start_task command. When you end a task in one of these ways, you will be scored 100 points minus the amount of hints you have displayed for that task at a value of -10 each. This is defined in the scenario task manifest.
Destroy your cluster when you are done
simulator infra destroy
Once you have finished you should destroy the environment to ensure that no additional costs are incurred. You run this command in the launch container.
The following scenarios are currently shipped with the simulator:
container-ambush
container-defeat-in-detail
container-phalanx-formation
etcd-inverted-wedge
master-shell-scrape
master-encirclement
network-feint
network-hammer-and-anvil
network-hedgehog-defence
network-swarming
node-amphibious-operations
node-raiding
node-shock-tactics
policy-echelon-formation
policy-fire-support
policy-force-dispersal
policy-vertical-envelopment
rbac-contact-drill
rbac-sangar
rbac-flanking-maneuver
rbac-shoot-and-scoot
secret-high-ground
secret-tank-desant
But you can write your own and we really welcome any contributions of new scenarios :)
Simulator uses terraform to provision its infrastructure. Terraform in turn honours all the rules for configuring the AWS CLI. Please follow these.
You can provide your credentials via the AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY environment variables, containing your AWS Access Key
and AWS Secret Key respectively. Note that setting your AWS credentials using
either these (or legacy) environment variables will override the use of
AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE and AWS_PROFILE. The AWS_DEFAULT_REGION and
AWS_SESSION_TOKEN environment variables are also used, if applicable.
https://www.terraform.io/docs/backends/types/s3.html
All the AWS_* configuration environment variables you have set will be propagated into the container
- If you get a timeout when running
simulator infra createafter about 10 minutes, the region you are using is probably running slowly. You should runsimulator infra destroyand then retrysimulator infra create AWS_REGIONvsAWS_DEFAULT_REGION- There have been some issues with the Go AWS client region configuration- Multi-account
Refer to the simulator terraform documentation
Simulator, whether run in the launch container or on the host machine, will generate its own SSH RSA key pair. It will configure the cluster to allow access only with this keypair and automates writing SSH config and keyscanning the bastion on your behalf using custom SSH config and known_hosts files. This keeps all simulator-related SSH config separate from any other SSH configs you may have. All simulator-related SSH files are written to ~/.kubesim and are files starting cp_simulator_
If you delete any of the files then simulator will recreate them and reconfigure the infrastructure as necessary on the next run
Refer to the scenario launch documentation
Refer to the Launch scenario flow documentation
Refer to the Tasks YAML file Format documentation
kubesim is a small script written in BASH for getting users up and running with simulator as fast as possible. It pulls the latest version of the simulator container and sets up some options for running the image. It can be installed with the following steps:
# cURL the script from GitHub curl -o kubesim https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-simulator/simulator/master/kubesim # Make it executeable chmod a+x kubesim # Place the script on your path cp kubesim /usr/local/bin
To ensure all Git hooks are in place run the following:
make setup-dev
Development targets are specified in the Makefile.
You can see all the available targets with descriptions by running make help
We follow the conventional commit specification. Please ensure your commit messages adhere to this spec.
- Simulator CLI tool - Runs in the launch container and orchestrates everything
- Launch container - Isolates the scripts from the host
- Terraform Scripts for infrastructure provisioning - AWS infrastructure
- Perturb.sh - Sets up a scenario on a cluster
- Scenarios - The scenario setup scripts and definitions
- Attack container - Runs on the bastion providing all the tools needed to attack a cluster in the given cloud provider
-
If you need to make changes to the format you should update this documentation.
-
Any changes should be accompanied by a bump of the version in the
kindproperty -
Use the
migrate-hintsdevtool to update the existing scenarios en-masse. You can make this tool available on your PATH by runningmake devtools
The simulator API docs are available on godoc.org:
Guidelines for contributors, and instructions on working with specific parts of Simulator are in the Contributor Guide.