English | 中文
KubeSphere is a distributed operating system providing cloud native stack with Kubernetes as its kernel, and aims to be plug-and-play architecture for third-party applications seamless integration to boost its ecosystem. KubeSphere is also a multi-tenant enterprise-grade container platform with full-stack automated IT operation and streamlined DevOps workflows. It provides developer-friendly wizard web UI, helping enterprises to build out a more robust and feature-rich platform, which includes most common functionalities needed for enterprise Kubernetes strategy, see Feature List for details.
The following screenshots give a close insight into KubeSphere. Please check What is KubeSphere for further information.
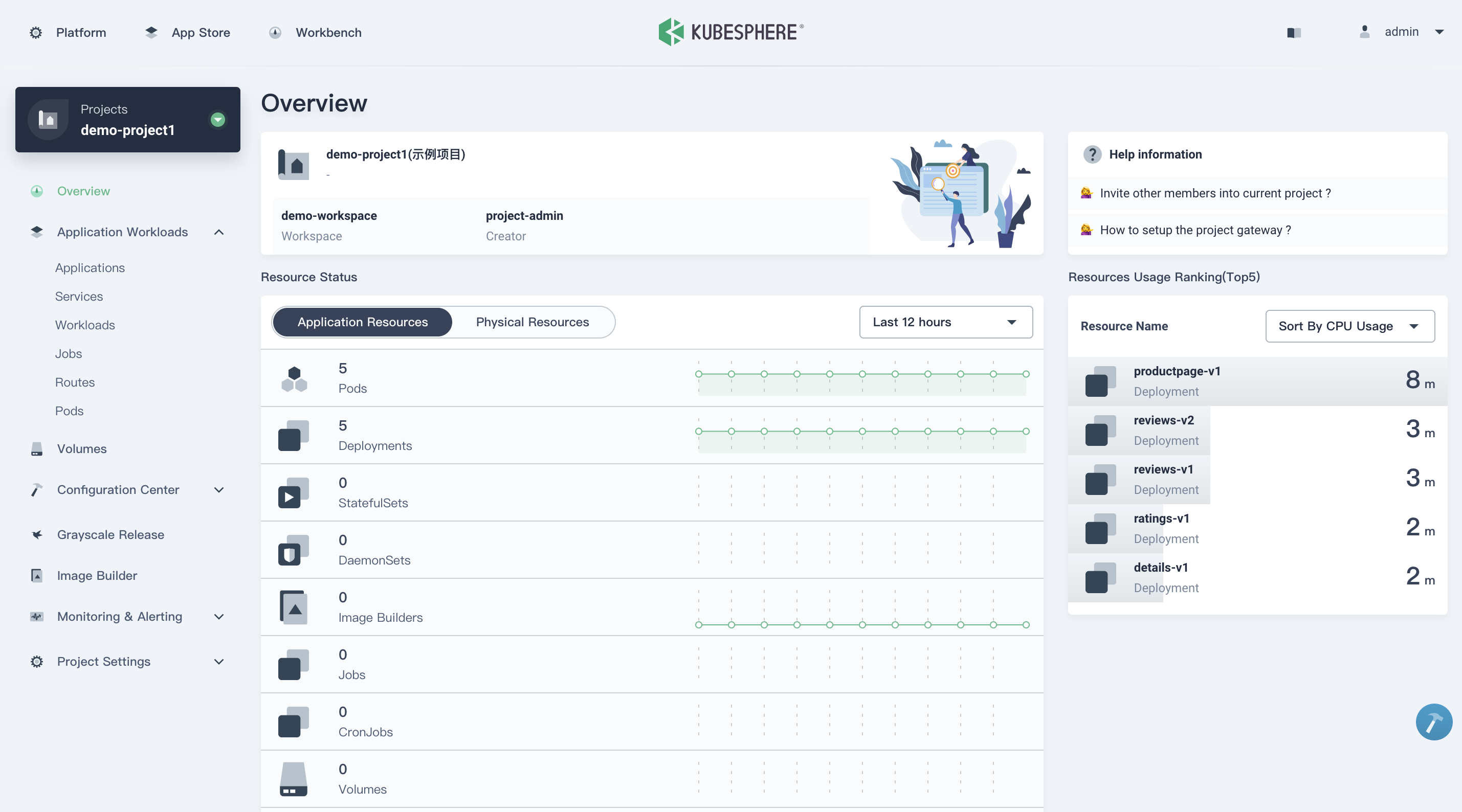
| Workbench | Project Resources |
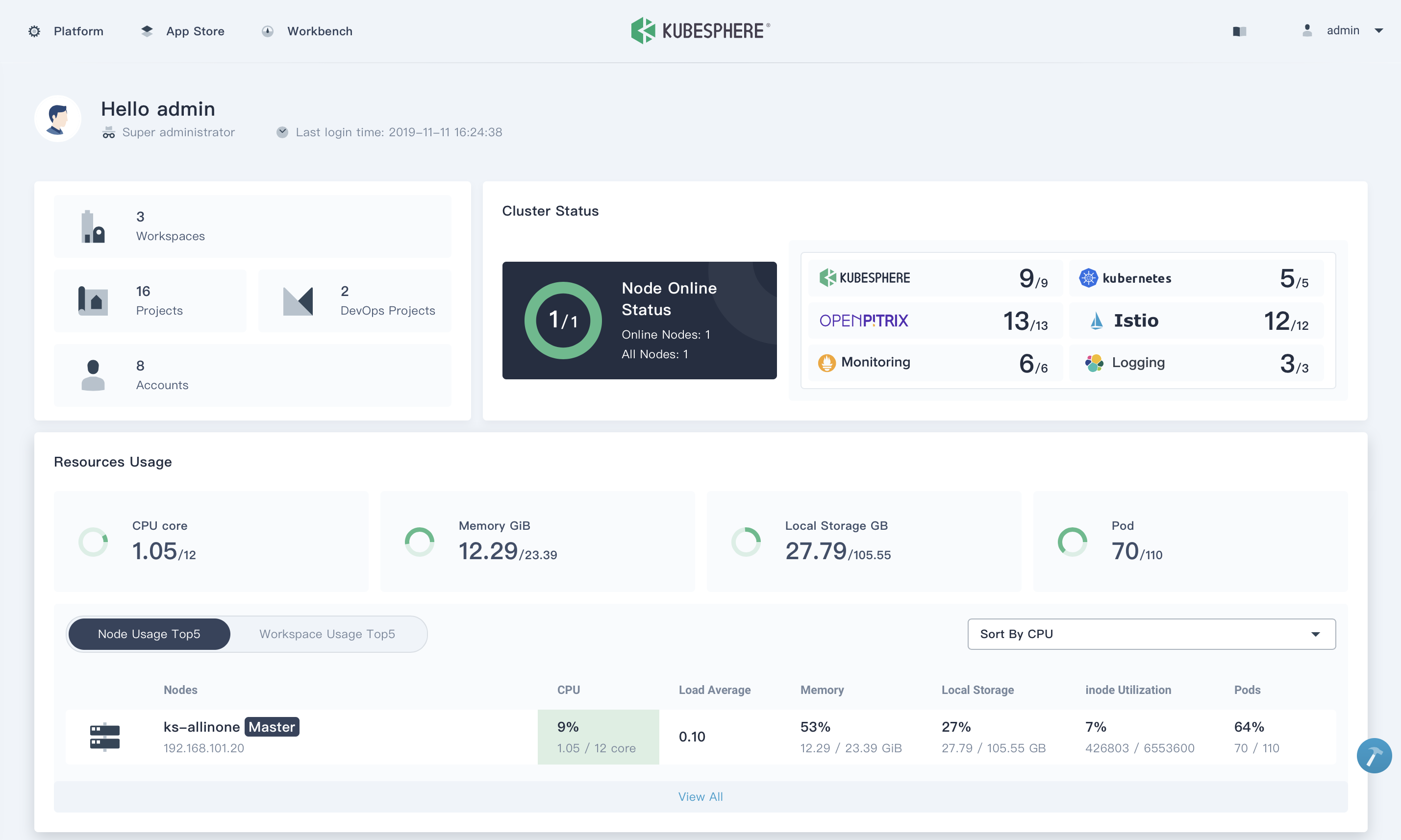 |
 |
| CI/CD Pipeline | App Store |
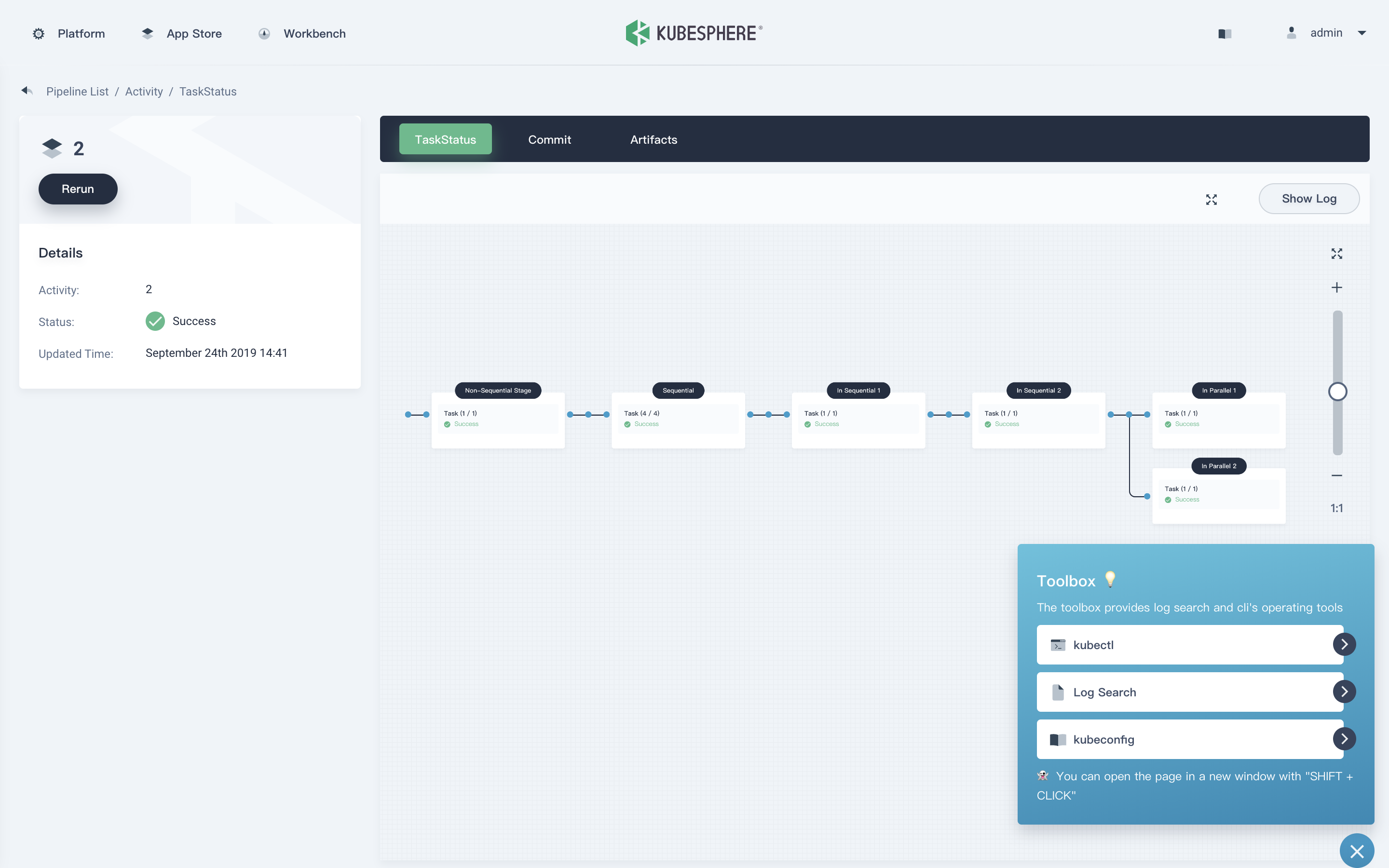 |
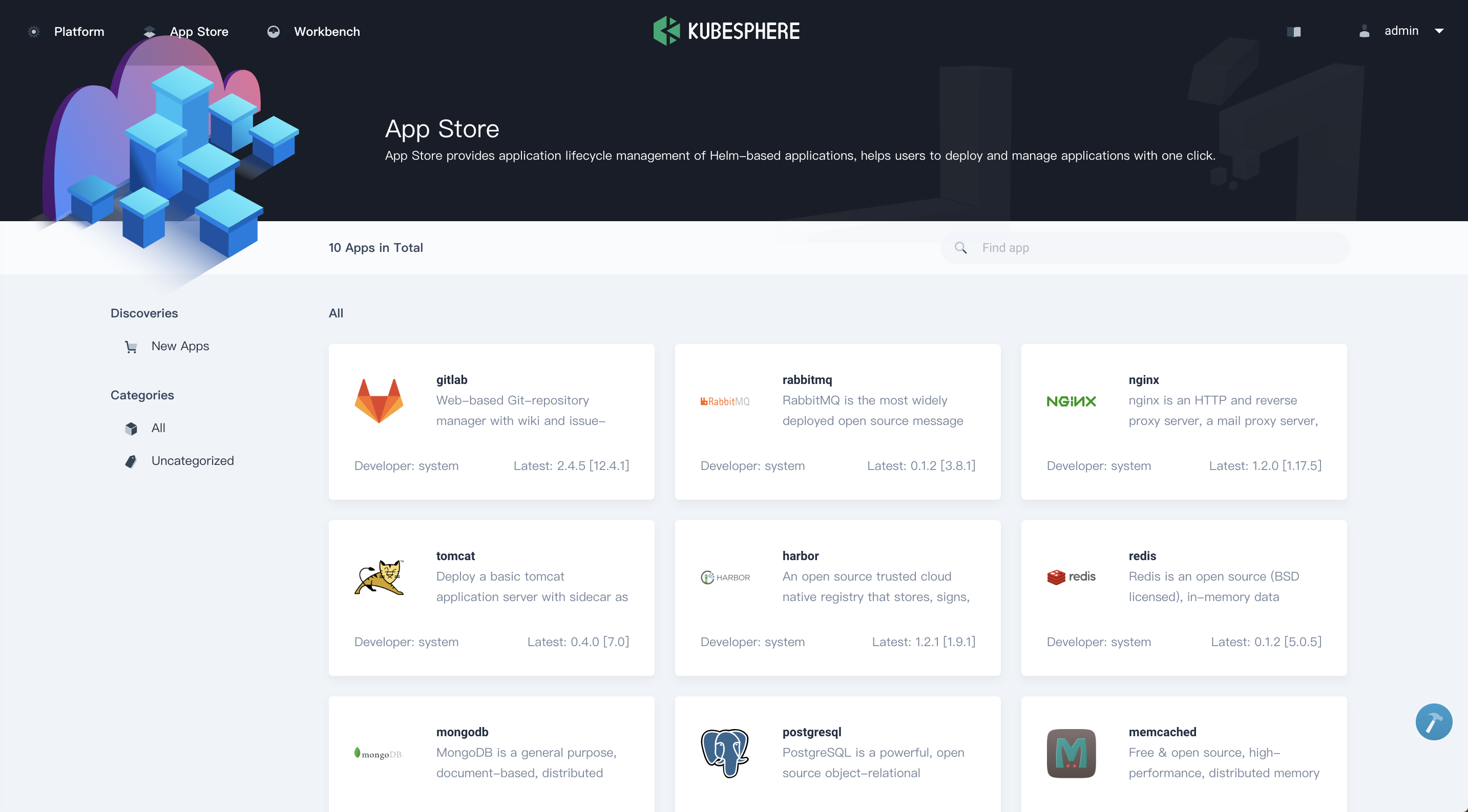 |
Using the account demo1 / Demo123 to log in the demo environment. Please note the account is granted view access. You can also have a quick view of KubeSphere Demo Video.
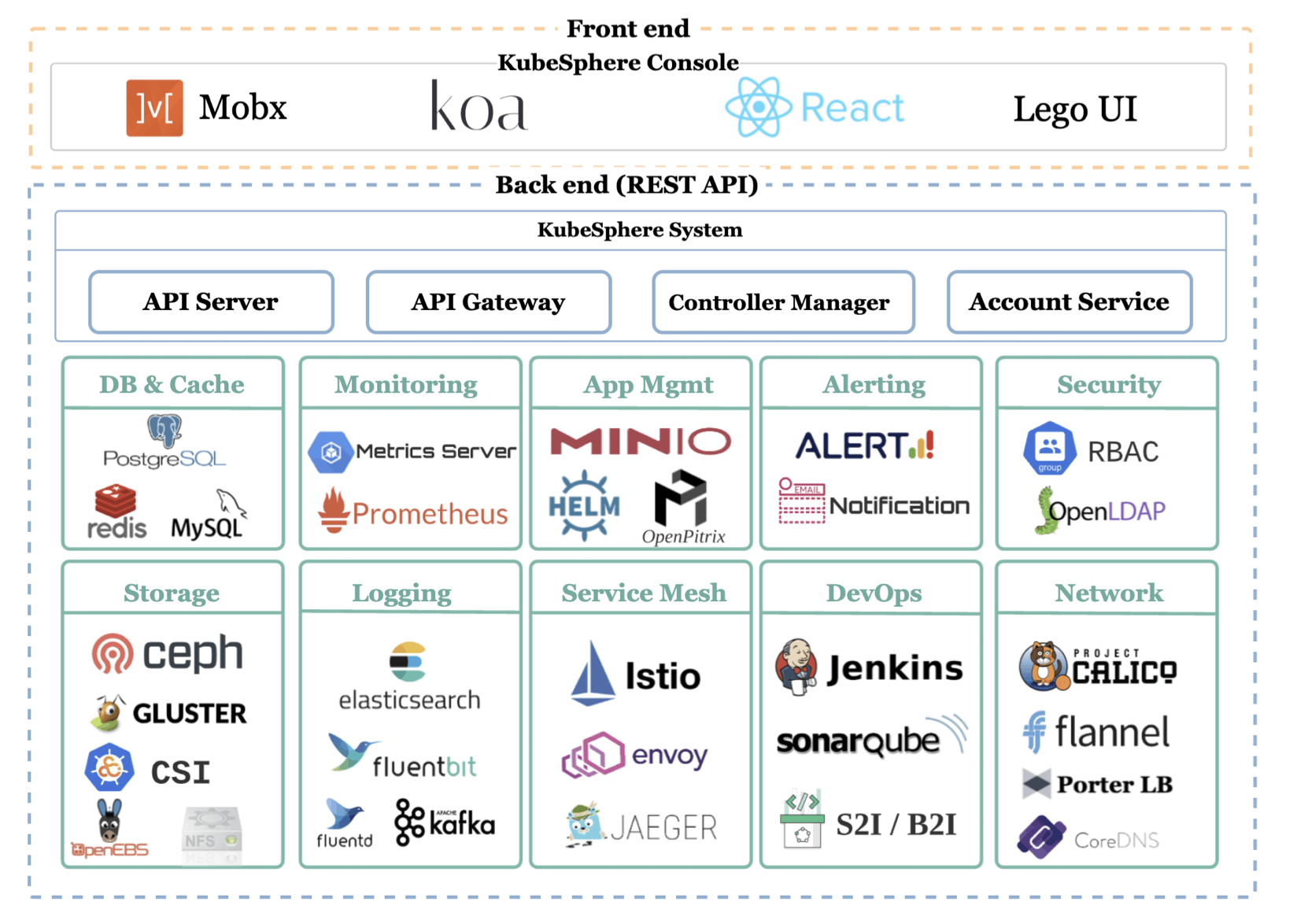
KubeSphere uses a loosely-coupled architecture that separates the frontend from the backend. External systems can access the components of the backend which are delivered as Docker containers through the REST APIs. See Architecture for details.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Provisioning Kubernetes Cluster | Support deploy Kubernetes on your infrastructure out of box, including online and air gapped installation |
| Kubernetes Resource Management | Provide web console for creating and managing Kubernetes resources, with powerful observability including monitoring, logging, events, alerting and notification |
| DevOps System | Provide out-of-box CI/CD based on Jenkins, and offers automated workflow tools including binary-to-image (B2I) and source-to-image (S2I) |
| Application Store | Provide application store for Helm-based applications, and offers application lifecycle management |
| Service Mesh (Istio-based) | Provide fine-grained traffic management, observability and tracing for distributed microservice applications, provides visualization for traffic topology |
| Rich Observability | Provide multi-dimensional monitoring metrics, and provides multi-tenant log query and collection, support alerting and notification for both application and infrastructure |
| Multi-tenant Management | Provide unified authentication with fine-grained roles and three-tier authorization system, supports AD/LDAP authentication |
| Infrastructure Management | Support node management and monitoring, and supports adding new nodes for Kubernetes cluster |
| Storage Support | Support GlusterFS, CephRBD, NFS, Local (default) etc. open source storage solutions, provide CSI plugins to consume storage from cloud providers |
| Network Support | Support Calico, Flannel, etc. open source network solutions, provides load balancer plug-in Porter for Kubernetes installed on physical machines |
| GPU Support | Support add GPU node, support vGPU, enables running ML applications on Kubernetes, e.g. TensorFlow |
Please See the Feature and Benefits for further information.
KubeSphere 2.1.1 was released on February 23rd, 2020. See the Release Notes For 2.1.1 for the updates.
KubeSphere can run anywhere from on-premise datacenter to any cloud to edge. In addition, it can be deployed on any version-compatible running Kubernetes cluster.
Kubernetes version:1.15.x, 1.16.x, 1.17.xHelm version>=2.10.0,see Install and Configure Helm in Kubernetes, (Helm v3 will be supported in KubeSphere 3.0.0)- An existing Storage Class in your Kubernetes cluster, use
kubectl get scto verify it - The CSR signing feature is activated in kube-apiserver, see RKE installation issue.
Install KubeSphere using kubectl.
- If there are 1 Core and 2 GB RAM available in your cluster, use the command below to set up a default minimal installation only. You can enable other components after installation if more resource added in later on. See Pluggable Components Installation for detailed information.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubesphere/ks-installer/master/kubesphere-minimal.yaml- If there are 8 Cores and 16 GB RAM available in your cluster, use the command below to install a complete KubeSphere, i.e. with all components enabled:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubesphere/ks-installer/master/kubesphere-complete-setup.yamlKubeSphere Installer can help you to install KubeSphere and Kubernetes on your linux machines. It provides All-in-One and Multi-Node installation options.
- Operating Systems
- CentOS 7.5 (64 bit)
- Ubuntu 16.04/18.04 LTS (64 bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7.4 (64 bit)
- Debian Stretch 9.5 (64 bit)
- Hardware
- CPU:2 Cores, Memory:4 GB, Disk Space:100 GB
Note: Please disable the firewall, or ensure your firewall meets the port requirements.
curl -L https://kubesphere.io/download/stable/latest > installer.tar.gz \
&& tar -zxf installer.tar.gz && cd kubesphere-all-v2.1.1/scripts
$ ./install.shChoose "1) All-in-one" to start the default minimal installation.
You can enable other components after installation, see Pluggable Components Installation.
- KubeSphere Documentation (En/中)
- API Documentation
This document walks you through how to get started contributing KubeSphere.
If you need any help with KubeSphere, please join us at Slack Channel.
Please submit any KubeSphere bugs, issues, and feature requests to KubeSphere GitHub Issue.
The Powered by KubeSphere page includes users list of the project. You can submit your institution name and homepage if you are using KubeSphere.
Currently, KubeSphere has released the following 5 major editions. The future releases include multicluster, big data, AI, SDN, etc. See Plans for 2.1.1 and 3.0.0 for more details.
Express Edition => v1.0.x => v2.0.x => v2.1.0 => v2.1.1 => v3.0.0


KubeSphere is a member of CNCF and a Kubernetes Conformance Certified platform
, which enriches the CNCF CLOUD NATIVE Landscape.