Removes all code except c/c++ type comments from source files. The idea is to see how well commented your source files are. If they tell a story without the need to understand the code, you're good to go. If not, somebody needs write a story.
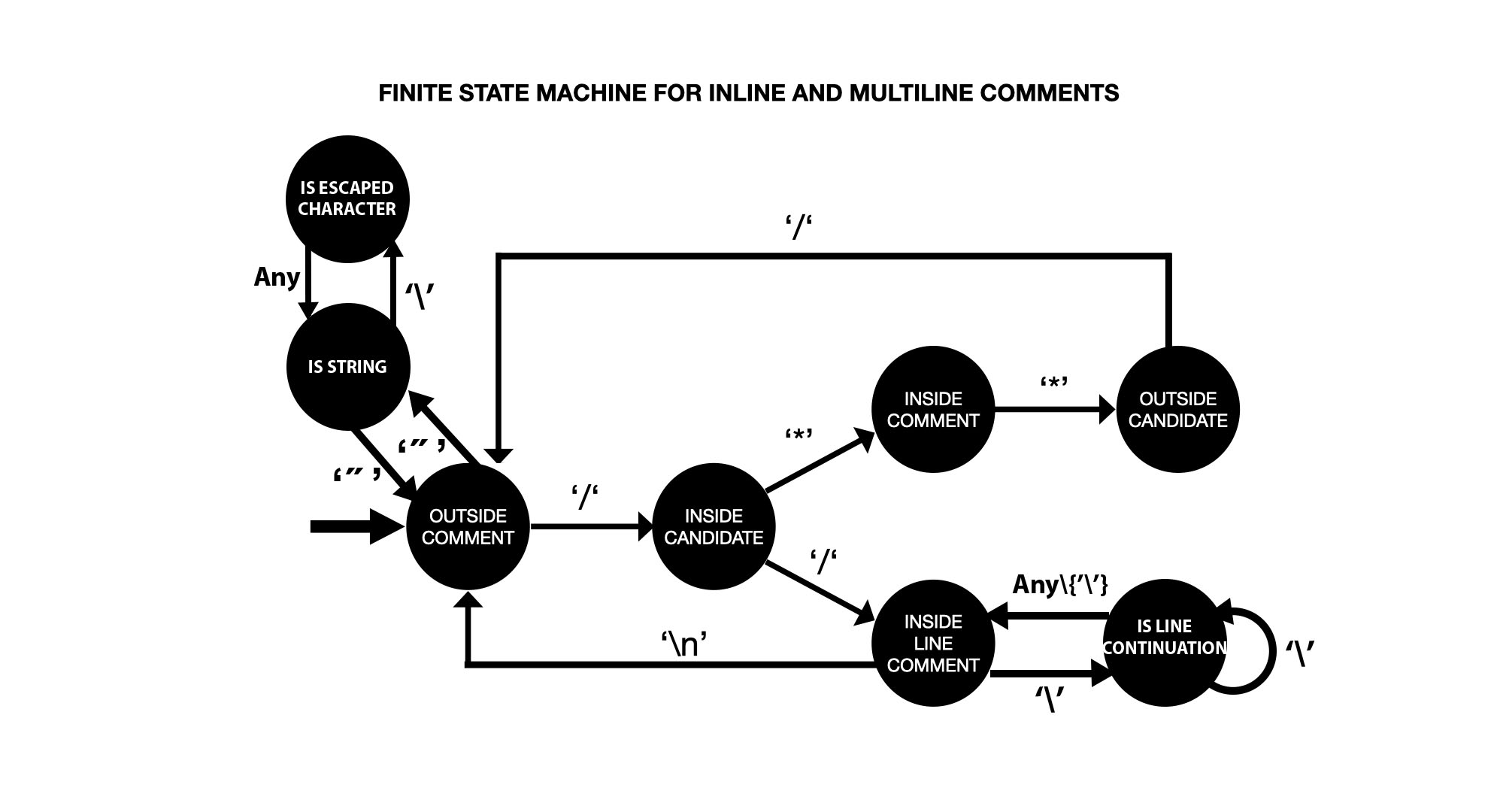
This program is also an exercice to get introduced to Finite State Machine and their use in syntax analysis.
Clone project:
$ git clone https://github.com/bouzinabdotcom/CCommentator
Go to directory:
$ cd CCommetator
Make:
$ make
To run to tool:
$ ./ccommentator filename [newfilename]
The brackets mean that newfilename is optional the output file will automatically be comments.filename
Example:
$ ./ccommentator source.c
Outputs comments.source.c on the same directory.
You could also make use of the shell's stdin and stdout.
Example:
$ ./ccommentator < main.c | grep comments
This will print the lines that contain the string comment in the comments of main.c
This project uses Catch2 for unit testing.
To test, go to test directory:
$ cd test
$ make
For now, two tests are available: test.removecode and test.comment_sm .
$ ./test.removecode
Let's use ccommentator on it's source code!
$ ./ccommentator main.c
main.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include<string.h>
#include "removecode.h"
void printhelp(){
/**
*
* Prints help
*/
puts("How to use:");
puts("$ ./ccommentator filename [newfilename]");
}
void parse_args(int argc, char *argv[], char** filename, char** newfilename){
/**
* Parses arguments and alters filename and newfilename
*
*
*/
switch(argc) {
case 1: //if only one arg is suplied (executable name)
// use standard io
//use filename as a flag to communicate the use of std io
*filename = (char*) malloc((strlen("std")+1)*sizeof(char));
strcpy(*filename, "std");
break;
case 2: //if one extra argument is suplied (missing newfilename)
*filename = *(argv+1); //point to it using filename
//allocate memory for newfilename as big as the size of filename plus a "comments." copied to the beginning
*newfilename = (char*)malloc((strlen(*filename)+strlen("comments."))*sizeof(char));
strcpy(*newfilename, "comments."); //put comments. in the beginning
strcat(*newfilename, *filename); //add filename after comment.
break;
case 3: //if 2 extra arguments are suplied
//just point to them
*filename = *(argv+1);
*newfilename = *(argv+2);
break;
default: //if more arguments -> too many arguments and print help
puts("Error: too many arguments.");
printhelp();
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
srand(time(NULL));
int random = rand();
char randomname[30];
sprintf(randomname, "tmp%d", random);
char *filename = NULL, *newfilename = NULL;
parse_args(argc, argv, &filename, &newfilename); //parse command line arguments
if(strcmp(filename, "std")==0){
buffer_to_file(stdin, randomname);
removeCode(open_iofile(randomname, 0), stdout);
remove(randomname);
}
else
removeCode(open_iofile(filename, 0), open_iofile(newfilename, 1)); //remove code
//Garbage Collection
if(argc==2 && newfilename!=NULL) free(newfilename);
if(argc==2 && filename!=NULL) free(filename);
//no need to collect the files since they only exist inside removeCode.
return 0;
}comments.main.c:
/**
*
/**
* Parses arguments and alters filename and newfilename
//if only one arg is suplied (executable name)
// use standard io
//use filename as a flag to communicate the use of std io
//if one extra argument is suplied (missing newfilename)
//point to it using filename
//allocate memory for newfilename as big as the size of filename plus a "comments." copied to the beginning
//put comments. in the beginning
//add filename after comment.
//if 2 extra arguments are suplied
//just point to them
//if more arguments -> too many arguments and print help
//parse command line arguments
//remove code
//Garbage Collection
//no need to collect the files since they only exist inside removeCode.
Can you understand what it does ?
This tool came to be after I saw one of my progamming profs. use a python script to strip source files out of their code leaving just the comments and as always I got curious about it. So I tried to replicate it using basic tests to search for comments and leave them while replacing characters outside the comments with whitespace. I got lost in the complexity and was sure there was a better way to doing it. The better (and easier) route was to ask for the script's source code, read it, understand it and then try to replicate it. So I did that and got a detailed response containing, in addition to the source code (that turned out to be using libclang through python), a roadmap to illuminate the pathway leading to creating my own version (Thanks a lot!).