This repository contains an unofficial CodeBLEU implementation that supports Linux and MacOS. It is available through PyPI and the evaluate library.
The code is based on the original CodeXGLUE/CodeBLEU and updated version by XLCoST/CodeBLEU. It has been refactored, tested, built for macOS, and multiple improvements have been made to enhance usability
Available for: Python, C, C#, C++, Java, JavaScript, PHP.
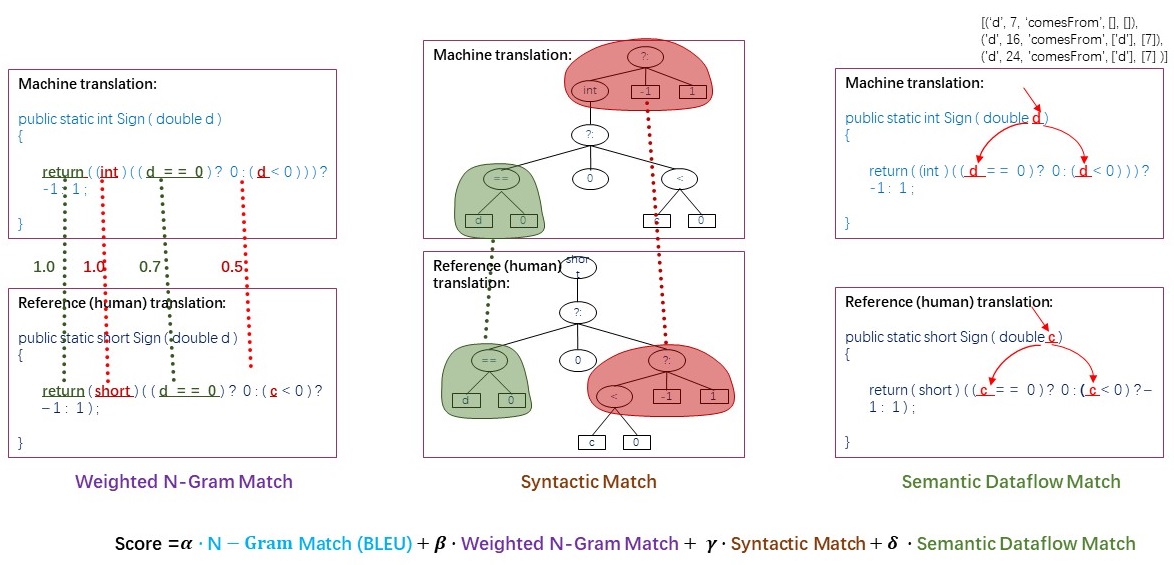
An ideal evaluation metric should consider the grammatical correctness and the logic correctness. We propose weighted n-gram match and syntactic AST match to measure grammatical correctness, and introduce semantic data-flow match to calculate logic correctness.
(from CodeXGLUE repo)
In a nutshell, CodeBLEU is a weighted combination of n-gram match (BLEU), weighted n-gram match (BLEU-weighted), AST match and data-flow match scores.
The metric has shown higher correlation with human evaluation than BLEU and accuracy metrics.
As this library require so file compilation it is platform dependent.
Currently available for Linux (manylinux) and MacOS with Python 3.8+.
The metrics is available as pip package and can be installed as indicated above:
pip install codebleuor directly from git repo:
pip install git+https://github.com/k4black/codebleu.gitfrom codebleu import calc_codebleu
prediction = "def add ( a , b ) :\n return a + b"
reference = "def sum ( first , second ) :\n return second + first"
result = calc_codebleu([reference], [prediction], lang="python", weights=(0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25), tokenizer=None)
print(result)
# {
# 'codebleu': 0.5537,
# 'ngram_match_score': 0.1041,
# 'weighted_ngram_match_score': 0.1109,
# 'syntax_match_score': 1.0,
# 'dataflow_match_score': 1.0
# }where calc_codebleu takes the following arguments:
refarences(list[str]orlist[list[str]]): reference codepredictions(list[str]) predicted codelang(str): code language, seecodebleu.AVAILABLE_LANGSfor available languages (python, c_sharp c, cpp, javascript, java, php at the moment)weights(tuple[float,float,float,float]): weights of thengram_match,weighted_ngram_match,syntax_match, anddataflow_matchrespectively, defaults to(0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25)tokenizer(callable): to split code string to tokens, defaults tos.split()
and outputs the dict[str, float] with following fields:
codebleu: the finalCodeBLEUscorengram_match_score:ngram_matchscore (BLEU)weighted_ngram_match_score:weighted_ngram_matchscore (BLEU-weighted)syntax_match_score:syntax_matchscore (AST match)dataflow_match_score:dataflow_matchscore
Alternatively, you can use k4black/codebleu from HuggingFace Spaces (codebleu package required):
import evaluate
metric = evaluate.load("dvitel/codebleu")
prediction = "def add ( a , b ) :\n return a + b"
reference = "def sum ( first , second ) :\n return second + first"
result = metric.compute([reference], [prediction], lang="python", weights=(0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25))Feel free to check the HF Space with online example: k4black/codebleu
Contributions are welcome!
If you have any questions, suggestions, or bug reports, please open an issue on GitHub.
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.
Official CodeBLEU paper can be cited as follows:
@misc{ren2020codebleu,
title={CodeBLEU: a Method for Automatic Evaluation of Code Synthesis},
author={Shuo Ren and Daya Guo and Shuai Lu and Long Zhou and Shujie Liu and Duyu Tang and Neel Sundaresan and Ming Zhou and Ambrosio Blanco and Shuai Ma},
year={2020},
eprint={2009.10297},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.SE}
}