CLI Node music player - a frontend for mplayer with Winamp key bindings.
Features:
- Smooth, one-character interactions with Winamp key bindings:
z - x - c - v - b: the bottom row of your keyboard works for playbackjto enter jump mode
- Supports jump to file with autocomplete
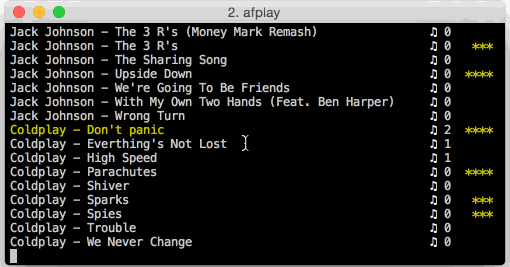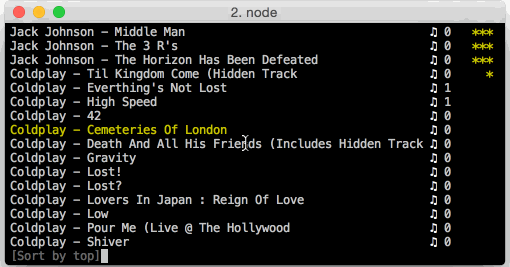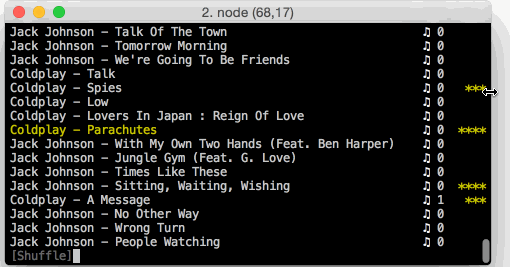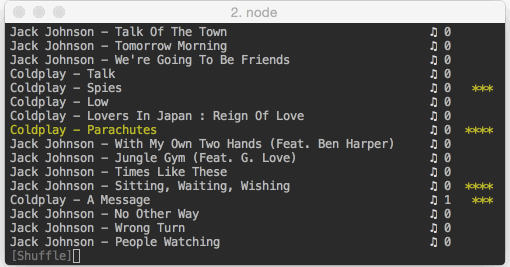
- Songs can be rated (1 - 5 stars); play count and last played are also tracked.
- Works on all major platforms, even the JSON metadata file is portable.
- The playlist can be sorted by rating, most frequently played, last played
- Shuffle, filter and repeat modes
npm install -g nplay
Install dependencies:
- Linux:
apt-get install mplayer - OSX: none, uses the builtin
afplayercommand - Windows: download mplayer, save
mplayer.exein the same directory wherenplay.jsis.
1.1.0: Added--merge1.0.0: Modernized the code base, and significantly improved the UI0.2.x: Added--ls
z - Previous
x / Enter - Play
c - Pause
v - Stop
b - Next
s - Shuffle mode (can combine with filter mode)
r - Repeat mode
f - Filter mode (ratings >= 3)
t - Top mode (sort by # played, then by rating; can combine with filter mode)
l - Last played mode (sort by last played)
1...5 - Rate song
j - Jump
Ctrl-C - Exit
- Esc: return to currently playing song
- Up / Down arrows: Move up and down one song at a time
- Page up / Page down: Move up and down half a screen at a time
- Home / End: Move to the beginning / end of the playlist
- Shuffle mode (
s): randomly shuffles all the songs. Can be combined with filter mode for a randomized, filtered playlist. - Filter mode (
f): filters the playlist to all the songs with a rating>= 3. - Top mode (
t): sorts the playlist by the number of times a song has been played, then by rating. Can be combined with filter mode to filter out unrated songs. - Last played mode (
l): sorts the playlist by last played
Each song has the following metadata:
- a rating between 1 to 5 (
1 ... 5) - a counter of times the song has been played. A song must play for at least 60 seconds for this counter to be incremented.
- a date for when the song was last played.
The ratings db is stored as a simple JSON file under ~/.nplay.db.json. Files are tracked by their file name only (no path), so you can copy the database to a different computer with different paths and still have everything work as long as the file names match.
You can pass paths (to directories or to files) to nplay to play the files. Directories are traversed recursively.
nplay /home/m/mp3
When no arguments are passed, nplay reads ~/.nplay.json and uses the paths set there. The idea is that you are mostly listening to the same library of files:
{
"directories": [ "/home/m/mp3" ]
}
To toggle between utf rendering and ASCII rendering, press u.
On OSX and Windows, nplay does not use utf-8 characters for rendering, because the default terminal font produces terrible rendering.
On OSX, this is fixable: make sure you switch the font from the default Monaco font to the Menlo font. On Windows, it seems that the default fonts just don't have good rendering for the star character.
Next, enable full utf-8 rendering by adding "utf": true to ~/.nplay.json, e.g.:
{ "directories": [ '...' ], "utf": true }This will give you the nicer symbols that you can see in the screenshots.
If you are using nplay on multiple computers, you can now easily merge two metadata files using --merge:
nplay --merge /path/to/other/.nplay.db.json > updated.json
mv updated.json ~/.nplay.db.json
--merge will read in a .nplay.db.json file from another computer and merge it with the local database. Any entries missing from the local db are added. If the two databases have different values for a rating, play count or other numeric value, the larger value is chosen (e.g. better rating, higher play count, more recent playback time).
The --merge operation does not overwrite the current database - it just produces stdout output, so you can preview the changes with a tool like diff or meld. Move the resulting file to ~/.nplay.db.json if you want to keep the changes.
--ls produces a list of files in the following format: rating,filename. E.g.:
5,/home/m/mp3/foo.mp3
This is useful for doing things managing files based on their rating:
nplay --ls | grep "^[4,5]," | sed 's/.,//g' | tr '\n' '\0' | xargs -0 -n 1 -I {} echo {}
Above, you might replace echo {} with cp {} /media/usb to copy files or rm {} to delete the file.
Note that the xargs -I {} is for OSX compatibility, and -p makes xargs confirm each command with y/n.