- Brian Collica
- James Koo
- Ryan Roggenkemper
- Ben Searchinger
This repository contains R and Python code for reproducing our analysis of data from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). The model is a two-stage process whereby participants are filtered based their estimated risk for being amyloid-beta positive, and then subsequently classified as either high or low risk for future Alzheimer's Disease conversion.
While our analysis approach included many difficulties, our overall result was that filtering patients based on Alzheimer's risk factors improved performance when predicting conversion probabilities.
All data required are available through ADNI and the Image and Data Archive provided by the Laboratory of Neuro Imaging at the University of Southern California.
The repository has five main directories: ADNI_data, processed_data, R, nitorch, and CNN. The following raw data files must be downloaded from ADNI and put into ADNI_data:
ADNIMERGE.csv: a collection of key metrics and observations for all ADNI participantsUPENNBIOMK_MASTER.csv: cerebrospinal fluid analysis (University of Pennsylvania).UCBERKELEYAV45_01_14_21.csv: AV45 PET analysis (University of California, Berkeley).UCBERKELEYFDG_05_28_20.csv: FDG PET analysis (University of California, Berkeley).UCBERKELEYAV1451_01_14_21.csv: tau PET analysis (University of California, Berkeley).ADNI_UCD_WMH_09_01_20.csv: white matter hyperintensities (University of California, Davis).ADNI_PICSLASHS_05_05_20.csv: medial temporal lobe measurements (University of Pennsylvania).
Additionally, image data must be downloaded and put into the appropriate place within CNN. Note that the image files must be Nifti (.nii) formatted. This is not necessarily the default file format within ADNI, however all image files can be downloaded as Nifti from the ADNI website. MRI image files go into the MRI_holdout and MRI_training files within the MRI_Data directory, and the corresponding csv file descriptions go into the MRI_csv directory. The same structure holds for PET scans. Only the holdout files are required for code replication, as trained models exist in the trained_cn_ad_mri and trained_cn_ad_pet_2 directories.
The holdout set used for final evaluation consists of data from 36 individuals. Their individual ADNI subject IDs can be obtained by utilizing the Advanced Search (beta) functionality in the Search tab at https://www.loni.usc.edu/.
- Search for pre-processed "MPR; GradWarp; B1 Correction; N3; Scaled" MRI images for CN, AD, SCM, EMCI, and LMCI participants with of the ADNI study.
- Download the 2,595 results as a
.csv. - Search for pre-processed "AV1451 Coreg, Avg, Std Img and Vox Siz, Uniform Resolution" PET images for CN, AD, SCM, EMCI, and LMCI participants with of the ADNI study.
- Download the 1,255 results as a
.csv. - Inner join the two files based on the Subject ID column to get observations of 36 unique participants to use as the holdout set.
- Save this merged file as
holdout.csvin theprocessed_datadirectory.
Once the data files have been placed in the ADNI_data and CNN directories, run the following scripts with the working directory set at the top level of the repo.
The R script, R/amyloid_pos.R, will output two .csv files to the processed_data directory: adnim.csv and amyloid_pos_data.csv. The dimensions of the files should be 15171 x 58 and 12330 x 57 respectively. amyloid_pos_data.csv contains new variables which describe a subject's amyloid-beta status to be used in subsequent analysis. The variables are as follows:
upenn_pos_bl: 1 if subject was amyloid-beta positive at baseline CSF measurements provided by Upenn, 0 otherwise.upenn_any_pos: 1 if subject was amyloid-beta positive at any time period CSF measurement provided by Upenn, 0 otherwise.av45_pos_bl: 1 if subject was amyloid-beta positive at baseline AV45 analysis provided by UC Berkeley, 0 otherwise.first_vis_pos: 1 if subject was amyloid-beta positive at their first visit AV45 analysis (not necessarily baseline) provided by UC Berkeley, 0 otherwise.av45_any_pos: 1 if subject was amyloid-beta positive at any time period AV45 analysis provided by UC Berkeley, 0 otherwise.abeta_pos: 1 if subject had a raw ABETA measurement below 977 at any time period, 0 otherwise.beta_pos_vote: 1 if any one ofabeta_pos,av45_any_pos, orupenn_any_posis 1, 0 otherwise.
The R scripts, R/MRI_volume.R and R/PET_volume.R, will output three .csv files to the processed_data directory: master_mri_volume.csv, master_pet_volume.csv, and master_pet_suvr.csv. The dimensions of the files should be 1127 x 47, 1108 x 127, and 1108 x 127 respectively.
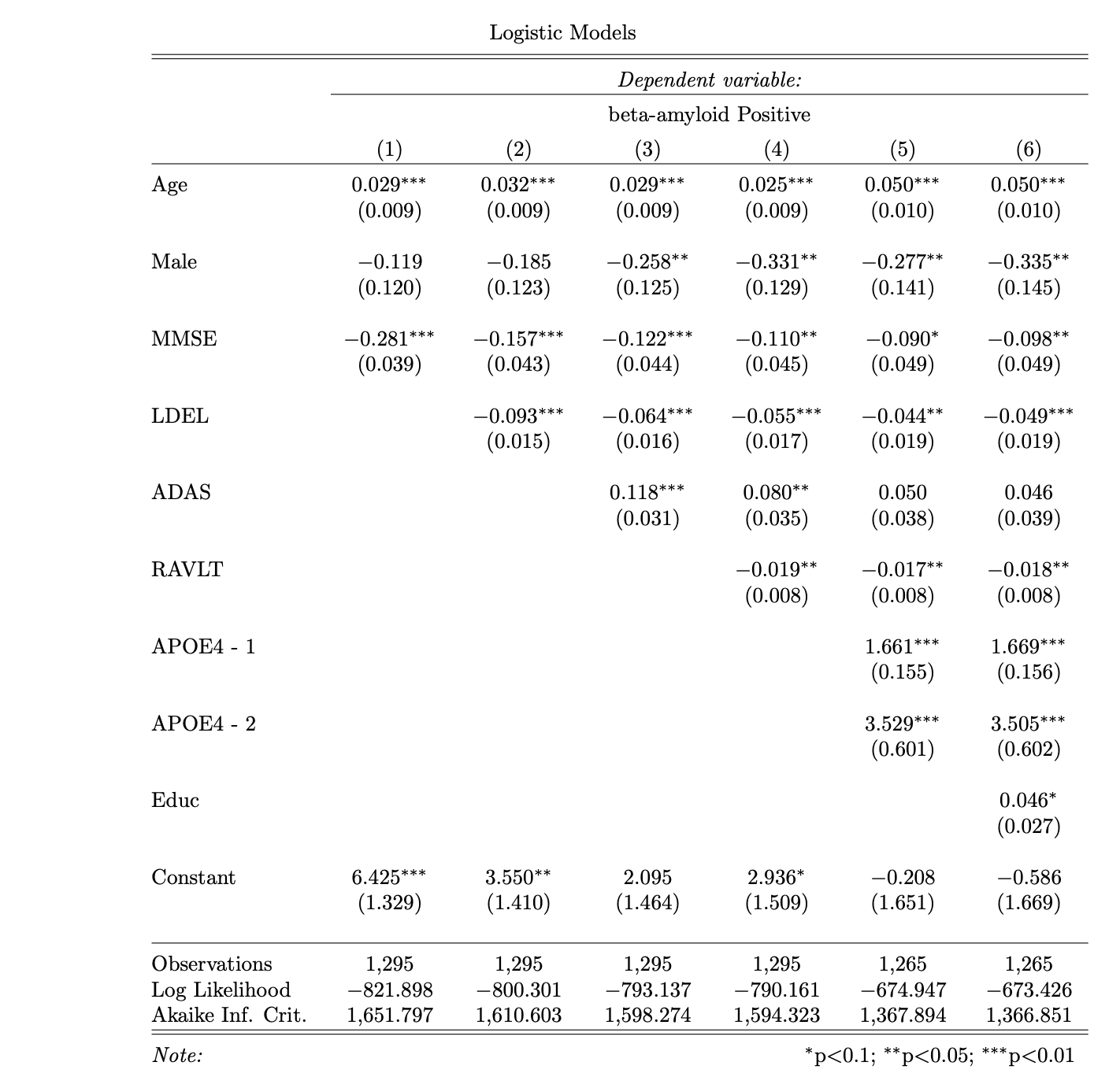
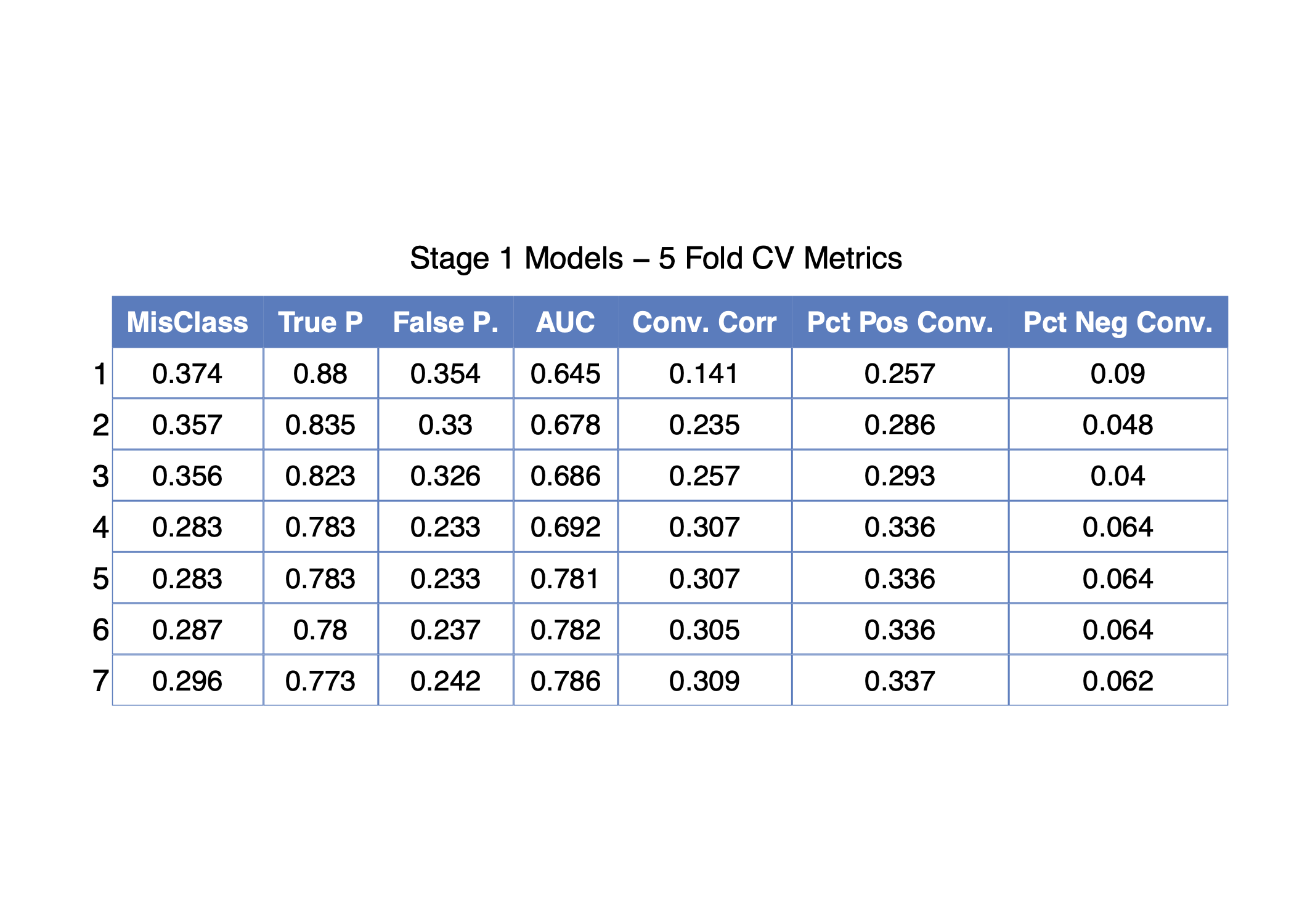
The R script, R/amyloid_model_analysis.R, performs 5-fold cross-validation for seven different candidate models of amyloid-beta positivity as a function of baseline measurements. The binary response variable is beta_pos_vote as described above. All candidate models are variations of logistic regression with different classes of predictors. In general, the models start out by containing variables collected from minimally invasive sources, such as cognitive assessment tests, and subsequently add predictors loosely based on the level of invasiveness to the subject required to obtain the information.
For example, the predictors for model 1 include age, sex, and the subject's baseline score on the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE_bl). Model 2 includes age, sex, MMSE, and the subject's baseline delayed recall score on the Logical Memory test (LDELTOTAL_bl), and so on. Models 1 - 4 do not contain any genetic markers, but models 5 - 7 include genetic results for the presence of Apolipoprotein E on either one (APOE_1) or two (APOE_2) alleles. The regression table below displays results for models 1 - 6 using observations from baseline visits of the full training data.
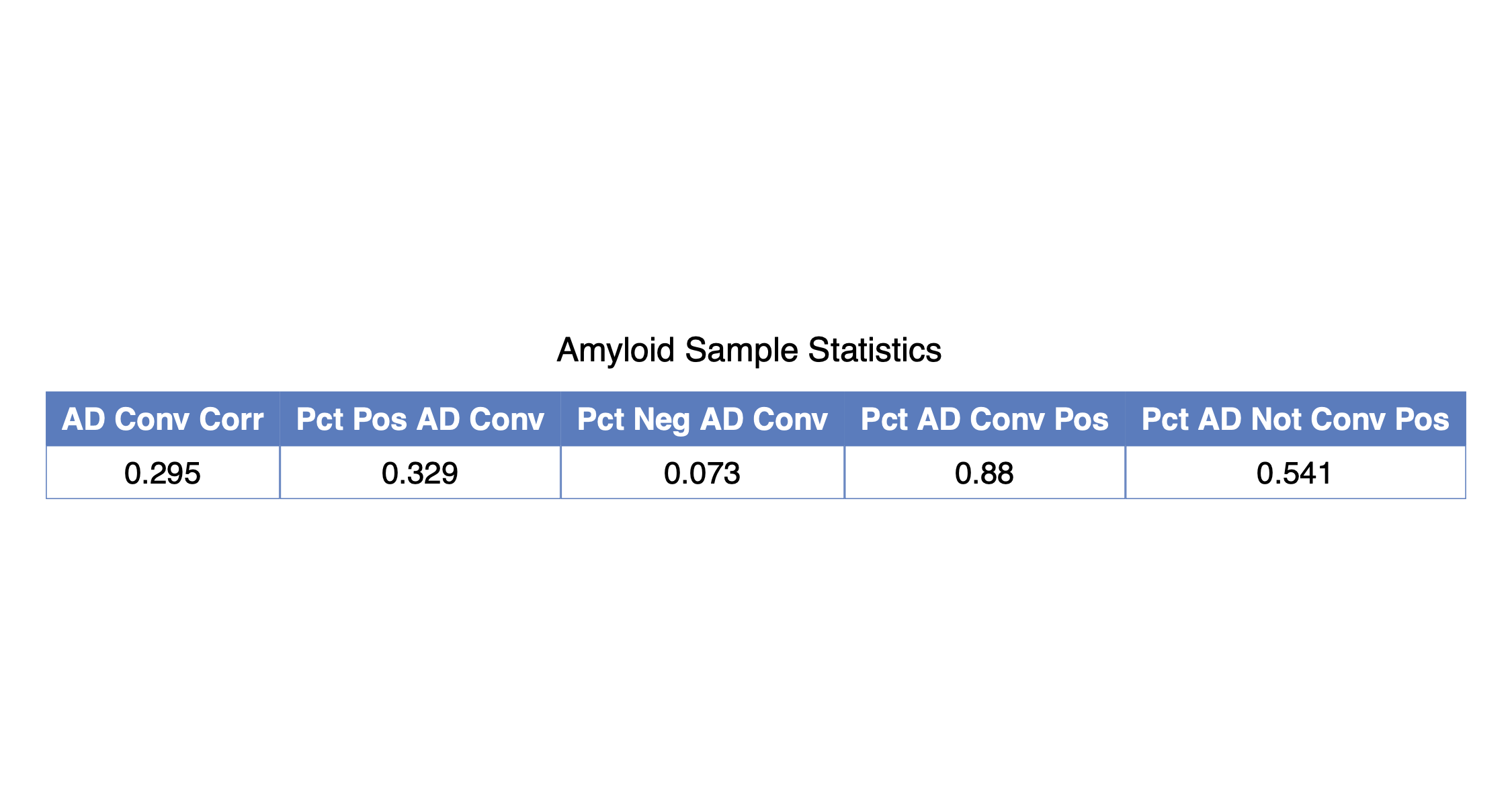
The script will output two .csv files to the processed_data directory: amyloid_cv_table.csv and amyloid_sample_table.csv. The first contains the cross-validated estimates of the various performance metrics, and the second contain summary statistics regarding the relationship between amyloid-beta positivity and Alzheimer's Disease conversion rates in the sample of individuals considered in this analysis.
PDFs and PNGs of these tables are also created and saved in the figures directory.
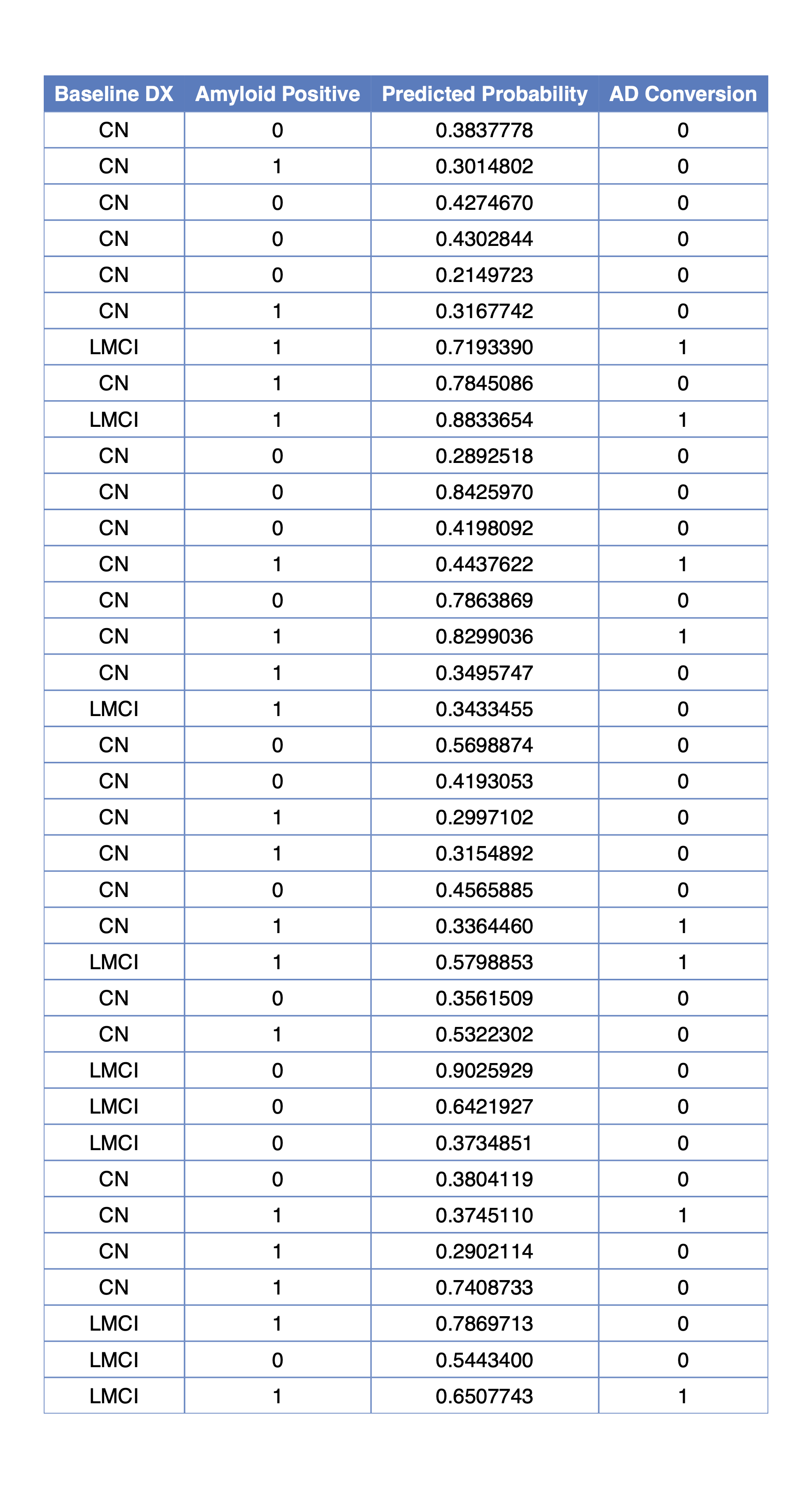
The R script, R/stage1.R, predicts amyloid-beta status for the 36 individuals included in the holdout set and outputs the results into stage1_table.csv in the processed_data directory, along with figures in the figures directory.
The iPython notebooks MRI_Ensemble and PET_Ensemble each use a 9 layer 2D CNN to classify patients in the training set as either cognitively normal (CN) or Alzheimer's disease (AD). They consider MRI and tau PET scans separately, to later ensemble together.
Each model uses 10 coronal central brain slices to ultimately classify patients as CN or AD. This means there are 10 models for each modality each corresponding to a specific slice. These slices are preconfigured, and whole brain scan Nifti files should be placed into the correct directories without modifications.
A validation split of 10% of the training dataset is automatically computed. Then, for each slice, models are trained using 5 fold cross-validation. The fold with the highest validation accuracy is retained and saved into the corresponding directory, noted above.
If only replication is desired, then it's not advisable to retrain all models as the process is time consuming. However, the code is all designed to be parallelized, so access to a computing cluster significantly increases computation speed. Whether or not the models are retrained, the script then serially loads in each model for holdout prediction. Each of the
The processed_data directory by default.
Note that the steps laid out above are for a single modality, that is either PET or MRI. While these steps are the same, they must be run twice--once for each modality.
Also note that nitorch is a custom package that only appears to exist in this Github repository. We do not recommend trying to modify these files or install any other packages called nitorch.
There should now be two additional csv files within the processed_data directory, one with MRI predictions and one with PET predictions. There should also be a file named final_preds.csv within the directory, which gives the true AD conversion labels as well as the Stage 1 model prediction labels. The default ensemble predictions are also contained in final_preds.csv, but they can be recalculated using the rule MRI_prediction + PET_prediction >= 1 if desired. This gives equal weighting to both modalities, and guarantees that consistent positive predictions for a single modality will guarantee a positive prediction for the ensemble.
The iPython notebook Analysis.ipynb within the CNN directory assess the accuracy metrics of the ensemble Stage 2 model. If the ensemble predictions were recalculated, then the recalculated values should replace the default values in the MRI_PET_Ensemble column of final_preds.csv. The script then generates the confusion matrices shown below, and saves them in the figures directory.
As an alternative to the neural network ensemble, we also propose using a penalized logistic regression on brain volumetric measurements provided by labs at UPENN and UC Berkeley. The measurements come from MRI and tau PET scans. (add more here)
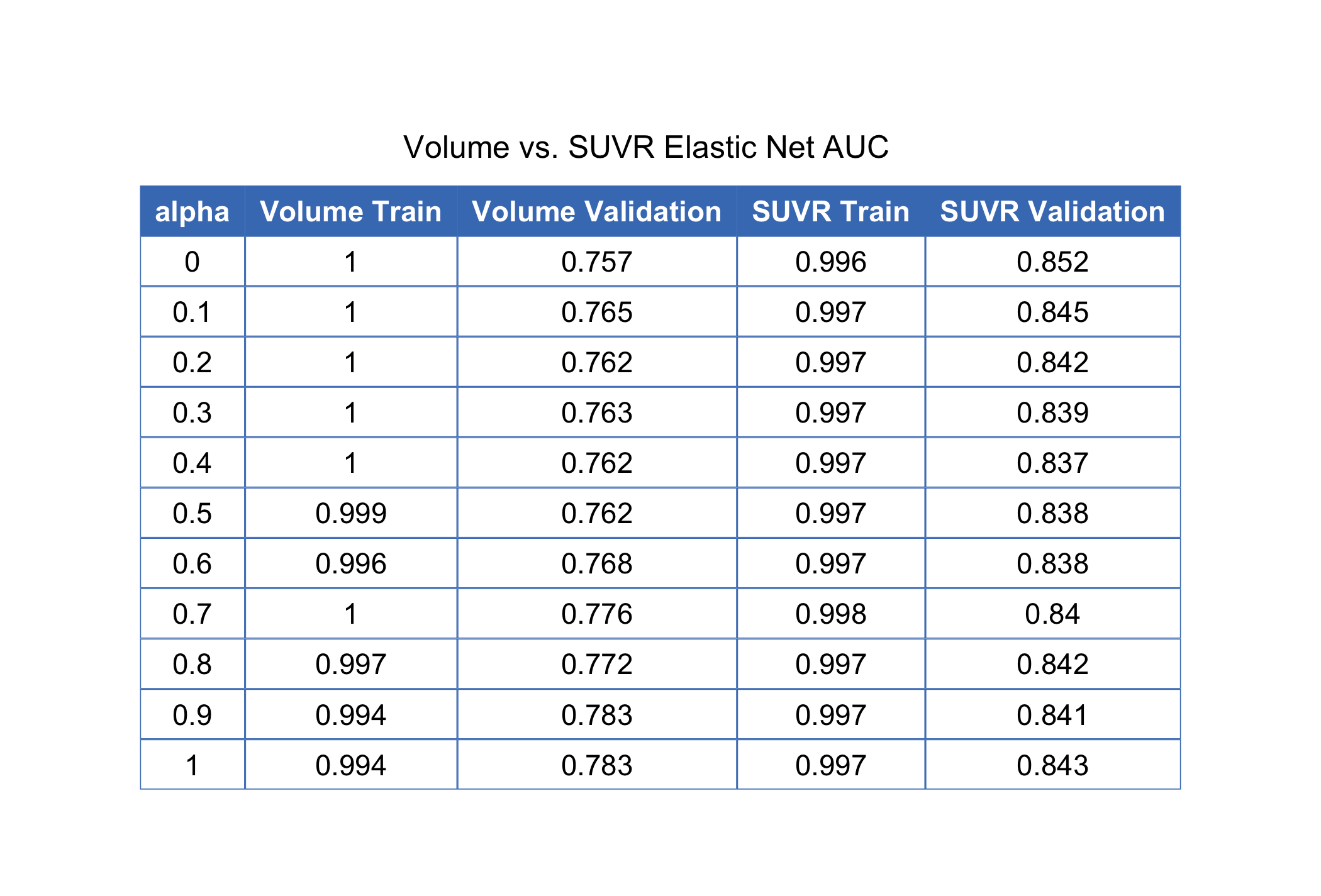
The R script, R/volumetric_analysis.R, combines volume measurements from MRI scans separately with volume and SUVR measurements from tau PET scans. The data are then split into training and validation sets leaving out the holdout patients entirely. A custom labeling scheme is implemented to code patients as either AD or not which replicates the type of individuals in the holdout set and also what one might normally encounter in a clinical setting.
The script outputs two training sets (training_set_volume.csv and training_set_suvr.csv) and two validation sets (validation_set_volume.csv and validation_set_suvr.csv) to the processed_data directory. Figures of the AUC tables for all models are also output, as well as a .csv containing the values. The model with the best cross-validated performance tends to use the MRI volume + PET SUVR data with alpha = 0. The corresponding penalty is approximately 0.0518844.
The training and validation sets are combined into a final file titled final_set0.0518844239876985.csv which houses the full penalty value and is written to the processed_data directory. This file is then read into R/stage2.R script which fits the model on the combined data and predicts the results for individuals in the holdout set who received these scans. Those predictions are written to processed_data/volume_holdout_preds.csv.