Official repository for A Comparison of Discrete and Soft Speech Units for Improved Voice Conversion. Audio samples can be found here. Colab demo can be found here.
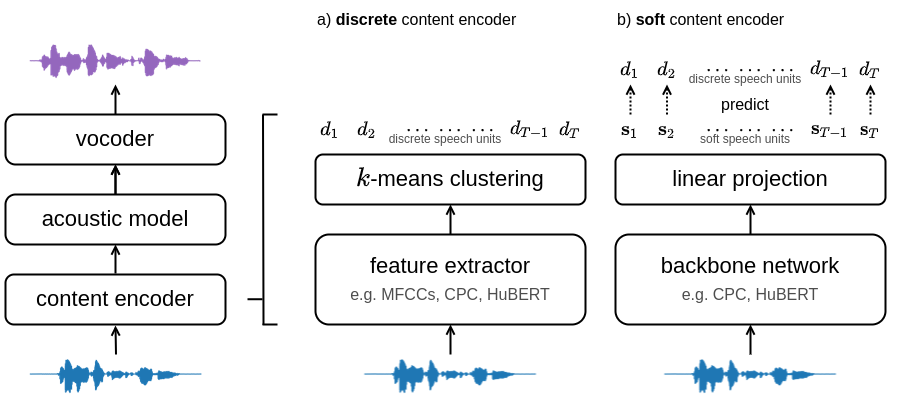
Abstract: The goal of voice conversion is to transform source speech into a target voice, keeping the content unchanged. In this paper, we focus on self-supervised representation learning for voice conversion. Specifically, we compare discrete and soft speech units as input features. We find that discrete representations effectively remove speaker information but discard some linguistic content – leading to mispronunciations. As a solution, we propose soft speech units learned by predicting a distribution over the discrete units. By modeling uncertainty, soft units capture more content information, improving the intelligibility and naturalness of converted speech.
For modularity, each component of the system is housed in a separate repository. Please visit the following links for more details:
import torch, torchaudio
# Load the content encoder (either hubert_soft or hubert_discrete)
hubert = torch.hub.load("bshall/hubert:main", "hubert_soft", trust_repo=True).cuda()
# Load the acoustic model (either hubert_soft or hubert_discrete)
acoustic = torch.hub.load("bshall/acoustic-model:main", "hubert_soft", trust_repo=True).cuda()
# Load the vocoder (either hifigan_hubert_soft or hifigan_hubert_discrete)
hifigan = torch.hub.load("bshall/hifigan:main", "hifigan_hubert_soft", trust_repo=True).cuda()
# Load the source audio
source, sr = torchaudio.load("path/to/wav")
assert sr == 16000
source = source.unsqueeze(0).cuda()
# Convert to the target speaker
with torch.inference_mode():
# Extract speech units
units = hubert.units(source)
# Generate target spectrogram
mel = acoustic.generate(units).transpose(1, 2)
# Generate audio waveform
target = hifigan(mel)If you found this work helpful please consider citing our paper:
@inproceedings{
soft-vc-2022,
author={van Niekerk, Benjamin and Carbonneau, Marc-André and Zaïdi, Julian and Baas, Matthew and Seuté, Hugo and Kamper, Herman},
booktitle={ICASSP},
title={A Comparison of Discrete and Soft Speech Units for Improved Voice Conversion},
year={2022}
}