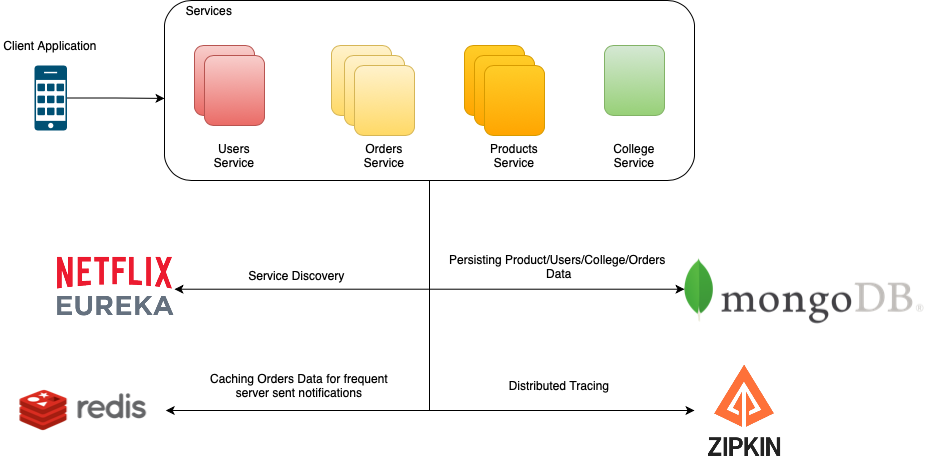
Backend services are the heart and soul of every application, and so a lot of things like the type of database(DB) to use, minimising DB interactions and API calls, implementing efficient caching and load-balancing mechanisms, scalability, cost-efficiency, etc. have to be kept in mind while writing a production-grade application's backend services. Starting with the basics, I implemented a microservices based architecture as backend for my flutter application called College OLX using Spring Boot. The figure below shows how microservices architecture arranges an application as a collection of loosely coupled services which can be modified and scaled independently.
- The whole application is divided into several loosly coupled microservices to make scaling/modification of the application easier.
- Netflix's Eureka is used as a service discovery server which records the information regarding each of the services and routes requests in a load-balanced way as per need.
- NoSQL MongoDB database is used because of its document-oriented storage of data and faster read requests as the Read to write request ratio is considered to be 4:1. Moreover, since no arbitary join operations are needed in the application, MongoDB seemed to be the best choice.
- Redis Cache is used to cache frequently queried orders database, which is responsible for pushing real-time updates of product orders to client application through Server Sent Events or SSE. SSE was preferred over websocket connections because the communication is only supposed to be one-sided i.e., from server to client application.
- Zipkin is used for distributed request tracing, which forms a crucial element of microservice architecture as it helps in debugging the microservices by tracing request flow between the services.
- Users Service
- Products Service
- Colleges Service
- Orders Service
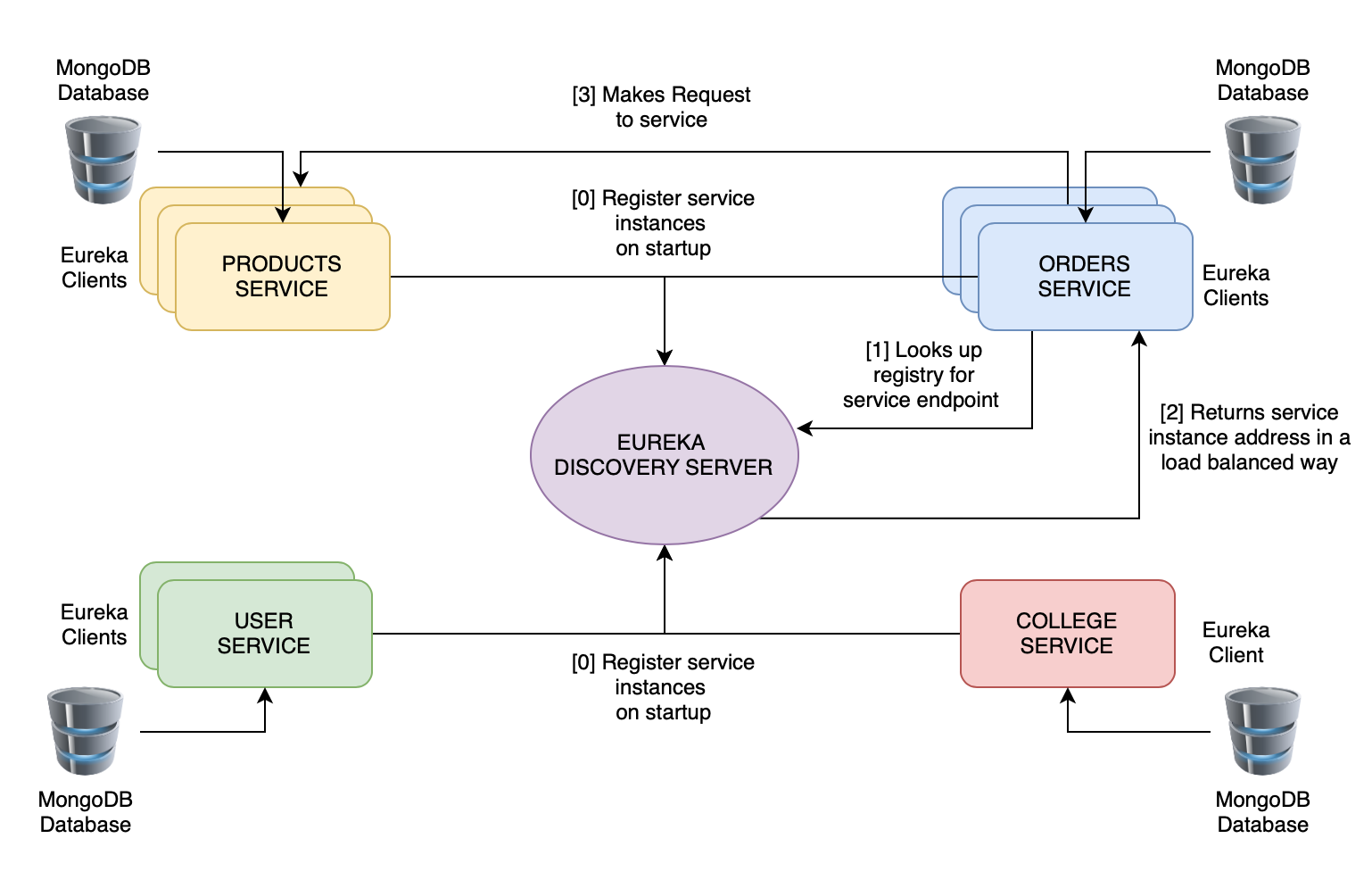
Inter-service communication happens through Eureka Server so an additional Discovery Server has also been implemented. The schematic diagram above represents how Orders Service communicates with Products service through Eureka Server. Following are the steps:
- At their startup, each of the four services register themselves with the Discovery Server
- When one service requires to communicate with the other, it looks up the Discovery Server for the target service's address
- The Discovery Server returns the address of the required service in a load-balanced way if more than one instances of the target service is active
- Request is now made to the target service from the client service
This type of service discovery is known as client-side service discovery as client is the one doing all the work!
Spring Initializer has been used to create spring applications of the above mentioned services(except Discovery Server) with the following dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Data MongoDB
- Eureka Discovery Client
For Discovery server only one dependency of "Eureka Server" has been used.
Eureka servers have a tendency of registering themselves to enable communication between multiple Eureka servers. But since we only have one discovery server, we don't need it to register itself. So add the following lines to application.properties file:
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
Next, add the following annotation the DiscoveryServerApplication class in DiscoveryServerApplication.java file to mark the application as an Eureka Server:
@EnableEurekaServer
Now Run the application. By default it will run in port 8761, which can be altered by specifying the server.port property.
Specify the following properties for each of the four services in their application.properties file:
server.port=port_number_for_each_service
spring.data.mongodb.database=db_name_for_each_service
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017
spring.application.name=service-name
Add the Eureka Client Annotation to the application's main java class:
@EnableEurekaClient
After doing so for all the four services, run them and check Eureka Server's url (by default in port 8761) to see if your services have been registered. Note: Make sure MongoDB is active in your machine before running the above services.
Create a model class to specify the structure of objects to be stored in the database. Orders service has the following model class:
public class Order {
@Id
private String id;
private String sellerId;
private String renterId;
private String productId;
private String status;
private String userStatus;
private long timestamp;
public Order() { }
public Order(String sellerId, String renterId, String productId, String status, String userStatus, long timestamp) {
this.sellerId = sellerId;
this.renterId = renterId;
this.productId = productId;
this.status = status;
this.userStatus = userStatus;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
//INCLUDES GETTERS AND SETTERS...
}
Note: The empty constructor is for RestTemplate.
Create a repository file to act as an interface between your application and the mongoDB database. The following OrderRespository interface extends the MongoRepository interface and so its methods like findById can be called using an object of OrderRepository.
public interface OrderRepository extends MongoRepository<Order, String> {
List<Order> findByRenterIdAndStatus(String renterId, String status, Sort sort);
List<Order> findBySellerIdAndStatus(String sellerId, String status, Sort sort);
List<Order> findByProductIdAndStatus(String productId, String status);
}
Spring manages the implementations of the above methods (Cool, right!?)
Create a REST controller class which tells the application where to route http requests. Following is the controller class for Orders Service:
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/order")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@GetMapping("/getAll")
public ResponseEntity<List<Order>> getAllOrders(){
List<Order> orders = orderRepository.findAll();
return new ResponseEntity<>(orders, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
All the requests made to Orders Service with /order suffix in the URL are mapped to methods of this class. So, a GET request to http://localhost:service_port/order/getAll is routed to the getAllOrders function. Autowired annotation makes sure that only one object of the OrderRepository class is formed. That's how basic APIs with no interaction with other services can be made.
Make a RestTemplate Bean in the main application class. Beans are used for dependency injection in java. Read more about it here
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory = new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory();
restTemplate.setRequestFactory(requestFactory);
return restTemplate;
}
LoadBalanced bean makes sure that addresses of service instances are returned in a load balanced way.
Now inside the controller class, get an instance of RestTemplate object:
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
Use this object to make requests to other services which are registered in the Eureka Server.
String uri = "http://products-service/product/getStatus?id=abshsjaskdka"
String status = restTemplate.getForObject(uri, String.class);
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- The "products-service" in the uri is the spring.application.name property of the target service.
- "restTemplate.getForObject" parses the response into the specified object and returns the object.
- Make sure the Class passed in the getForObject method has an empty constructor because RestTemplate lazily sets the values of the class data members
- In the background, RestTemplate looks up the Discovery Server to get the real address of the products-service instance, and then makes the request to one of its instances in a load balanced way.
- Setup Services
- Write Basic APIs
- Implement Service Discovery
- Server sent events(SSE) in Orders Service
- API Gateway
- Automated FCM Notifications
- Zipkin Integration