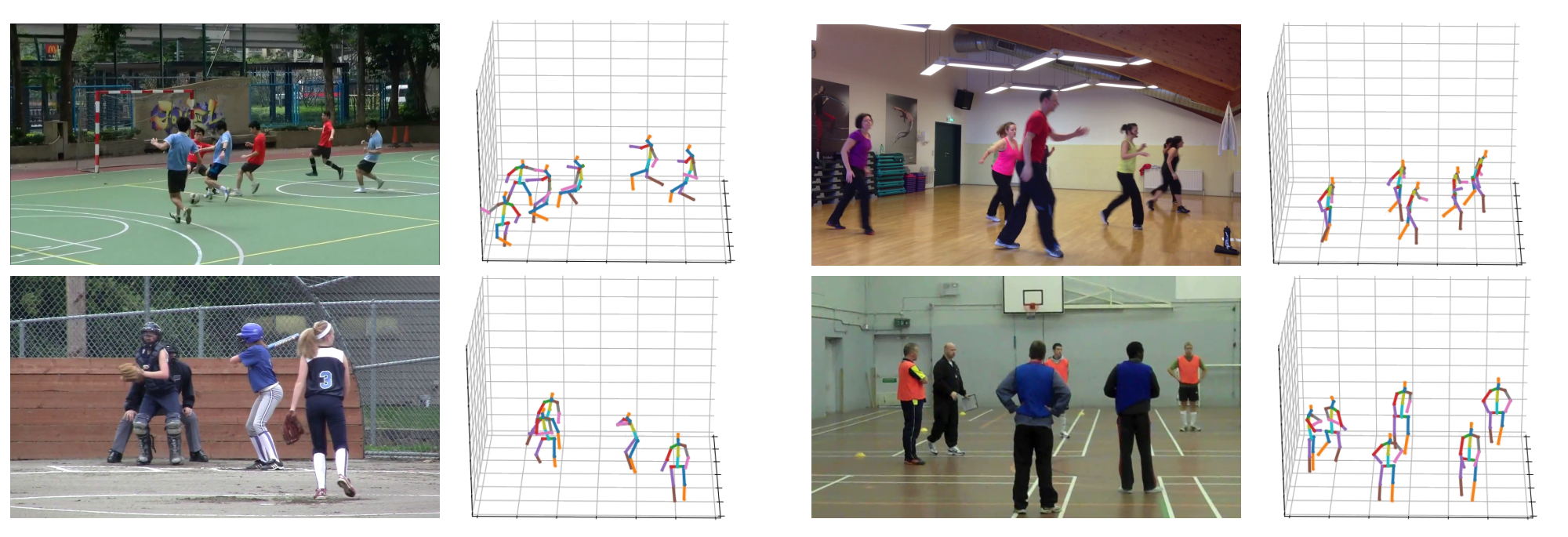
This repository contains the code and models for the following paper.
Graph and Temporal Convolutional Networks for 3D Multi-person Pose Estimation in Monocular Videos
Cheng Yu, Bo Wang, Bo Yang, Robby T. Tan
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2021.
- 06/07/2021 evaluation code (PCK_abs camera-centric) and pre-trained model for MuPoTS dataset tested and released
- 04/30/2021 evaluation code (PCK person-centric), pre-trained model, and estimated 2D joints for MuPoTS dataset released
Pytorch >= 1.3
Python >= 3.6
Create an enviroment.
conda create -n gntcn python=3.6
conda activate gntcn
Install the latest version of pytorch (tested on pytorch 1.3 - 1.7) based on your OS and GPU driver installed following install pytorch. For example, command to use on Linux with CUDA 11.0 is like:
conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=11.0 -c pytorch
Install opencv-python, torchsul, tqdm, and scipy to run the evaluation code
pip install opencv-python
pip install --upgrade torchsul
pip install tqdm
pip install scipy
Download the pre-trained model and processed human keypoint files (H36M and MuPoTS) here, and unzip the downloaded zip file to this project's directory, two folders and one pkl file are expected to see after doing that (i.e., ./ckpts, ./mupots, and points_eval.pkl).
Copy the two two folders and the pkl file to the root directory of the project, you should see the following directory structure.
${GnTCN_ROOT}
|-- ckpts
|-- models
|-- mupots
|-- util
|-- points_eval.pkl
|-- calculate_mupots_depth.py
|-- other python code, LICENSE, and README files
...
MuPoTS eval set is needed to perform evaluation, which is available on the MuPoTS dataset website (download the mupots-3d-eval.zip file, unzip it, and run get_mupots-3d.sh to download the dataset). After the download is complete, MultiPersonTestSet.zip (5.6 GB) is avaiable. Unzip it and move the folder MultiPersonTestSet to the root directory of the project to perform evaluation on MuPoTS test set. Now you should see the following directory structure.
${GnTCN_ROOT}
|-- ckpts
|-- models
|-- MultiPersonTestSet <-- Newly added MuPoTS eval set
|-- mupots
|-- util
|-- points_eval.pkl
|-- calculate_mupots_depth.py
|-- other python code, LICENSE, and README files
...
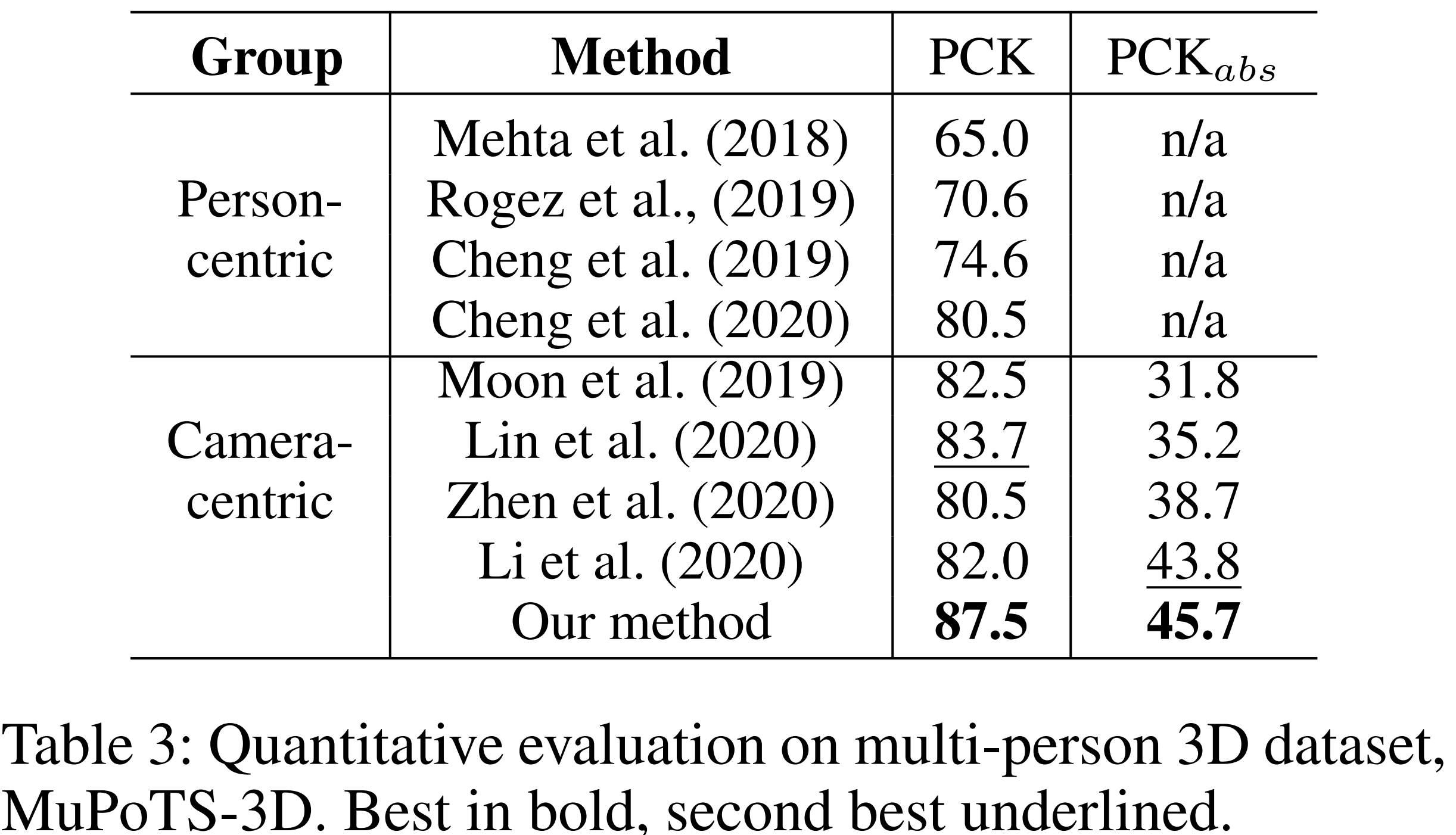
The following is a snapshot of the Table 3 in the paper, which shows the quantitative evaluation results on MuPoTS-3D. To reproduce the results (PCK and PCK_abs) in the table, please follow the instructions in the next section.
To keep this repository simple and small, 2D pose estimator is not included (HRNet was used as the 2D pose estimator as mentioned in the paper). Therefore, the estimated 2D points are provided in the data package to make it easy to reproduce the results reported in our paper. To evaluate the person-centric 3D human pose estimation:
python calculate_mupots_detect.py
python eval_mupots.py
After running the above code, the following PCK (person-centric, pelvis-based origin) value is expected, which matches the number reported in Table 3, PCK 87.5 (percentage) in the paper.
...
PCK_MEAN: 0.8764509703036868
To evaluate camera-centric (i.e., camera coordinates) 3D human pose estimation:
python calculate_mupots_detect.py
python calculate_mupots_depth.py
python eval_mupots_dep.py
After running the above code, the following PCK_abs (camera-centric) value is expected, which matches the number reported in Table 3, PCK_abs 45.7 (percentage) in the paper.
...
PCK_MEAN: 0.45785827181758376
The Ground-truth 2D joints are included in the data package as well to demonstrate the upper-bound performance of the model, where the 2D ground-truth keypoints are used as input to mimic the situation that there is no error in 2D pose estimation. To evaluate with GPU:
python calculate_mupots_gt.py
python eval_mupots.py
After running the above code, the following PCK (person-centric, pelvis-based origin) value is expected.
...
PCK_MEAN: 0.8985102807603582
Similar to the evaluation above where 2D ground-truth keypoints are used for MuPoTS. The following evaluation code takes 2D Ground-truth joints of the Human3.6M as input to simulate the situation when there is no error in 2D pose estimator, how the proposed method performs. Please note the MPJPE value from this evaluation is lower than the one reported in the paper because the result in Table 5 in the paper was calculated based on the estimated 2D keypoints (i.e., with errors) not from ground-truth.
If GPU is available and pytorch is installed successfully, the GPU evaluation code can be used,
python eval_gt_h36m.py
After running the above code, the following MPJPE value is expected.
...
MPJPE: 0.0180
If GPU is not available or pytorch is not successfully installed, the CPU evaluation code can be used,
python eval_gt_h36m_cpu.py
Result is the same as the GPU evaluation code.
Please note that we didn't include 2D pose estimator code in this repository to keep it simple, please use off-the-shelf 2D pose estimation methods to get 2D joints first, and together with the code from this repository to infer 3D human pose on testing videos (the TCN takes multiple frames as input). In particular, as stated in the paper: we use the original implementation of HRNet as the 2D pose estimator and extract PAF from OpenPose.
The code is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE for details.
If this work is useful for your research, please cite our paper.
@article{Cheng_Wang_Yang_Tan_2021,
title={Graph and Temporal Convolutional Networks for 3D Multi-person Pose Estimation in Monocular Videos},
author={Cheng, Yu and Wang, Bo and Yang, Bo and Tan, Robby T.},
journal={Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
year={2021},
month={May},
volume={35},
number={2},
pages={1157-1165}
}