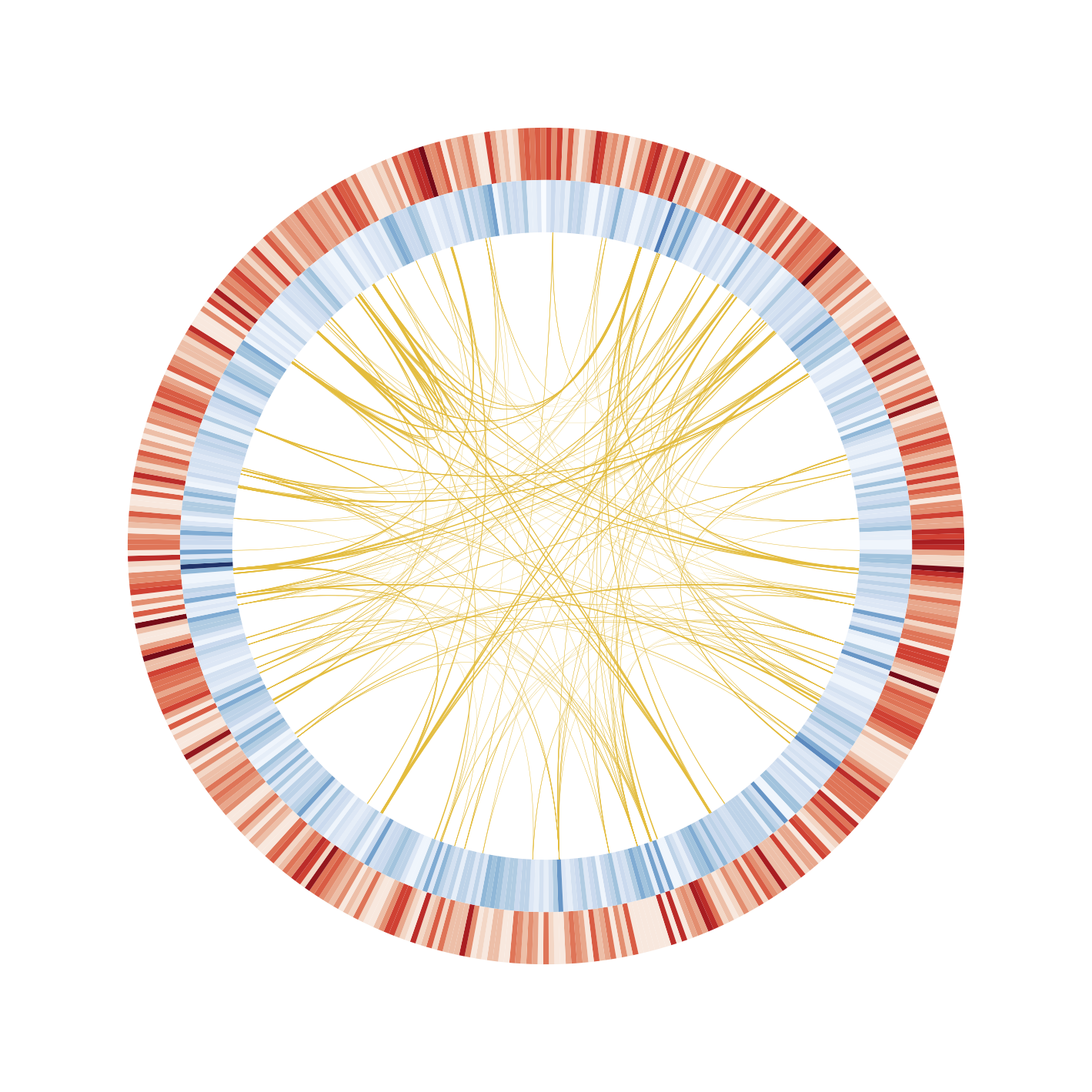
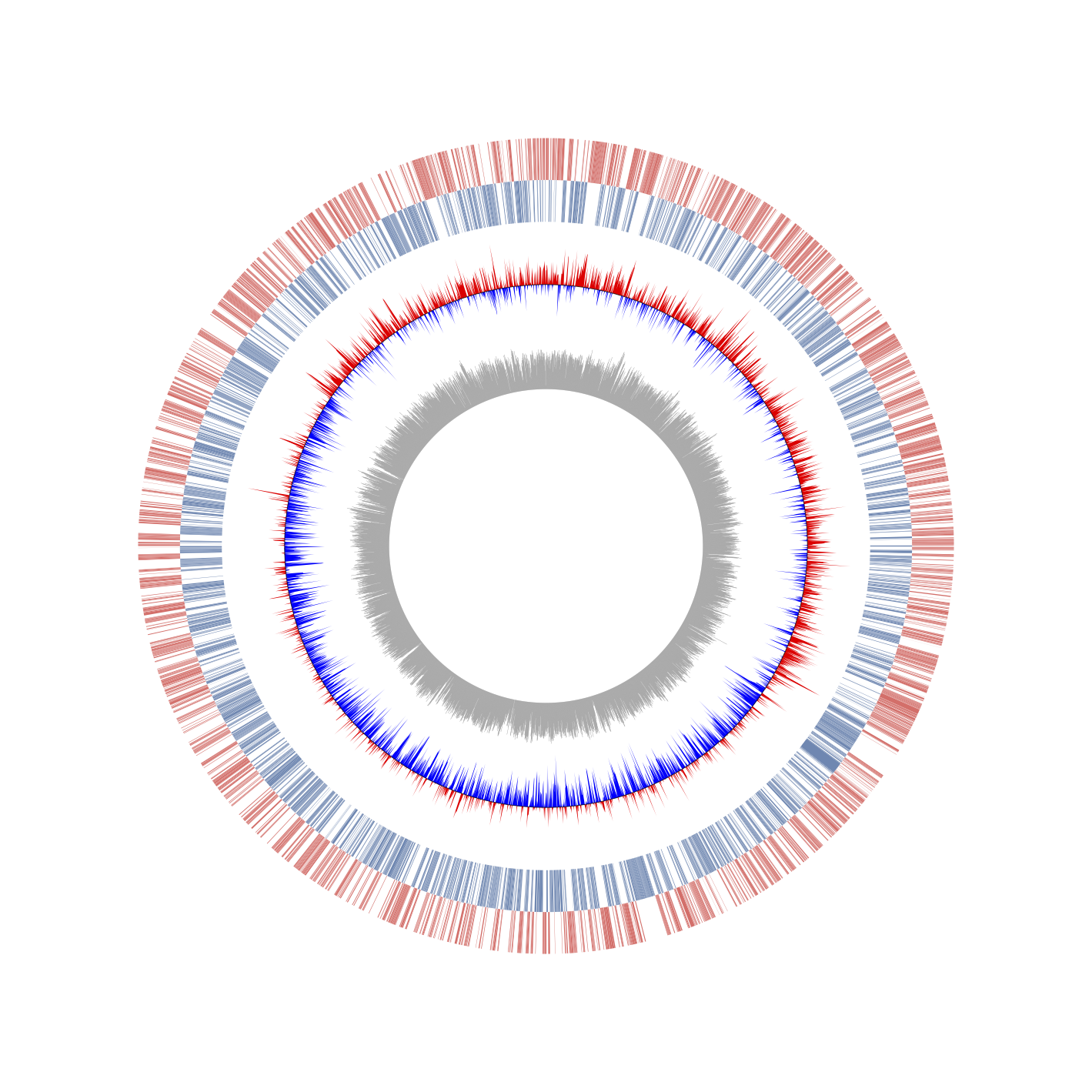
Circos is one of the most famous software for the visualization of genomic similarities and features. However, the execution requires such a complicated process and many extra input files. The software is also written based on Perl; it limits the integration with the other software for biological analysis. Various biological data analysis packages are described in Python. However, there are no python packages to visualize a Circos plot. The file format such as GenBank, GFF for describing genomic annotations has been organized. Therefore, if these formatted files could be used as input for the visualization, complicated extra files are not needed to prepare. Here, it provides a python matplotlib based circular genome visualization package, PyCircos (pseudonym). It enables us to represent genome features by only input of the Genbank format file. Also, by the entry of comparative genome analysis results by using BLAST or LAST, users can easily visualize multi genomic locus similarity with a simple python script.
- python 3.6.2 later
- matplotlib 3.0.0 later
- Biopython
-
Download the github packages using the following single command.
git clone https://github.com/ponnhide/pyCircos -
Install the necessary Python packages using the following commands.
pip install matplotlib
pip install biopython
Go to the sample/tutorial/ directory and execute the following code
python how_to_use.py
If the script can work correctly, you can find the "test.pdf" as output in the directory.
Example 0
(sample/tutorial/how_to_use.py)
import sys
import numpy as np
sys.path.append("../../")
from pycircos import *
if __name__ == "__main__":
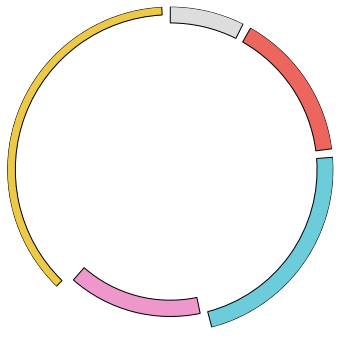
gcircle = Gcircle()
gcircle.add_locus("1", 1000, bottom=900, height=100) #name, length, bottom (0<=bottom<=1000), height (0<=bottom<=1000)
gcircle.add_locus("2", 2000, bottom=900, height=100, facecolor="#ED665D")
gcircle.add_locus("3", 3000, bottom=900, height=100, facecolor="#6DCCDA")
gcircle.add_locus("4", 2000, bottom=800, height=100, facecolor="#ED97CA")
gcircle.add_locus("5", 5000, bottom=950, height=50, facecolor="#EDC948")
gcircle.set_locus() #Creat figure object
data = np.random.rand(100)
gcircle.scatter_plot("1", data, bottom=900, height=-100)
data = np.random.rand(100)
gcircle.line_plot("2", data, bottom=600, height=100)
data = np.random.rand(100)
gcircle.line_plot("2", data, bottom=600, height=100)
data = np.random.rand(50)
gcircle.heatmap("3", data, bottom=600, height=100)
data = np.random.rand(50)
gcircle.bar_plot("4", data, bottom=600, height=-200)
data = np.random.rand(50)
gcircle.bar_plot("4", data, bottom=600, height=200)
gcircle.chord_plot(["4", 1000, 1100], ["1", 200, 400], bottom=400)
gcircle.chord_plot(["5", 1000, 1100, 950], ["3", 1000, 2000, 600], color="#FF0000")
gcircle.chord_plot(["5", 4000, 4500, 950], ["2", 500, 1000, 400], color="#F2BE2B")
gcircle.save() Example 1
Visualization of CDS, GC-skew and GC-amount from Genbank (sample/prokayote1/prokaryote_1.ipynb)
Example 2
Visualization of homology links in the genome (sample/prokayote2/prokaryote_2.ipynb)