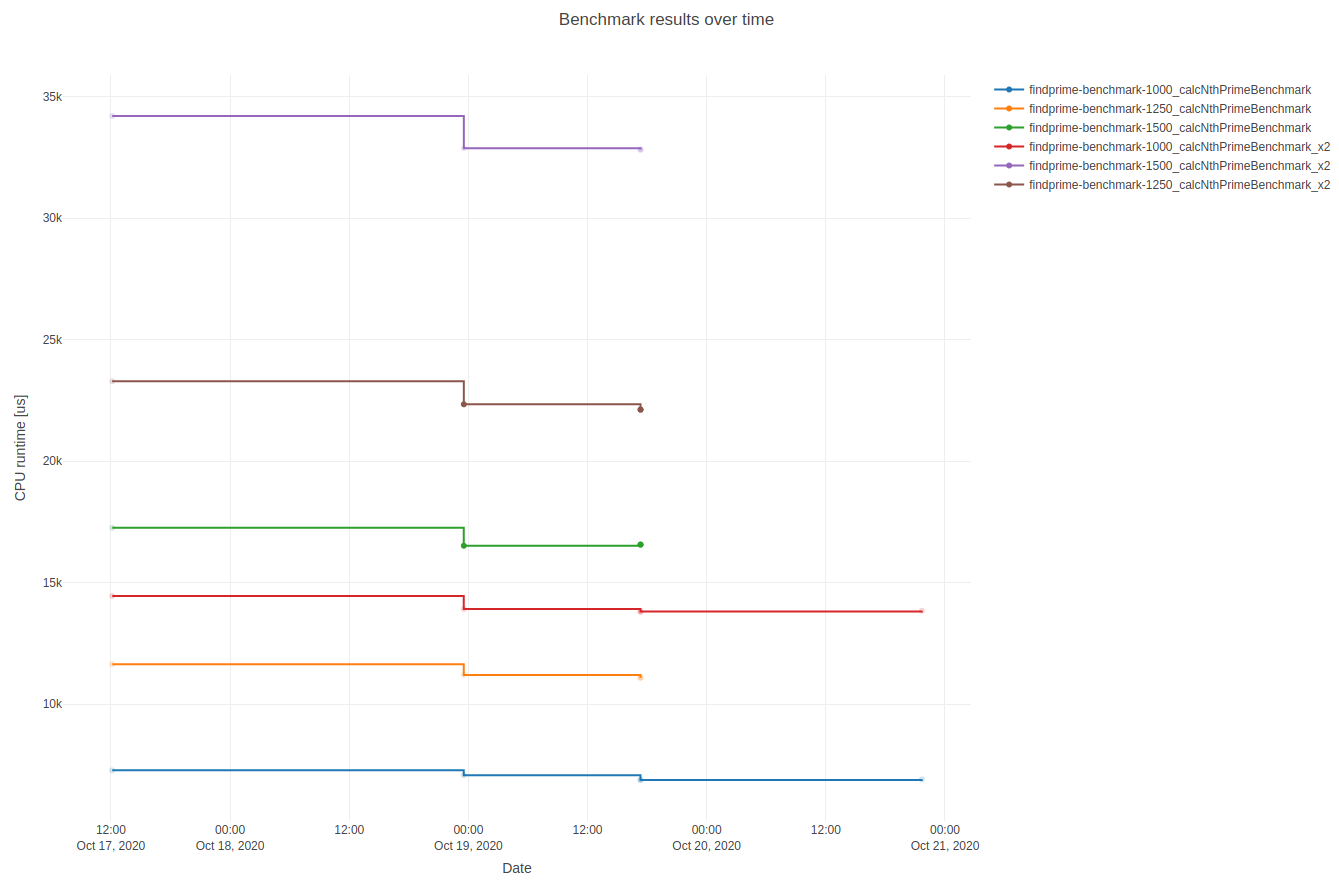
beast is a simple tool to execute and post-process a set of google benchmarks. The basic feature is plotting multiple benchmark results in one single plot (powered by plotly). It is also possible to configure access to a mongoDB database and push results to it.
Download the latest release from:
and install the .deb package via sudo dpkg -i.
beast will search for executables with a predefined regular expression pattern in your current working directory as a default. Check beast --help for an overview about possible options. We will use the C++ example from the repo directory to show the basic functionality (of course you will need to clone the repo for that):
cd to the example_benchmark directory and call:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build . --target allyou will get some small benchmark executables which can be plotted with beast:
If you want to use beast's database related functionality, you need to set up a mongoDB database, either by installing the Community Edition from https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/ in your desired environment or by using the cloud based solution https://www.mongodb.com/cloud/atlas.
Assuming a successful database setup, the only thing which is left to be done is a little configuration via beast config. Set the mongoDB-URI, the database name and the collection name with the according --set... commands. Note: The collection does not have to be existent, it will be created with the first push to it.
Finally you should be able to push your most recent generated benchmark results via beast dbpush or to retrieve and plot previous pushed data with the beast dbplot command:
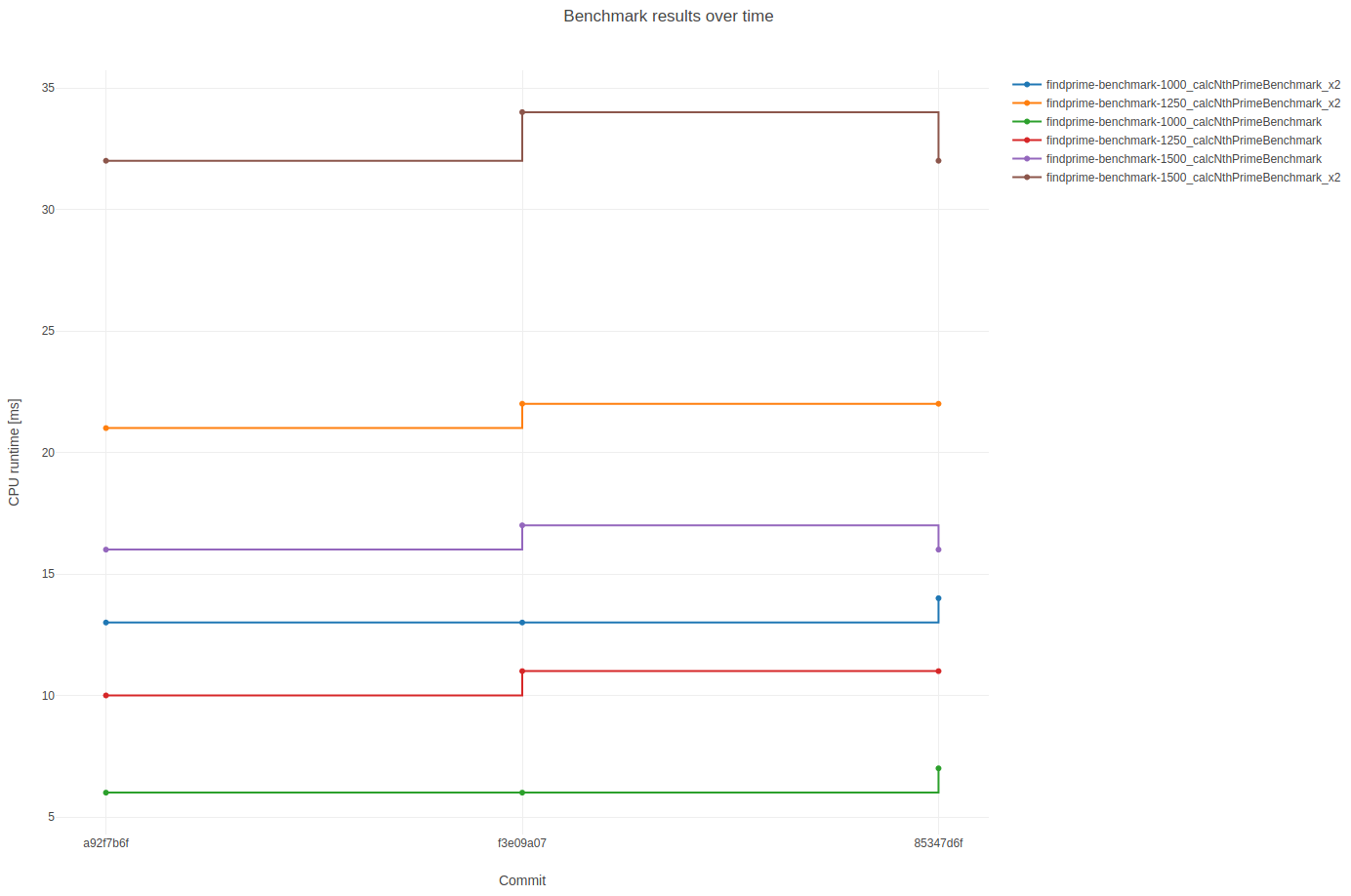
To run benchmarks on a certain commit range of a git repository, you need to provide the needed information in a small yaml file.
Example for the beast repo:
version: 1
repo_path: <PATH_TO_BEAST_REPO> # absolute or relative to cwd
branch_name: master
from_commit: a92f7b6f4e5da30908577b9109040987f6ca9bf6
to_commit: 85347d6fd06acbd700be5237a94ca49486bb5e25
build_commands: |
mkdir build
cd build && cmake ..
cd build && cmake --build . --target all
benchmark_regex: .*benchmark[^.]*$Adapt the yaml to your needs and set the path to it with beast config --set-repocheck-yaml. Run and plot the benchmarks with beast repocheck (check out --help for more details).