@inproceedings{Dakkak:2019:ARS:3330345.3331057,
author = {Dakkak, Abdul and Li, Cheng and Xiong, Jinjun and Gelado, Isaac and Hwu, Wen-mei},
title = {Accelerating Reduction and Scan Using Tensor Core Units},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Supercomputing},
series = {ICS '19},
year = {2019},
isbn = {978-1-4503-6079-1},
location = {Phoenix, Arizona},
pages = {46--57},
numpages = {12},
url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3330345.3331057},
doi = {10.1145/3330345.3331057},
acmid = {3331057},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
}
cmake version >=3.8 is required. (there's a problem with hunter using cmake 3.10.2)
cd /tmp
wget https://cmake.org/files/v3.10/cmake-3.10.1-Linux-x86_64.sh
sudo sh cmake-3.10.1-Linux-x86_64.sh --prefix=/usr/local --exclude-subdir
you may also want to remove the default installation sudo apt-get remove cmake
you need to install from source if on ppc64le
To compile the project run the following commands
mkdir -p build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ..
make
if you get errors about nvcc not supporting your gcc compiler, then you may want to use
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_CUDA_HOST_COMPILER=`which gcc-6` ..
The following benchmakrs are currently available
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
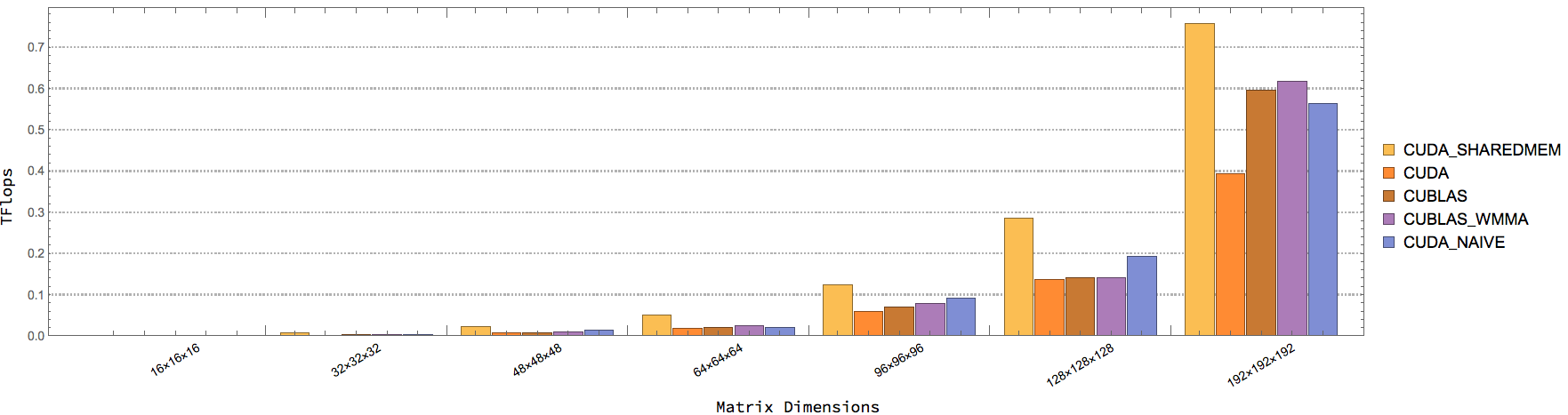
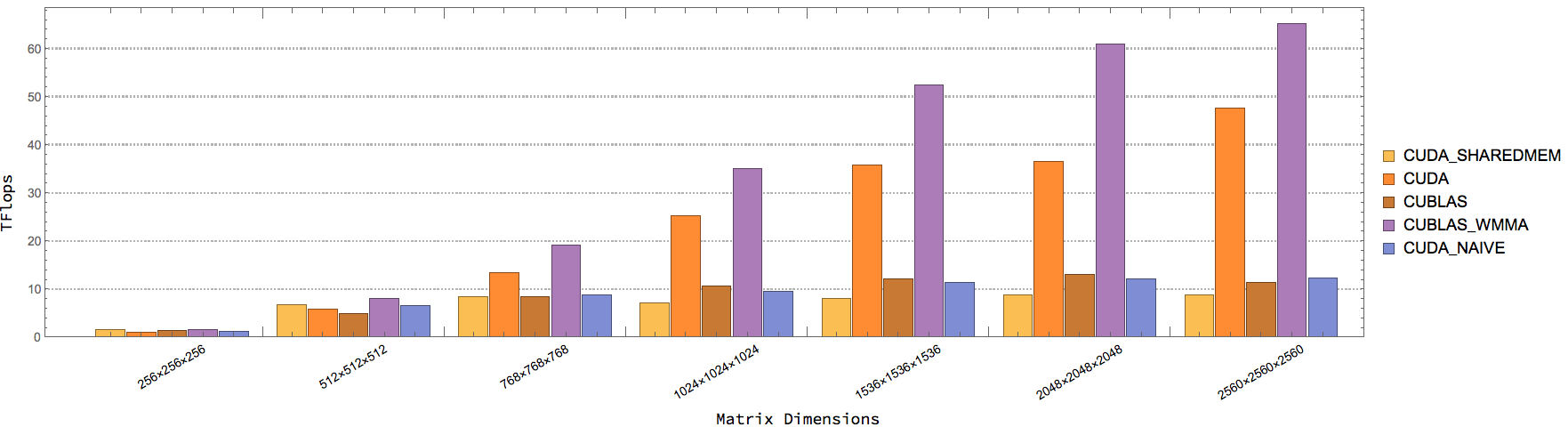
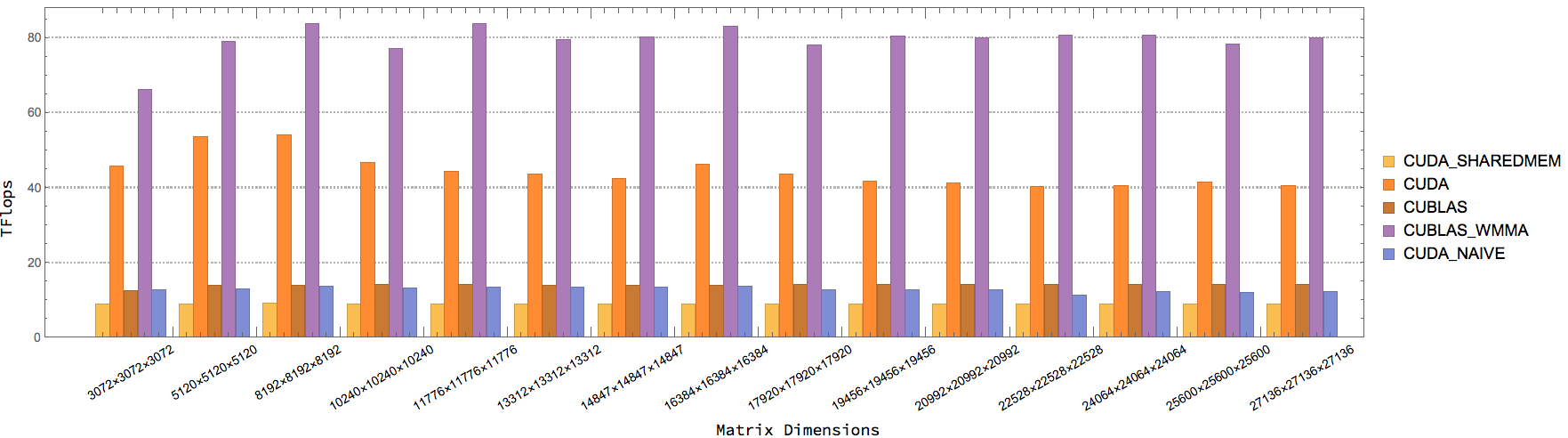
| CUBLAS_WMMA_GEMM | CUBLAS GEMM w/ Tensor Cores. AType, BType = half, CType = float |
| CUBLAS_GEMM | CUBLAS GEMM w/o Tensor Cores. AType, BType = half, CType = float |
| CUTLASS_WGEMM | CUTLASS GEMM w/ Tensor Cores. AType, BType = half, CType = float |
| CUDA_WMMA_GEMM_NAIVE | Naive CUDA GEMM w/ Tensor Cores. AType, BType = half, CType = float |
| CUDA_WMMA_GEMM_SHAREDMEM | Shared memory CUDA GEMM w/ Tensor Cores. Atype, BType = half, CType = float |
| CUDA_WMMA_GEMM | Optimized CUDA GEMM (from CUDA Samples). AType, BType = half, CType = float |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
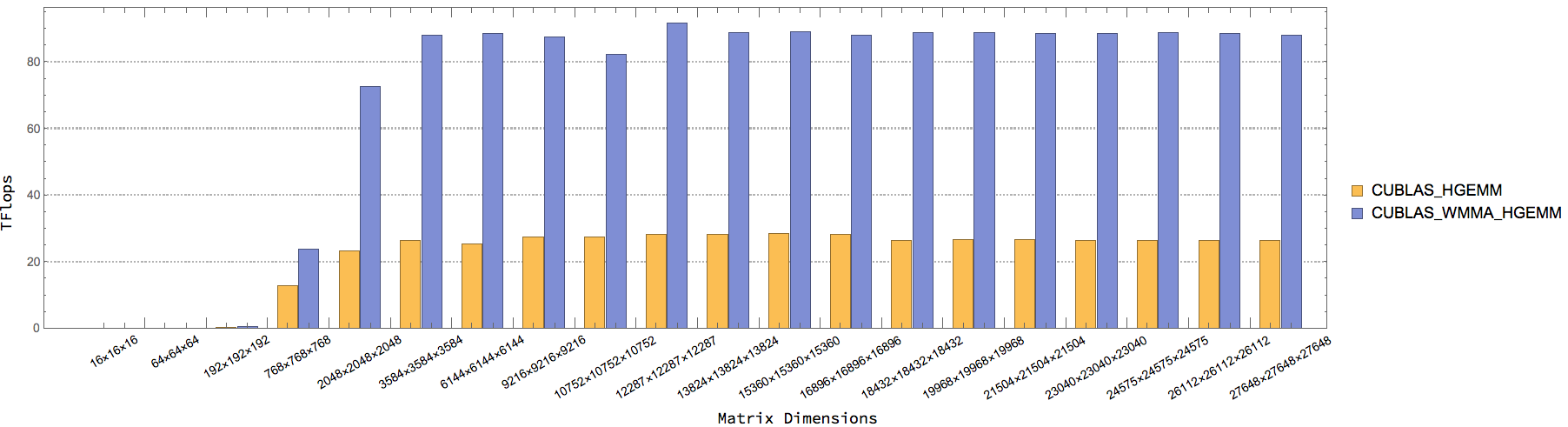
| CUBLAS_WMMA_HGEMM | CUBLAS HGEMM w/ Tensor Cores. AType, BType = half, CType = half |
| CUBLAS_HGEMM | CUBLAS HGEMM w/o Tensor Cores. AType, BType = half, CType = half |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
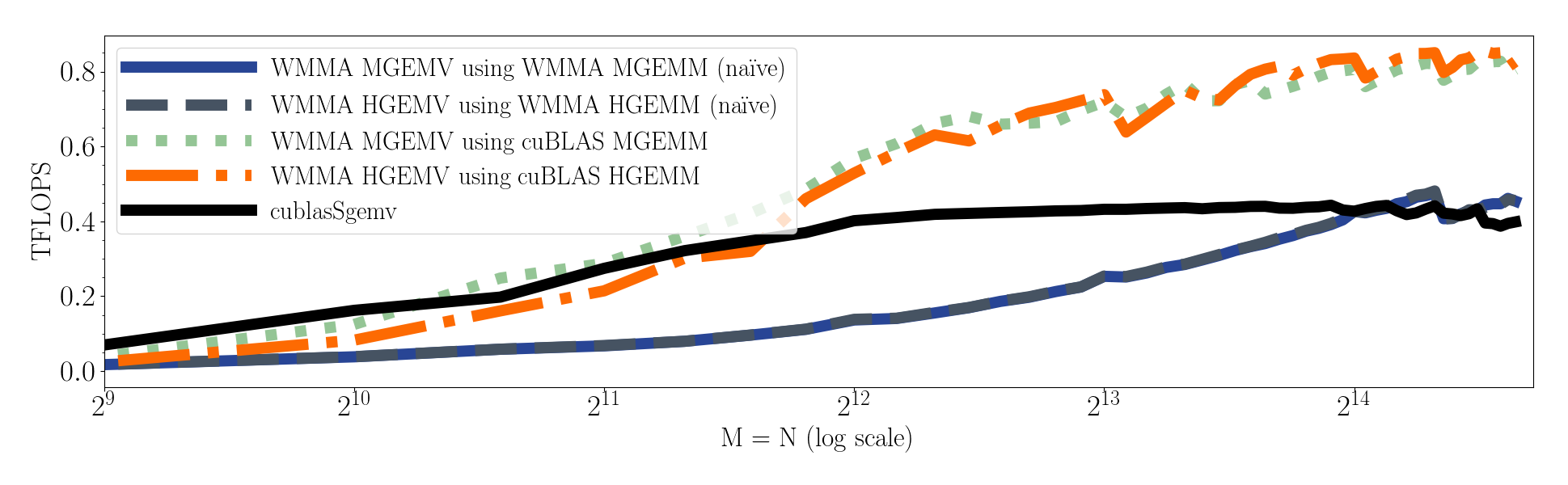
| CUBLAS_GEMV | cublasSgemv y = alpha * Ax + beta * y. AType, xType, yType = float |
| CUDA_WMMA_GEMV_CUBLAS | Use CUBLAS GEMM w/ Tensor Cores for GEMV. AType, xType = half, yType = float |
| CUDA_WMMA_GEMV_NAIVE | Use Naive CUDA GEMM w/ Tensor Cores for GEMV. AType, xType = half, yType = float |
| CUDA_WMMA_GEMV_SHAREDMEM | Use Shared memory CUDA GEMM w/ Tensor Cores for GEMV. AType, xType = half, yType = float |
inType = half, outType = half
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CUB_BLOCK_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM | cub::BlockScan. segment_size = THREADS_PER_BLOCK * ITEMS_PER_THREAD |
| CUB_WARP_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM | cub::WarpScan. segment_size = LOGICAL_THREADS_PER_WARP |
| THRUST_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM | thrust::inclusive_scan_by_key, inType = half, outType = half |
| CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM_16 | use Tensor Cores. segment_size = 16. each warp calculates WMMA_TILES_PER_WARP * 16 segments |
| CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM_16N | use Tensor Cores. segment_size = 16n where n is a positive integer. each warp calculates 16 segment |
| CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM_256 | use Tensor Cores. segment_size = 16. each warp calculates WMMA_TILES_PER_WARP segments |
| CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM_256N | use Tensor Cores. segment_size = 256n where n is a positive integer. each warp calculates 1 segment |
WWMMA_TILES_PER_WARP and WARPS_PER_BLOCK tuning for CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM_16 and CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM_256
(WMMA_TILES_PER_WARP = 2, WARPS_PER_BLOCK = 4) is the best.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CUB_FULL_PREFIXSUM | cub::DeviceScan::ExclusiveSum. inType = half, outType = half |
| THRUST_FULL_PREFIXSUM | thrust::inclusive_scan. inType = half, outType = half |
| CUDA_WMMA_FULL_PREFIXSUM_3KERS_256 | use CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM_256 as the first kernel and use cub::DeviceScan::ExclusiveSum for scanning the partial sums, the third kernel adds the partials sums. inType = half, outType = half |
| CUDA_WMMA_FULL_PREFIXSUM_3KERS | use CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_PREFIXSUM_256N as the first kernel and use cub::DeviceScan::ExclusiveSum for scanning the partial sums, the third kernel adds the partials sums. inType = half, outType = half |
| CUDA_WMMA_FULL_PREFIXSUM_CG | one kernel. use cooperative groups grid sysnchrozation to scan the partial sums. inType = half, outType = half |
Note: There's a bug in cub::WarpScan for LOGICAL_THREADS_PER_WARP = 16.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
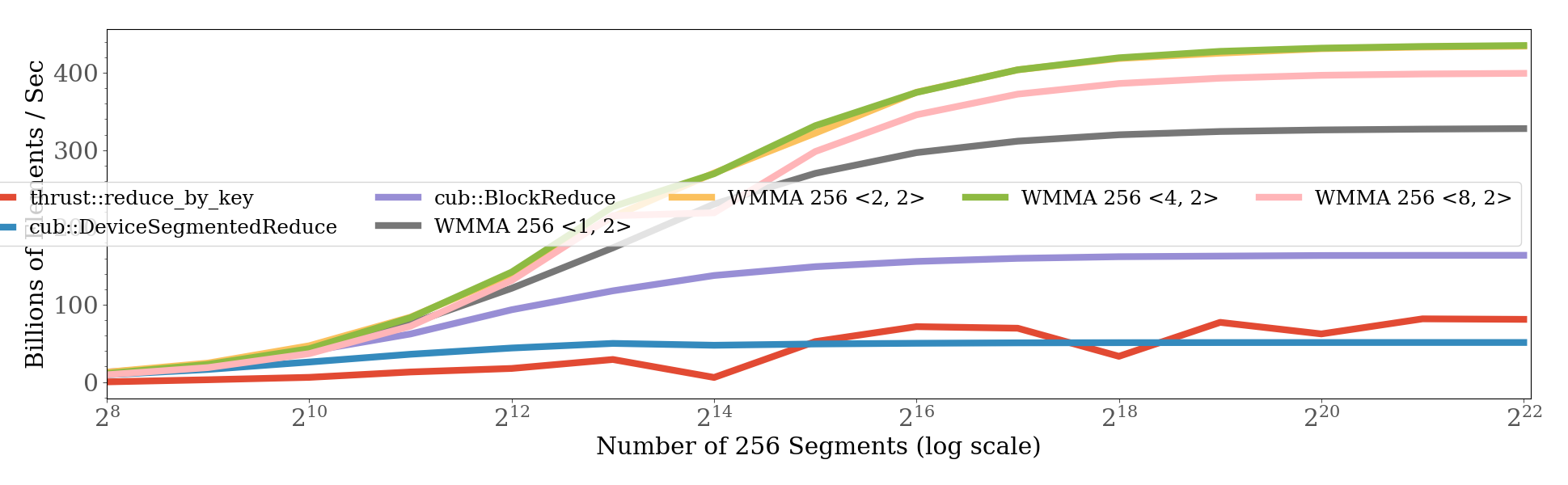
| CUB_BLOCK_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION | cub::BlockReduce. segment_size = THREADS_PER_BLOCK * ITEMS_PER_THREAD |
| CUB_DEVICE_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION | cub::DeviceSegmentedReduce::Sum |
| THRUST_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION | thrust::reduce_by_key |
| CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION_16 | use Tensor Cores. segment_size = 16. each warp calculates WMMA_TILES_PER_WARP * 16 segments |
| CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION_16N | use Tensor Cores. segment_size = 16n where n is a positive integer. each warp calculates 16 segment |
| CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION_256 | use Tensor Cores. segment_size = 16. each warp calculates WMMA_TILES_PER_WARP segments |
| CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION_256N | use Tensor Cores. segment_size = 256n where n is a positive integer. each warp calculates 1 segment |
WWMMA_TILES_PER_WARP and WARPS_PER_BLOCK tuning for CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION_16 and CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION_256
(WMMA_TILES_PER_WARP = 1, WARPS_PER_BLOCK = 8) is the best.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
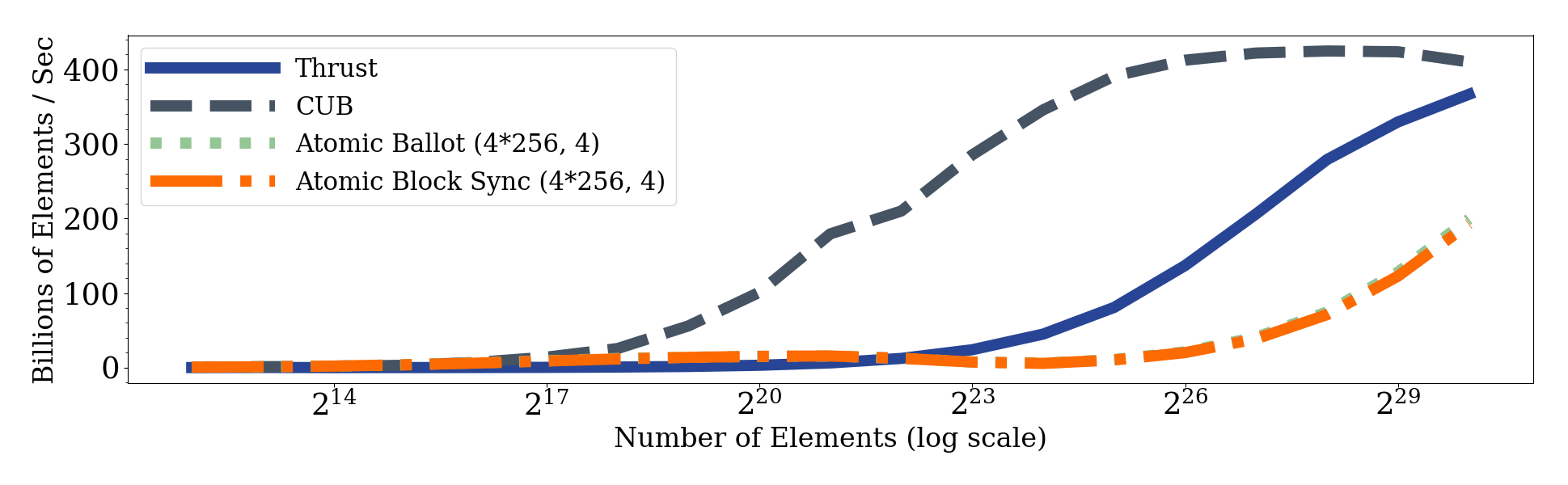
| CUB_FULL_REDUCTION | cub::DeviceReduce::Sum. inType = half, outType = half |
| THRUST_FULL_REDUCTION | thrust::reduce. inType = half, outType = half |
| CUDA_WMMA_FULL_REDUCTION_2KERS | use CUDA_WMMA_SEGMENTED_REDUCTION_256N as the first kernel and use cub::DeviceSegmentedReduce::Sum for reducing the all segments. inType = half, outType = half |
| CUDA_WMMA_FULL_REDUCTION_CG | one kernel. use cooperative groups grid sysnchrozation. inType = half, outType = half |
| CUDA_WMMA_FULL_REDUCTION_ATOMIC_W_BLOCK_SYNC | one kernel. use atomicAdd with block synchronization. inType = half, outType = half |
| CUDA_WMMA_FULL_REDUCTION_ATOMIC_W_ATOMIC_BALLOT | one kernel. use atomicAdd with ballot. inType = half, outType = half |
you can benchmark each primitive individually using
./bench --benchmark_filter=[name_of_primitive]
for example
./bench --benchmark_filter=WMMA_GEMM
futher controls over the benchmarks are explained in the --help option
./bench
The above will output to stdout somthing like
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Benchmark Time CPU Iterations UserCounters...
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SGEMM/1000/1/1/-1/1 5 us 5 us 126475 K=1 M=1000 N=1 alpha=-1 beta=1
SGEMM/128/169/1728/1/0 539 us 534 us 1314 K=1.728k M=128 N=169 alpha=1 beta=0
SGEMM/128/729/1200/1/0 1042 us 1035 us 689 K=1.2k M=128 N=729 alpha=1 beta=0
SGEMM/192/169/1728/1/0 729 us 724 us 869 K=1.728k M=192 N=169 alpha=1 beta=0
SGEMM/256/169/1/1/1 9 us 9 us 75928 K=1 M=256 N=169 alpha=1 beta=1
SGEMM/256/729/1/1/1 35 us 35 us 20285 K=1 M=256 N=729 alpha=1 beta=1
SGEMM/384/169/1/1/1 18 us 18 us 45886 K=1 M=384 N=169 alpha=1 beta=1
SGEMM/384/169/2304/1/0 2475 us 2412 us 327 K=2.304k M=384 N=169 alpha=1 beta=0
SGEMM/50/1000/1/1/1 10 us 10 us 73312 K=1 M=50 N=1000 alpha=1 beta=1
SGEMM/50/1000/4096/1/0 6364 us 5803 us 100 K=4.096k M=50 N=1000 alpha=1 beta=0
SGEMM/50/4096/1/1/1 46 us 45 us 13491 K=1 M=50 N=4.096k alpha=1 beta=1
SGEMM/50/4096/4096/1/0 29223 us 26913 us 20 K=4.096k M=50 N=4.096k alpha=1 beta=0
SGEMM/50/4096/9216/1/0 55410 us 55181 us 10 K=9.216k M=50 N=4.096k alpha=1 beta=0
SGEMM/96/3025/1/1/1 55 us 51 us 14408 K=1 M=96 N=3.025k alpha=1 beta=1
SGEMM/96/3025/363/1/0 1313 us 1295 us 570 K=363 M=96 N=3.025k alpha=1 beta=0
Output as JSON using
./bench --benchmark_out_format=json --benchmark_out=test.json
or preferably
./bench --benchmark_out_format=json --benchmark_out=`hostname`.json
mkdir -p build && cd build && rm -fr * && cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ..
If you see this error:
***WARNING*** CPU scaling is enabled, the benchmark real time measurements may be noisy and will incur extra overhead.
you might want to disable the CPU frequency scaling while running the benchmark:
sudo cpupower frequency-set --governor performance
./mybench
sudo cpupower frequency-set --governor powersavepython plot/plot.py plot/spec/full_reduction.yml
or generate all figures
python plot/plot.py all
Install nvidia-docker, then, list the available benchmarks.
nvidia-docker run --rm raiproject/tensorcore_bench:latest bench --benchmark_list_tests
You can run benchmarks in the following way (probably with the --benchmark_filter flag).
nvidia-docker run --privileged --rm -v `readlink -f .`:/data -u `id -u`:`id -g` raiproject/tensorcore_bench:amd64-latest ./run_benchmarks.sh
--privilegedis needed to set the NUMA policy for NUMA benchmarks.-v `readlink -f .`:/datamaps the current directory into the container as/data.--benchmark_out=/data/\`hostname`.jsontells thebenchbinary to write out to/data, which is mapped to the current directory.-u `id -u`:`id -g`tells docker to run as userid -uand groupid -g, which is the current user and group. This means that files that docker produces will be modifiable from the host system without root permission.