Welcome To fastpages
An easy to use blogging platform, with support for Jupyter notebooks, Word docs, and Markdown.
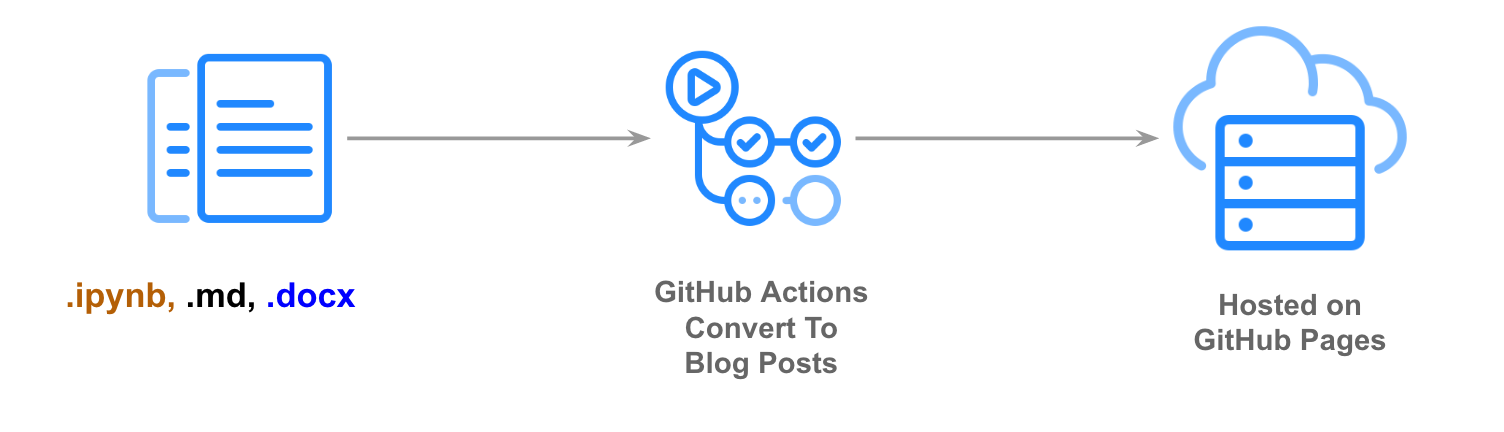
fastpages uses GitHub Actions to simplify the process of of creating Jekyll blog posts on GitHub Pages from a variety of input formats.
fastpages provides the following features:
- Create posts containing code, outputs of code (which can be interactive), formatted text, etc directly from Jupyter Notebooks; Notebook posts support features such as:
- Write posts on your local machine and preview them with live reload.
- Create posts, including formatting and images, directly from Microsoft Word documents.
- Create and edit Markdown posts entirely online using GitHub's built-in markdown editor.
- Embed Twitter cards and YouTube videos.
- Categorization of blog posts by user-supplied tags for discoverability.
See below for a more detailed list of features.
- Welcome To
fastpages - Running the blog on your local machine
- Using The GitHub Action & Your Own Custom Blog - Optional Inputs
- Contributing To Fastpages
- FAQ
Setup Instructions
-
Generate a copy of this repo by clicking on this link. Name your repo anything you like except {your-username}.github.io.
-
GitHub Actions will automatically open a PR on your new repository ~ 30 seconds after the copy is created. Follow the instructions in that PR to continue.
For a live walk-through of the setup steps (with some additional tips) see this video tutorial of setting up a fastpages blog by Abdul Majed.
Front-Matter related options
In a notebook, front matter is defined as a markdown cell at the beginning of the notebook with the following contents:
# "Title"
> "Awesome summary"
- toc: false
- branch: master
- badges: true
- comments: true
- categories: [fastpages, jupyter]
- image: images/some_folder/your_image.png
- metadata_key1: metadata_value1
- metadata_key2: metadata_value2Similarly, in a markdown document the same front matter would be defined like this at the beginning of the document:
---
- title: "My Title"
- summary: "Awesome summary"
- toc: false
- branch: master
- badges: true
- comments: true
- image: images/some_folder/your_image.png
- categories: [fastpages, jupyter]
- metadata_key1: metadata_value1
- metadata_key2: metadata_value2
---Additional metadata is optional and allows you to set custom front matter.
Note that anything defined in front matter must be valid YAML. Failure to provide valid YAML could result in your page not rendering in your blog. For example, if you want a colon in your title you must escape it with double quotes like this:
- title: "Deep learning: A tutorial"
See this tutorial on YAML for more information.
Configure Title & Summary
- Replace
Title, with your desired title, andAwesome summarywith your desired summary.
Note: It is recommended to enclose these values in double quotes, so that you can escape colons and other characters that may break the YAML parser.
Table of Contents
fast_templatewill automatically generate a table of contents for you based on markdown headers! You can toggle this feature on or off by settingtoc:to eithertrueorfalse.
Colab And GitHub Badges
This option works for notebooks only
- The
branchfield is used to optionally render a link your notebook to Colab and GitHub in your blog post post. It'll default tomasterif you don't specify it in the notebook. - If you do not want to show Colab / GitHub badges on your blog post (perhaps because your repo is private and the links would be broken) set
badgestofalse. This defaults totrue
Categories
-
You can have a comma seperated list inside square brackets of categories for a blog post, which will make the post visible on the tags page of your blog's site. For example:
- categories: [fastpages, jupyter]
You can see a preview of what this looks like here.
- You can toggle the display of tags on/off by setting
show_tagstotrueorfalsein_config.yml:
# Set this to true to display tags on each post
show_tags: trueEnabling Comments
Blog posting is powered by Utterances, an open-source and ad-free way of implementing comments. All comments are stored in issues on your blog's GitHub repo. You can turn this on setting comments to true. This defaults to false.
To enable comments with Utterances you will need to do the following:
- Make sure the repo is public, otherwise your readers will not be able to view the issues/comments.
- Make sure the utterances app is installed on the repo, otherwise users will not be able to post comments.
- If your repo is a fork, navigate to it's settings tab and confirm the issues feature is turned on.
Setting an Image For Social Media
On social media sites like Twitter, an image preview can be automatically shown with your URL. Specifying the front matter image provides this metadata to social media sites to render this image for you. You can set this value as follows:
- image: images/diagram.png
Note: for this setting you can only reference image files and folders in the /images folder of your repo.
Writing Blog Posts With Jupyter
Hide Input/Output Cells
Place the comment #hide at the beginning of a code cell and it wil hide both the input and the output of that cell. If you only want to hide just the input or the output, use the hide input Jupyter Extension
Collapsable Code Cells
You may want to have code code be hidden from view under a collapsed element that the user can expand, rather than completely hiding the code from the reader.
- To include code in a collapsable cell that is collapsed by default, place the comment
#collapseat the top of the code cell. - To include code in a collapsable cell that is open by default, place the comment
#collapse_showor#collapse-showat the top of the code cell.
Embedded Twitter and YouTube Content
In a markdown cell in your notebook, use the following markdown shortcuts to embed Twitter cards and YouTube Videos.
> youtube: https://youtu.be/your-link
> twitter: https://twitter.com/some-linkAutomatically Convert Notebooks To Blog Posts
-
Save your notebook with the naming convention
YYYY-MM-DD-*.into the/_notebooksor/_wordfolder of this repo, respectively. For example2020-01-28-My-First-Post.ipynb. This naming convention is required by Jekyll to render your blog post.-
Be careful to name your file correctly! It is easy to forget the last dash in
YYYY-MM-DD-. Furthermore, the character immediately following the dash should only be an alphabetical letter. Examples of valid filenames are:2020-01-28-My-First-Post.ipynb 2012-09-12-how-to-write-a-blog.ipynb
-
If you fail to name your file correctly,
fastpageswill automatically attempt to fix the problem by prepending the last modified date of your file to your generated blog post, however, it is recommended that you name your files properly yourself for more transparency.
-
-
Commit and push your file(s) to GitHub in your repository's master branch.
-
GitHub will automatically convert your files to blog posts. It will take ~5 minutes for the conversion process to take place. You can click on the Actions tab of your repo to view the logs of this process. There will be two workflows that are triggered with each push you make to your master branch: (1) "CI" and (2) "GH Pages Status". Both workflows must complete with a green checkmark for your latest commit before your site is updated.
-
If you wish, you can preview how your blog will look locally before commiting to GitHub. See this section for a detailed guide on running the preview locally.
Writing Blog Posts With Markdown
If you are writing your blog post in markdown, save your .md file into the /_posts folder with the same naming convention (YYYY-MM-DD-*.md) specified for notebooks.
Writing Blog Posts With Microsoft Word
Save your Microsoft Word documents into the /_word folder with the same naming convention (YYYY-MM-DD-*.docx) specified for notebooks.
Running the blog on your local machine
See the development guide.
Using The GitHub Action & Your Own Custom Blog
The fastpages action allows you to convert notebooks from /_notebooks and word documents from /_word directories in your repo into Jekyll compliant blog post markdown files located in /_posts. Note: This directory structure is currently inflexible for this Action, as it is designed to be used with Jekyll.
If you already have sufficient familiarity with Jekyll and wish to use this automation in your own theme, you can use this GitHub Action by referencing fastai/fastpages@master as follows:
...
uses: fastai/fastpages@master
...An illustrative example of what a complete workflow may look like:
jobs:
build-site:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
...
- name: convert notebooks and word docs to posts
uses: fastai/fastpages@master
...
- name: Jekyll build
uses: docker://jekyll/jekyll
with:
args: jekyll build
- name: Deploy
uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3
if: github.event_name == 'push'
with:
deploy_key: ${{ secrets.SSH_DEPLOY_KEY }}
publish_branch: gh-pages
publish_dir: ./_siteNote that this Action does not have any required inputs, and has no output variables.
Optional Inputs
BOOL_SAVE_MARKDOWN: Either 'true' or 'false'. Whether or not to commit converted markdown files from notebooks and word documents into the _posts directory in your repo. This is useful for debugging. default: falseSSH_DEPLOY_KEY: a ssh deploy key is required if BOOL_SAVE_MARKDOWN = 'true'
See the API spec for this action in action.yml
Detailed instructions on how to customize this blog are beyond the scope of this README. ( We invite someone from the community to contribute a blog post on how to do this in this repo! )
Contributing To Fastpages
Please see the contributing guide.
FAQ
- Q: Where are the markdown files in
_posts/that are generated from my Jupyter notebooks or word documents? A: The GitHub Actions workflow in this repo converts your notebook and word documents to markdown on the fly before building your site, but never commits these intermediate markdown files to this repo. This is in order to save you from the annoyance of your local environment being constantly out of sync with your repository. You can optionally see these intermediate markdown files by setting theBOOL_SAVE_MARKDOWNandSSH_DEPLOY_KEYinputs to the fastpages action in your.github/workflows/ci.yamlfile as follows:
...
- name: convert notebooks and word docs to posts
uses: fastai/fastpages@master
with:
BOOL_SAVE_MARKDOWN: true
SSH_DEPLOY_KEY: ${{ secrets.SSH_DEPLOY_KEY }}
...-
Q: Can I use
fastpagesfor Jekyll docs sites or for things that are not Jekyll blog posts? A: At the moment,fastpagesis a highly opinionated solution that works only for Jekyll blog posts. If you want to write documentation for your module or library with Jupyter notebooks, we suggest you use fastai/nbdev which is expressly built for this purpose. -
Q: What is the difference between fast_template and fastpages? Which one should I use? A: Because
fastpagesis more flexible and extensible, we recommend using it where possible.fast_templatemay be a better option for getting folks blogging who have no technical expertise at all, and will only be creating posts using Github's integrated online editor.