This repository contains datasets which can be used for quantifying website aesthetics.
Paper: "Calista: A deep learning-based system for understanding and evaluating website aesthetics"
Cite as:
@article{DELITZAS2023,
title = {Calista: A deep learning-based system for understanding and evaluating website aesthetics},
journal = {International Journal of Human-Computer Studies},
volume = {175},
pages = {103019},
year = {2023},
issn = {1071-5819},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2023.103019},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1071581923000253},
author = {Alexandros Delitzas and Kyriakos C. Chatzidimitriou and Andreas L. Symeonidis}
}
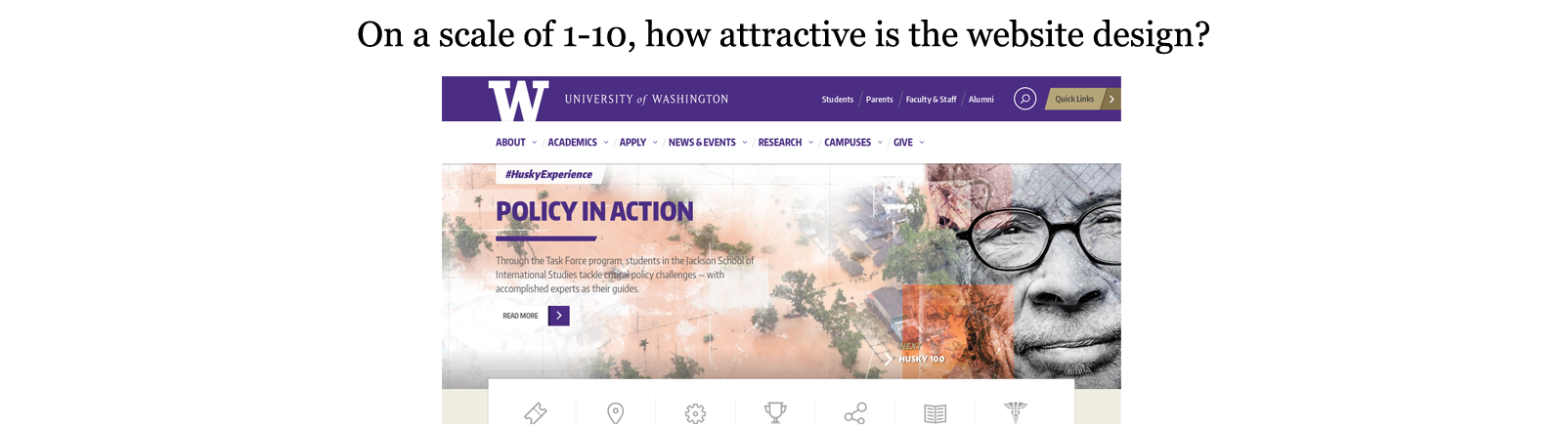
Rating-based evaluation: The user is asked to rate an item by providing an explicit numerical value on a scale
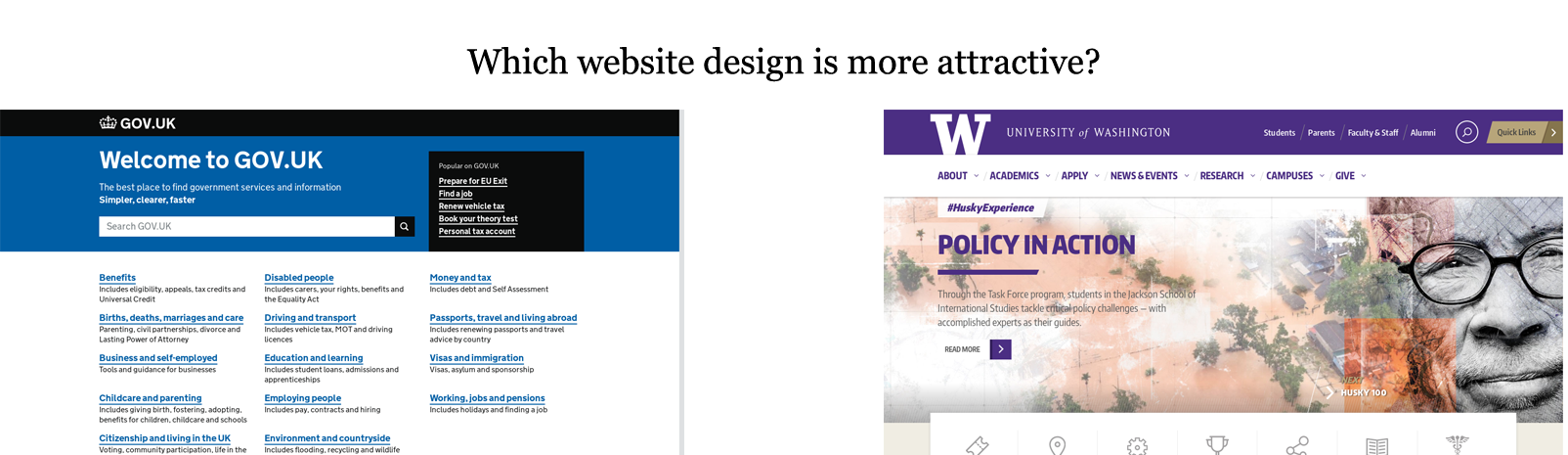
Comparison-based evaluation: The user is asked to compare 2 items at a time and choose which of the two is preferable
Asking users to compare pairs of items is a more natural and reliable alternative to numerical ratings. Because of the virtues of comparison-based evaluation as a data collection method, we created a dataset to study and quantify website aesthetics.
Data were collected via Calista Crowdsourcing App that is currently running on https://data.calista.app.
Note: This dataset will be regularly updated as we collect new data
This dataset contains aesthetic evaluations on 100 webpages that were randomly selected from the Top 5000 websites list by Alexa Rankings.
During the evaluation process, 2 webpages were displayed at a time and the users were asked to choose which website design is more attractive.
From the total of 249 user sessions that were completed through our application, 174 passed the answer consistency check (69.88%). Through this process, we managed to collect 5094 pairwise comparisons.
We also utilized the Bradley-Terry model in order to extract a rank for each webpage through the comparison-based data collected. The final aesthetics scores are on the scale 1-10.
-
alexa_rankings/top-5000-websites.json: Contains the Top 5000 websites list by Alexa Rankings.
Format:
{ "Webpage URL": "Category" } -
images/: Contains the webpage screenshots in PNG format. The file website_data.json has information about the webpages.
Format:
{ "Webpage URL": { "category": "The website category according to the Top 5000 Website list", "sampleIndex": "The website position in the file top-5000-websites.json", "idInDataset": "The webpage ID in the dataset. Its screenshot is ID.png" } } -
data/votesessions.json: Contains the data from each user session collected through the crowdsourcing application
Format:
[ { "_id": { "$oid": "ObjectID" }, "acc": "Gets the value true if the user session was accepted. Otherwise, false", "d": "Date and time that the vote session started", "vot": [ { "imL": "Image ID displayed at the left side", "imR": "Image ID displayed at the left", "imC": "The ID of the image that was chosen by the user" }, ... ], "__v": "Not useful for analysis" }, ... ]Note: A user session is considered as accepted on two conditions:
-
The user evaluated all the session's pairwise image comparisons (a session has 32 comparisons)
-
The user passed the answer consistency check. Otherwise the user's answers are not considered reliable and the session is not accepted.
-
-
data/votesessions.csv: The same information with data/votesessions.json in CSV format.
-
data/comparisons.json: Contains the filtered comparison-based data of the accepted user sessions.
Format:
[ { "_id": "Comparison ID", "im1": "First image ID", "im2": "Second image ID", "w1": "Times that the first image won", "w2": "Times that the second image won", "t": "Total number of evaluations by users (t = w1 + w2)", "u": "Not useful for analysis" }, ... ] -
data/comparisons.csv: The same information with data/comparisons.json in CSV format.
-
rank_websites.R: A script that utilizes the Bradley-Terry model to extract a rank for each website based on the filtered comparison-based data.
-
website_scores.csv: Contains the output of rank_websites.R.
In an attempt to establish a better understanding of how people’s individual visual preferences differ, the first public dataset on website aesthetics was introduced in Katharina Reinecke and Krzysztof Z. Gajos, "Quantifying Visual Preferences Around the World", Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), 2014. The data was collected through LabintheWild (www.LabintheWild.org).
The full dataset can be found here under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 license.
The dataset contains 398 webpage screenshoots with 372,402 scorewise aesthetics ratings.
The users were asked to rate a webpage with a score between 1 to 9.
-
images/: Contains the webpage screenshots in PNG format.
-
data/ae_only_unambiguous_1000.csv: Contains the data used for the analyses of country influences, i.e., it does not contain culturally ambiguous participants who had lived in multiple countries in their lives (at least six months in another country) or whose parents were of a different nationality. We further excluded all countries with fewer than 1000 paired ratings from this dataset. The dataset consists of 441,478 paired ratings and 43 countries.
Note that for the preparation of this dataset the authors excluded participants
- who reported that they did not have normal or corrected-to-normal vision
- who reported that they had previously participated in the study
- who did not fill in the demographics
- who reported countries for their own or their parents backgrounds that suggested random picking from the top of the list
- whose sum of years spent in different countries was hugely different from their age
- who reported to be under 12 years of age and over 91.
-
preprocess/: Preprocessed data for Machine learning. The dataset was randomly divided into 300 training samples (75.4%) and 98 testing samples (24.6%).
-
preprocess/resized: Contains the images downsampled 4 times (resolution: 256 × 192).
-
preprocess/train_list.csv: Contains all the user ratings that the images in the training set received.
-
preprocess/train_means_list.csv: Contains the mean rating that the images in the training set received.
-
preprocess/test_list.csv: Contains the mean rating that the images in the test set received.
-