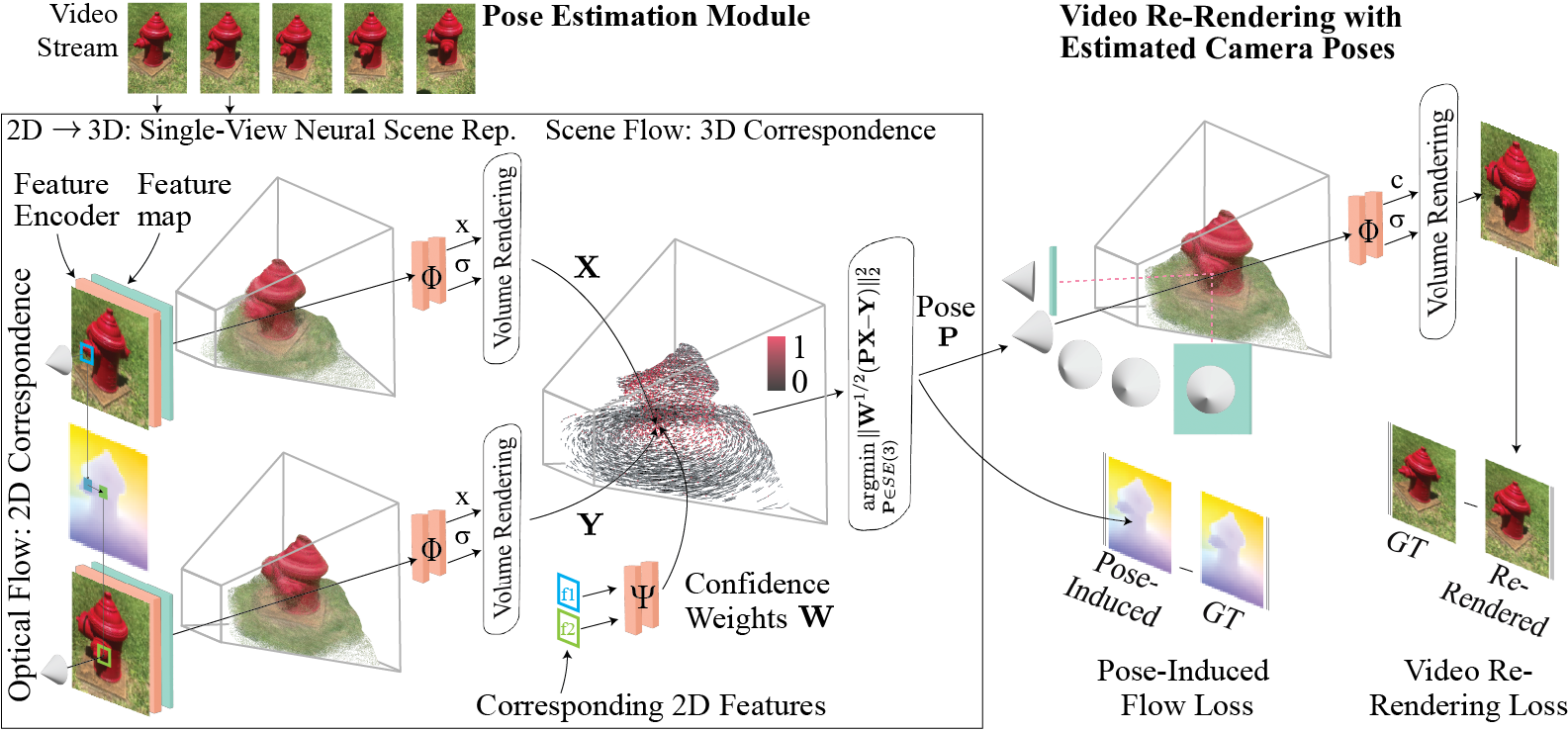
FlowCam: Training Generalizable 3D Radiance Fields without Camera Poses via Pixel-Aligned Scene Flow
Cameron Smith, Yilun Du, Ayush Tewari, Vincent Sitzmann
MIT
This is the official implementation of the paper "FlowCam: Training Generalizable 3D Radiance Fields without Camera Poses via Pixel-Aligned Scene Flow".
The code is organized as follows:
- models.py contains the model definition
- run.py contains a generic argument parser which creates the model and dataloaders for both training and evaluation
- train.py and eval.py contains train and evaluation loops
- mlp_modules.py and conv_modules.py contain common MLP and CNN blocks
- vis_scripts.py contains plotting and wandb logging code
- renderer.py implements volume rendering helper functions
- geometry.py implements various geometric operations (projections, 3D lifting, rigid transforms, etc.)
- data contains a list of dataset scripts
- demo.py contains a script to run our model on any image directory for pose estimates. See the file header for an example on running it.
See python run.py --help for a list of command line arguments.
An example training command for CO3D-Hydrants is python train.py --dataset hydrant --vid_len 8 --batch_size 2 --online --name hydrants_flowcam --n_skip 1 2.
Similarly, replace --dataset hydrants with any of [realestate,kitti,10cat] for training on RealEstate10K, KITTI, or CO3D-10Category.
Example training commands for each dataset are listed below:
python train.py --dataset hydrant --vid_len 8 --batch_size 2 --online --name hydrant_flowcam --n_skip 1 2
python train.py --dataset 10cat --vid_len 8 --batch_size 2 --online --name 10cat_flowcam --n_skip 1
python train.py --dataset realestate --vid_len 8 --batch_size 2 --online --name realestate_flowcam --n_skip 9
python train.py --dataset kitti --vid_len 8 --batch_size 2 --online --name kitti_flowcam --n_skip 0
Use the --online flag for summaries to be logged to your wandb account or omit it otherwise.
We use environment variables to set the dataset and logging paths, though you can easily hardcode the paths in each respective dataset script. Specifically, we use the environment variables CO3D_ROOT, RE10K_IMG_ROOT, RE10K_POSE_ROOT, KITTI_ROOT, and LOGDIR. For instance, you can add the line export CO3D_ROOT="/nobackup/projects/public/facebook-co3dv2" to your .bashrc.
The KITTI dataset we use can be downloaded here: https://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/raw_data.php
Instructions for downloading the RealEstate10K dataset can be found here: https://github.com/yilundu/cross_attention_renderer/blob/master/data_download/README.md
We use the V2 version of the CO3D dataset, which can be downloaded here: https://github.com/facebookresearch/co3d
You can query FlowCam for any set of images using the script in demo.py and specifying the rgb_path, intrinsics (fx,fy,cx,cy), the pretrained checkpoint, whether to render out the reconstructed images or not (slower but illustrates how accurate the geometry is estimated by the model), and the image resolution to resize to in preprocessing (should be around 128 width to avoid memory issues).
For example: python demo.py --demo_rgb /nobackup/projects/public/facebook-co3dv2/hydrant/615_99120_197713/images --intrinsics 1.7671e+03,3.1427e+03,5.3550e+02,9.5150e+02 -c pretrained_models/co3d_hydrant.pt --render_imgs --low_res 144 128. The script will write the poses, a rendered pose plot, and re-rendered rgb and depth (if requested) to the folder demo_output.
The RealEstate10K pretrained (pretrained_models/re10k.pt) model probably has the most general prior to use for your own scenes. We are planning on training and releasing a model on all datasets for a more general prior, so stay tuned for that.
This code uses an "OpenCV" style camera coordinate system, where the Y-axis points downwards (the up-vector points in the negative Y-direction), the X-axis points right, and the Z-axis points into the image plane.
If you find our work useful in your research, please cite:
@misc{smith2023flowcam,
title={FlowCam: Training Generalizable 3D Radiance Fields without Camera Poses via Pixel-Aligned Scene Flow},
author={Cameron Smith and Yilun Du and Ayush Tewari and Vincent Sitzmann},
year={2023},
eprint={2306.00180},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
If you have any questions, please email Cameron Smith at omid.smith.cameron@gmail.com or open an issue.